Practice Exercises - The Periodic Table - AP Chemistry Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. Trends in the periodic table show that elements become more metallic in character from the top of a group to the bottom. Which of these is an element whose properties are opposite those of the element at the top of its group?
(A) Krypton
(B) Strontium
(C) Uranium
(D) Bismuth
2. In which of the following atoms do the valence electrons feel the greatest effective nuclear charge?
(A) Ca
(B) K
(C) As
(D) Br
3. In which choice below are the elements ranked in order of increasing first ionization energy?
(A) P, Cl, S, Al, Ar, Si
(B) Ar, Cl, S, P, Si, Al
(C) Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar
(D) Al, Si, S, P, Cl, Ar
4. There are only two liquid elements at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. One of these is
(A) krypton
(B) bismuth
(C) uranium
(D) bromine
5. The atom with the smallest radius is
(A) strontium
(B) krypton
(C) tin
(D) bromine
6. Metallic behavior is generally associated with
(A) elements with low ionization energies
(B) elements with very negative electron affinities
(C) elements with small atomic radii
(D) elements with high electronegativies
7. One way to estimate the boiling point of Pd is to
(A) average the boiling points of Rh and Ag
(B) average the boiling points of Ni and Pt
(C) average the boiling points of Ir and Cu
(D) average the boiling points of Co and Au
8. In which of the following pairs of elements is the element with the lower boiling point listed first?
(A) Na, Cs
(B) Te, Se
(C) P, N
(D) Ba, Sr
9. In which of the following pairs is the first element expected to have a higher electronegativity than the second?
(A) O, P
(B) Cs, Rb
(C) I, Br
(D) Al, P
10. Which ion has the largest radius?
(A) Cl−
(B) K+
(C) S2−
(D) Ca2+
11. The effective nuclear charge that an electron in the valence shell feels generally increases
(A) from left to right across a period and down a group
(B) from left to right across a period and up a group
(C) from right to left across a period and down a group
(D) from left to right across a period and no change down a group
12. Which one of the following groups does not contain any metals?
(A) Xe, Hg, Ge, O
(B) Cl, Al, Si, Ar
(C) C, S, As, H
(D) Cu, P, Se, Kr
13. What is the correct order of decreasing size of the following ions?
(A) P3- > Cl− > K+ > Ca2+
(B) K+ > Cl− > P3− > Ca2+
(C) Ca2+ > K+ > Cl− > P3−
(D) K+ > Cl− > Ca2+ > P3−
14. Which pair of elements is expected to have the most similar properties?
(A) Potassium and lithium
(B) Sulfur and phosphorus
(C) Silicon and carbon
(D) Lithium and magnesium
15. Which of the following drawings is a correct representation of the trends of the change in electron affinities of the elements in the periodic table?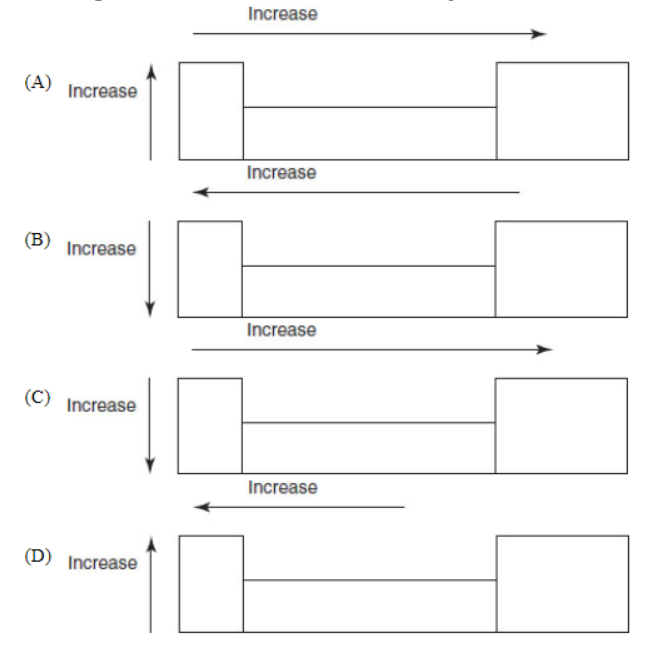

16. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of bromine?
(A) 35 p, 45 n, 35 e
(B) 45 p, 35 n, 45 e
(C) 80 p, 35 n, 80 e
(D) Neutrons cannot be determined unless an isotope is specified.
17. Chemical properties of elements are defined by the
(A) electrons
(B) ionization energy
(C) protons
(D) electronegativity
18. The average atomic mass of Ni is 58.693 amu. There are five stable isotopes of nickel: 58Ni, 60Ni, 61Ni, 62Ni, and 64Ni. Which of the following statements is correct?
(A) Ni-58 and Ni-60 are present in equal amounts.
(B) Ni-60 is the most abundant isotope.
(C) Ni-58 is the most abundant isotope.
(D) Ni-61, Ni-62, and Ni-64 are present in equal amounts.
19. Which one of the following equations correctly represents the process involved in the electron affinity of X?
(A) X(g) → X+(g) + e−
(B) X+(g) → X+(aq)
(C) X+(g) + e− → X(g)
(D) X(g) + e− → X−(g)
20. Which of the following elements has the most exothermic (most negative) electron affinity?
(A) Li
(B) F
(C) Be
(D) Na
21. In general, atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period. The main reason for this behavior is
(A) the number of neutrons in the nucleus increases
(B) the number of electrons increases
(C) the atomic mass increases
(D) the effective nuclear charge increases
22. An unusually big increase in ionization energy is seen upon comparing the successive ionization energies of an element when
(A) the first valence electron is removed
(B) the second valence electron is removed
(C) the eighth electron is removed
(D) the first core electron is removed
Free-Response
PES, photoelectron spectroscopy, may be used to determine the energy of the electrons in an element. The table shows the PES information for an element.
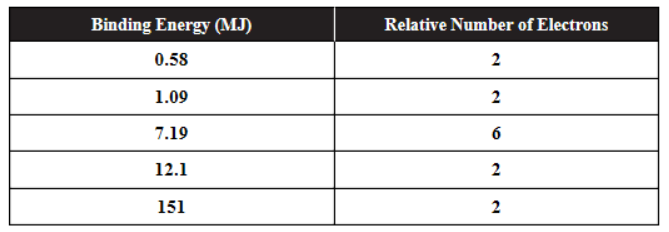
(a) Sketch a PES diagram based on the data provided. Write the electron configuration represented by each peak.
(b) Identify which element these data represent. Explain your reasoning.
(c) The first ionization energy of magnesium is higher than the first ionization energy of aluminum. Explain why this statement makes sense.
(d) The atomic radius of aluminum is 143 pm, while sulfur has an atomic radius of 103 pm. Explain why this statement makes sense.




