Practice Exercises - Stoichiometry - AP Chemistry Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. What is the volume (in L) of a solution that contains 3.12 moles of NaCl if the concentration of this solution is 6.67 M NaCl?
(A) 0.214 L
(B) 0.468 L
(C) 2.14 L
(D) 20.8 L
2. The only item on this list that changes as the temperature changes is
(A) molarity because it uses the volume of the solution, which changes with temperature
(B) mass percentage because this is a ratio that changes with temperature
(C) molar mass because it increases only as the temperature increases
(D) empirical formula since it depends on the percentage composition
3. Calculate the volume (in mL) of a 0.825 molar NH4ClO4 needed to prepare 5.00 liters of 0.0100 molar NH4ClO4.
(A) 0.0330 mL
(B) 0.0682 mL
(C) 33.0 mL
(D) 60.6 mL
4. When calculating the moles of sodium peroxide (Na2O2) produced if 32.5 g of sodium react with excess oxygen, 2Na(s) + O2(g) → Na2O2(s), which of the following is true?
(A) A limiting reactant calculation must be solved.
(B) The dilution of solutions process is used.
(C) The grams of sodium must be converted to moles of Na2O2 using a stoichiometric
calculation.
(D) The moles of Na2O2 must be converted to grams of sodium.
5. What weight of KClO3 (molar mass = 122.5 g/mol) is needed to make 200 mL of a 0.150 M solution of this salt?
(A) 2.73 g
(B) 3.68 g
(C) 27.3 g
(D) 164 g
6. In an experiment 35.0 mL of 0.345 M HNO3 is titrated with 0.130 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH will have been used when the indicator changes color?
(A) 92.9 mL
(B) 50.0 mL
(C) 35.0 mL
(D) 26.4 mL
7. In the reaction CaCO3 + 2HCl → H2O + CO2 + CaCl2, calculating the grams of CaCO3 (molar mass = 100.) needed to produce 3.00 L of CO2 at STP requires doing all of the following EXCEPT
(A) converting the moles of CO2 to grams of CO2
(B) converting moles of CO2 to moles of CaCO3
(C) using the conversion factor that 22.4 L of a gas is equivalent to 1 mole at STP
(D) using the molar mass of CaCO3 as a conversion factor
8. In mass spectrometry, organic compounds are deliberately fragmented in order to deduce their molecular structure. One fragment containing only carbon and hydrogen has 14.3% H. Which of the following is the fragment in question?
(A) CH
(B) CH4
(C) C4H
(D) CH2
9. To two decimal places, what is the molar mass of Al(NO3)3?
(A) 56.99 g mol–1
(B) 88.99 g mol–1
(C) 165.00 g mol–1
(D) 213.01 g mol–1
10. How many milligrams of Na2SO4 (molar mass = 142 g/mol) are needed to prepare 100. mL of a solution that is 0.00100 M in Na+ ions?
(A) 28.4 mg
(B) 14.2 mg
(C) 7.10 mg
(D) 1.00 mg
11. Which of the following compounds has the highest percentage by mass of sulfur?
(A) Al2S3 since there is more mass of sulfur per gram of compound
(B) CaSO4 because the molar mass of sulfur is greater than the molar mass of calcium
(C) Na2S because the ratio of the molar mass of sulfur to sodium is the highest
(D) SO2 because the element with the highest percentage is always written first in a formula
12. In the following reaction, how many moles of aluminum will produce 1.0 mol of iron and why?
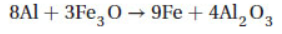
(A) 1 mol Al because aluminum has the lowest atomic mass
(B) 3/4 mol Al because 3/4 is the mole ratio of the oxides
(C) 3/8 mol Al since this is the mole ratio of the reactants
(D) 8/9 mol Al since this mole ratio cancels units correctly
13. A solution of oxalic acid (HO2CCO2H) is often used to react with iron(III) oxide (rust) stains with the following equation. It is also used to dissolve rust that may be clogging an old automobile radiator. How many mL of 1.00 molar oxalic acid can remove 100. grams of rust?
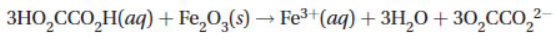
(A) 0.62 L HO2CCO2H
(B) 1.87 L HO2CCO2H
(C) 1878 mL HO2CCO2H
(D) 5636 mL HO2CCO2H
14. A substance has an empirical formula of CH2. Its molar mass is determined in a separate experiment as 83.5. What is the most probable molecular formula for this compound?
(A) C2H4 because it is the simplest formula after CH2
(B) C6H12 since it is the hydrocarbon with a molar mass close to the experimental molar mass
(C) C4H2 since it has subscripts that are simple multiples of the empirical formula
(D) C4H3O2 because this has a molar mass closest to 83.5
15. The mass of one atom of iron is
(A) 1.66 × 10–24 g
(B) 9.28 × 10–23 g
(C) 2.11 × 10–22 g
(D) 3.15 × 10–22 g
16. How many grams of the gas SO2 are in a 4.00 L sample of SO2 at STP?
(A) 256.2 g since this is the mass of 4 moles of SO2
(B) 11.4 g since this is obtained by converting L to mol using the molar volume of gases and then to mass by converting with the molar mass
(C) 358.7 g since this is obtained by multiplying by the molar volume, 22.4
(D) 2.78 × 10–3 g since this is obtained by dividing by the molar volume, 22.4
17. What is the percentage of potassium in K3PO4?
(A) 14.6%
(B) 18.4%
(C) 29.2%
(D) 55.3%
18. A 0.200-g sample of a compound containing only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen is burned, and 0.357 g of CO2 and 0.146 g of H2O are collected. What is the percentage of carbon in the original compound and what can that value be used for?
(A) 56.0% and this can be used to obtain the empirical formula
(B) 73.0% and this can be used to name the compound
(C) 48.7% and this, with the grams of hydrogen, can be used to determine the empirical formula
(D) 24.3% and this can be used to track CO2 in the atmosphere
19. In the following combustion reaction, when 5.50 g of glucose are burned in the presence of 2.50 L of oxygen at STP, what is the limiting reactant?
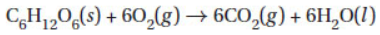
(A) C6H12O6 because this has the largest mass and therefore limits the reaction
(B) O2 when calculated since this reacts only with a small fraction of the glucose
(C) CO2 because the mass formed is the largest
(D) H2O since the mass of water formed is the largest
20. In the reaction
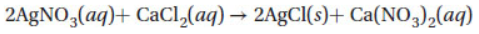
What is the molarity of calcium chloride in a 150.0 mL sample of calcium chloride if it takes 35.6 mL of 0.250 M AgNO3 to precipitate all of the chlorine from the calcium chloride?
(A) 0.00378 M CaCl2
(B) 0.0297 M CaCl2
(C) 1.50 M CaCl2
(D) 37.5 M CaCl2
21. In the reaction
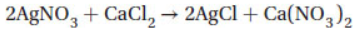
how many grams of which reactant will remain when a solution containing 20.0 g AgNO3 (molar mass = 170 g/mol) is reacted with a solution containing 15.0 g CaCl2 (molar mass = 111 g/mol)?
(A) 6.53 g CaCl2
(B) 6.53 g AgNO3
(C) 8.47 g CaCl2
(D) 45.9 g CaCl2
.png)
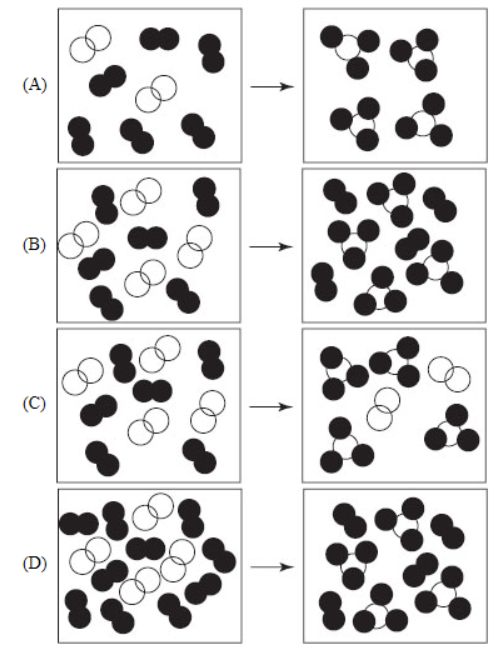
22. Which of the following molecular views of the reaction of hydrogen (filled circles) and nitrogen (open circles) gases to form ammonia indicates that hydrogen is the limiting reactant?
23. How many liters of air are needed to completely burn 1.00 mol of methane in air (20% oxygen) at STP according to the reaction
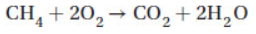
(A) 11.2 L
(B) 22.4 L
(C) 44.8 L
(D) 224 L
24. Determine the empirical formula for a compound that is 25% hydrogen and 75% carbon. Is this likely to be the molecular formula?
(A) CH. No, this cannot be the molecular formula because carbon forms 4 bonds.
(B) CH2. Yes, this can be the molecular formula because carbon often forms 2 bonds.
(C) CH4. Yes, this is a compound with carbon having 4 bonds.
(D) C2H8. No, this cannot be the molecular formula since carbon atoms have more than 4 bonds in this formula.
25. One granule of sucrose (C12H22O11, molar mass = 342) weighs 2.5 micrograms. How many sucrose molecules are in that granule and how many atoms are in that granule?
(A) 2.5 × 1017 molecules and 7.5 × 1017 atoms
(B) 4.4 × 1015 molecules and 2.0 × 1017 atoms
(C) 6.02 × 1017 molecules and 1.33 × 1016 atoms
(D) 4.4 × 1021 molecules and 9.8 × 1015 atoms
Free-Response
The following questions involve stoichiometry problems frequently encountered by the chemist in theoretical and laboratory situations. Use the appropriate stoichiometric methods to answer the following questions.
(a) One beaker holds a solution that contains 4.65 grams of sodium sulfide. A second beaker holds a solution that contains 8.95 grams of lead(II) nitrate. When the two solutions are mixed, what mass of PbS forms?
(b) Perform the calculations to determine the empirical formula of a CHNO compound that is analyzed and found to contain 52.63 percent carbon, 7.02 percent hydrogen, and 12.28 percent nitrogen.
(c) If the compound in part (b) has a molar mass of 228, what is the molecular formula?
(d) A neutralization reaction uses a 0.125 molar solution of sodium hydroxide to titrate 50.0 mL of an unknown sulfuric acid solution. If the reaction takes 23.5 mL of the sodium hydroxide to completely neutralize the sulfuric acid, what is the molarity of the sulfuric acid solution?




