Practice Exercises - Thermodynamics - AP Chemistry Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. Which of these must be negative for a reaction to be thermodynamically favored?
(A) ∆G°
(B) ∆H°
(C) ∆G°, ∆S°, and ∆G
(D) ∆G
2. Why is ∆H° a state function?
(A) It has the required superscript zero.
(B) Its value does not depend on the path between the initial and final states.
(C) It requires exactly 1 molar concentrations of all reactants.
(D) Its value is equal to the initial state minus the final state.
3. Scientists divide energy into two broad groups. They are
(A) chemical and solar
(B) electrical and nuclear
(C) potential and kinetic
(D) thermal and electromagnetic
4. How can you tell if a chemical reaction or a physical process is endothermic or exothermic?
(A) Use the ∆G° and ∆S° for the reaction at a given temperature to calculate the ∆H° of reaction or process.
(B) Observe how increasing the temperature of the reaction or process affects the proportion of products formed.
(C) Use Hess’s law and standard heats of formation to calculate the heat of reaction.
(D) All of the above.
5. When 0.400 g of CH4 is burned in excess oxygen in a bomb calorimeter that has a heat capacity of 3,245 J °C−1, a temperature increase of 6.795 °C is observed. What is the value of q and ∆H for this combustion reaction?
(A) 220 kJ mol−1 and −220 kJ mol−1
(B) −882 kJ and 882 kJ
(C) 477 kJ and −477 kJ
(D) −22.05 kJ and −22.05 kJ
6. In the diagram below, we have a U-shaped ramp where a stainless steel ball can roll without friction. As the ball rolls back and forth, which statement is correct?
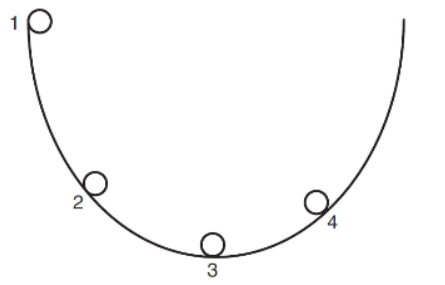
(A) Point 4 is the highest velocity, and point 3 is the lowest velocity.
(B) Point 1 is the highest potential energy, and point 3 is the highest kinetic energy.
(C) Point 1 is the highest kinetic energy, and point 3 is the lowest potential energy.
(D) Point 1 is the highest kinetic energy, and point 3 is the lowest velocity.
7. Which of the following describes a system that CANNOT be thermodynamically favored?
(A) ΔH° is positive, and ΔS° is negative.
(B) ΔH° is positive, and ΔS° is positive.
(C) ΔH° is negative, and ΔS° is negative.
(D) ΔH° is negative, and ΔS° is positive.
8. Which of the following must be true when KCl(s) is dissolved in water and dissociates into K+(aq) and Cl−(aq) and when you observe condensation of moisture on the outside of the glass beaker?
(A) The condensation is extra information. The dissociation equation tells us that the entropy change is positive.
(B) The condensation informs about the heat of the process. The dissociation informs about the entropy change.
(C) Only the heat of the solution process can be inferred from the condensation on the beaker.
(D) The condensation tells us that the process is exothermic. The dissolution reactions always increase the entropy.
9. The reaction with the greatest expected entropy decrease is
(A) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
(B) CH4(l) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
(C) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
(D) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(s) + 2H2O(g)
10. Water boils at 100 °C with a molar heat of vaporization of +43.9 kJ. At 100 °C what is the entropy change when water condenses?
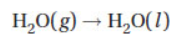
(A) Problem cannot be solved; ΔG° must also be known.
(B) Problem cannot be solved; this is not a chemical reaction.
(C) −439 J K−1
(D) −118 J K−1
11. Which of the following statements is not correct about the use of the graph shown below?
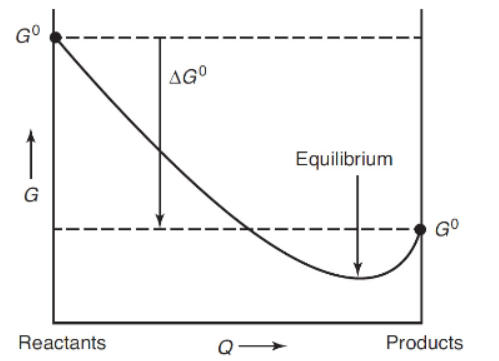
(A) If the value of Q is to the left of the minimum of the curved line, reactants will not be converted into products.
(B) The algebraic sign of the arrow for ΔG determines if the chemical reaction is thermodynamically favored.
(C) The minimum of the curved line indicates that the value of Q = K.
(D) If the value of Q is to the right of the minimum of the curved line, products will be converted into reactants.
12. A gas is allowed to expand from an initial volume and pressure (left piston) to a final volume and pressure (right piston). Estimate the value of w.
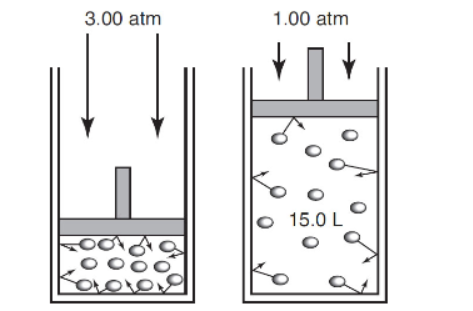
(A) +30.0 L atm
(B) +15.0 L atm
(C) −10.0 L atm
(D) The needed data are not given.
13. In question 12 the units of work are given as L atm. To convert L atm to the metric unit of joules, we need to know
(A) Avogadro’s constant and Planck’s constant
(B) the universal gas law constant in units of L atm mol−1 K−1
(C) the universal gas law constant in units of J mol−1 K−1
(D) both (B) and (C)
14. Which of the following is the LEAST probable for a combustion reaction?
(A) ΔG° is a large negative number.
(B) ΔS° is a large negative number.
(C) ΔH° is a large negative number.
(D) Keq is a large positive number.
15. Of the following molecular-level diagrams of argon gas, which illustrates the system with the most entropy and why?
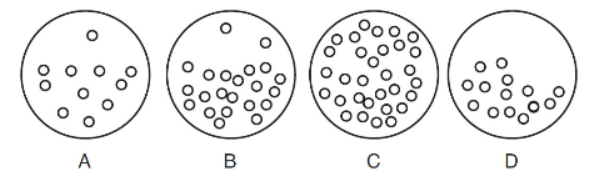
(A) The atoms are far apart and do not interact.
(B) The atoms are a liquid.
(C) This diagram has the most gas atoms and states to occupy.
(D) Argon atoms are dipoles that strongly attract.
16. The heat of formation of CH3CH2OH(l) = −258 kJ mol−1, and the heat of formation of CO2(g) = −393.5 kJ mol−1, and of H2O(g) = −241.8 kJ mol−1. What is ΔH° for the heat of combustion of ethanol to gaseous products?
(A) −5021.6 kJ
(B) −2510.8 kJ
(C) +5021.6 kJ
(D) −1255.4 kJ
17. The rate of reaction will be large if
(A) ΔG° is a large negative number
(B) ΔS° is a large negative number
(C) ΔH° is a large negative number
(D) None of the above can be used to estimate reaction rates.
18. Given the following thermochemical data:
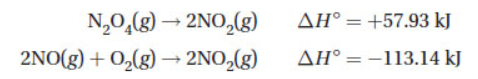
determine the heat of the reaction of
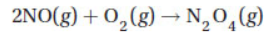
(A) −171.07 kJ
(B) −55.21 kJ
(C) +55.21 kJ
(D) +171.07 kJ
19. Which of the following can change the value of ΔG° for a chemical reaction?
(A) Changes in the total pressure
(B) Changes in the pressures of the reactants
(C) Changes in the concentrations of the reactants
(D) Changes in the temperature in °C
20. Which of the following processes is not an example of a repeated conversion of kinetic energy to potential energy and back again if the system does not lose energy due to friction?
(A) A vibrating spring, with one end attached to a ring stand and the other to a 100 g mass
(B) A ball bouncing vertically on a lab bench
(C) A pendulum with a 100 g mass attached to a ring stand
(D) A ball bouncing down a set of stairs
21. The standard heat of formation of SO3(g) is −396 kJ mol−1. The standard entropies of S(s), O2(g), and SO3(g) are 31.8, 205.0, and 256 J mol−1 K−1, respectively. Calculate the free energy at 25 °C for the decomposition of SO3 in the reaction
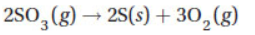
(A) −446 kJ
(B) −346 kJ
(C) +396 kJ
(D) +742 kJ
22. To determine the standard enthalpy (ΔH°) of the following combustion reaction
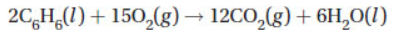
what do you need to know?
(A) The standard heat of combustion of carbon
(B) The standard heat of combustion of hydrogen
(C) The standard heat of formation for C6H6(l)
(D) All of the above
.png)
23. The evaporation of any liquid is expected to have
(A) a positive ΔH and a negative ΔS
(B) a negative ΔH and a negative ΔS
(C) a positive ΔH and a positive ΔS
(D) a negative ΔH and a positive ΔS
24. Which of the following is most likely to be true?
(A) Combustion of organic compounds has a negative ΔH°.
(B) A positive ΔG° indicates a thermodynamically favored reaction.
(C) A positive ΔS° always means that the reaction is thermodynamically favored.
(D) A thermodynamically favored reaction always goes to completion.
Free-Response
Answer the following questions using the concepts of thermodynamics and equilibrium and the methods for solving problems.
1. (a)Wite the balanced equation for the formation reaction of propyl amine, CH3CH2CH2NH2.
(b) Can propyl amine be formed in the reaction above? Explain why or why not.
(c) Can the heat of formation, 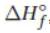 , be determined using the reaction above? Explain why or why not.
, be determined using the reaction above? Explain why or why not.
(d) Describe the experiments needed to determine the heat of formation, .png) , of propyl amine.
, of propyl amine.
2. Give succinct, logical descriptions of how scientists can experimentally obtain the following information.
(a) Describe experiments that can be used to determine the numerical value of Keq.
(b) Describe experiments that can be used to determine the numerical value of ΔH° for a substance.
(c) Describe experiments that can be used to determine the numerical value of ΔG° for a substance.
(d) Describe experiments that can be used to determine the numerical value of S° for a substance.
3. (a) What parameters define whether or not a given reaction is thermodynamically favored? Based on those parameters, what does it mean to say a reaction is thermodynamically favored? What indicates if a mixture of chemicals will proceed in the forward direction or in the reverse direction?
(b) What is the difference between E, ∆E, and ∆E°?
(c) Tables of thermodynamic data list heat of formation .png) , standard free energy
, standard free energy 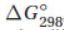 , and entropy S°. Why don’t entropy values have a delta symbol, ∆? What other difference does a table of entropy values have?
, and entropy S°. Why don’t entropy values have a delta symbol, ∆? What other difference does a table of entropy values have?
(d) The value of Kc for the reaction 2NO + O2 ⇌ N2O4 is 36 at a certain temperature. Calculate K for the following reactions.
(i) 6NO + 3O2 ⇌ 3N2O4
(ii) NO + 1/2 O2 ⇌ 1/2 N2 O4
(iii) 2N2O4 ⇌ 4NO + 2O2




