Practice Exercises - Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Electrochemistry - AP Chemistry Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. The difference between a voltaic and an electrolytic cell is that
(A) oxidation will occur only at the cathode in a voltaic cell
(B) the free-energy change, ΔG, is negative for an electrolytic cell
(C) the cathode is labeled as negative (-) in an electrolytic cell and as positive (+) in a voltaic cell
(D) the electrons flow from the cathode to the anode in both types of cells through the external wire
2. Consider a voltaic cell, 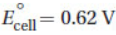 , composed of cobalt, copper, and their respective M2+ ions. If the E° for the cathode half-cell is 0.34 V, what is the E° for the anode half-cell?
, composed of cobalt, copper, and their respective M2+ ions. If the E° for the cathode half-cell is 0.34 V, what is the E° for the anode half-cell?
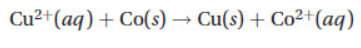
(A) -0.96 V
(B) -0.28 V
(C) 0.28 V
(D) 0.96 V
3. What does the line notation below indicate?
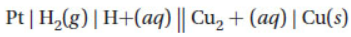
(A) Cu is the anode.
(B) Pt is the cathode.
(C) Cu(s) is a product of the cell reaction.
(D) Hydrogen gas is a product of the cell reaction.
4. Balance the following half-reaction in acid solution:
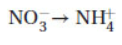
When balanced with the smallest whole-number coefficients, the sum of all the coefficients is
(A) 13
(B) 15
(C) 23
(D) 26
5. The following reactions are known to be thermodynamically favored:
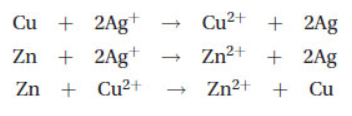
The activity series for the three elements from the easiest to oxidize to the most difficult to oxidize is
(A) Cu > Ag > Zn
(B) Zn > Cu > Ag
(C) Ag > Cu > Zn
(D) Ag > Zn > Cu
6. The standard reduction potential for PbO2 → Pb2+ is +1.46 V, and the standard reduction potential for Fe3+ → Fe2+ is +0.77 V. What is the standard cell voltage for the following reaction?
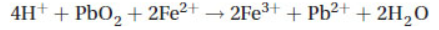
(A) +2.33 V
(B) +0.69 V
(C) -0.08 V
(D) -0.69 V
Questions 7 and 8 refer to the following half-cell reactions.
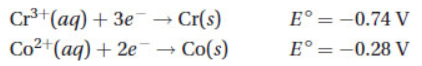
7. What would be the standard electrode potential for a voltaic cell properly constructed from these two half-cells?
(A) 1.02 V
(B) 0.64 V
(C) 0.46 V
(D) -1.02 V
8. What is the correct balanced overall equation for this voltaic cell?
(A) 3Co2+(aq) + 2Cr(s) → 3Co(s) + 2Cr3+(aq)
(B) 3Co(s) + 2Cr3+(aq) → 3Co2+(aq) + 2Cr(s)
(C) Co(s) + Cr3+(aq) → Co2+(aq) + Cr(s)
(D) 2Co(s) + 3Cr3+(aq) → 2Co2+(aq) + 3Cr(s)
_________________________________________________________________________
9. In the following pairs of compounds, which pair contains the element named with the same oxidation number?
(A) Sulfur in H2S2O7 and H2SO4
(B) Cobalt in Co(NH3)63+ and Co(NO3)2
(C) Mercury in HgCl2 and Hg2Cl2
(D) Oxygen in Na2O2 and H2O
10. Sodium metal cannot be electrolyzed from an aqueous Na2SO4 solution because
(A) the voltage needed is too high for any available instrument to achieve
(B) water is reduced to O2 before Na+
(C) Na+ has a high overpotential that keeps it from being reduced
(D) H+ has a more favorable reduction potential than Na+
11. Which of the following elements has the largest number of possible oxidation states?
(A) Fe
(B) Cl
(C) Ca
(D) Mn
12. For the reaction
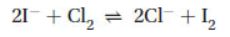
the standard cell voltage is +0.82 V. What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 45 °C? (R = 8.314 V C mol-1 K-1, and ℱ = 96,485 C mol-1)
(A) 9.8 × 1025
(B) 1.6 × 105
(C) 6.3 × 10-6
(D) 1.0 × 10-26
13. Calculate the ΔG° for the following reaction if the .png) for the reaction is 1.59 V.
for the reaction is 1.59 V.
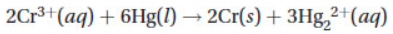
(A) -921 kJ
(B) -767 kJ
(C) -460 kJ
(D) -307 kJ
14. A metal is electrolyzed from aqueous solution by using an electrical current of 1.23 A for 2½ h, and 3.37 g of metal is deposited. In a separate experiment the number of electrons used for the reduction of the metal is 2. What is the metal?
(A) Al
(B) Ni
(C) Sn
(D) Mg
15. Using the two half-reactions listed below, a galvanic cell is constructed.
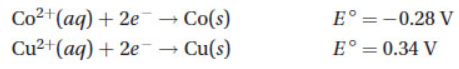
Once the cell is operational, which of the following species is contained in the anode compartment of the cell?
(A) Cu2+(aq) and Cu(s)
(B) Co(aq) only
(C) Cu2+(aq) only
(D) Co(aq) and Co
16. If the E° for the reaction X+ + e- → X is greater than the E° for A2+ + 2e- + A, which statement would be most correct?
(A) X+ will oxidize A2+.
(B) X will oxidize A2+.
(C) A will reduce X+.
(D) X will reduce A2+.
17. Which of the following compounds includes an element that has the same oxidation number as the chlorine in sodium chlorate, NaBrO3?
(A) K3Fe(CN)6
(B) K2Cr2O7
(C) Al(NO3)3
(D) (NH4)2CO3
18. With a current of 1.25 A, how many minutes will be required to deposit 2.00 g of copper on a platinum electrode from a copper(II) nitrate solution? (Faraday’s constant = 96,485 C mol-1)
(A) 4859 min
(B) 81.0 min
(C) 40.5 min
(D) 1.35 min
19. What is the minimum number of electrons needed to balance the following half-reaction with whole number coefficients?
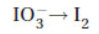
(A) 1e-
(B) 2e-
(C) 5e-
(D) 10e-
20. Shown below are two reduction half-reactions for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and oxaloacetate and their electrode potentials:
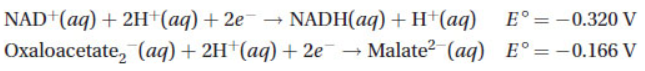
Determine the E°cell for the following reaction, and predict if the reaction is thermodynamically favored.
Oxaloacetate-2(aq) + NADH(aq) + H+(aq) → NAD+(aq) + Malate2-(aq)
(A) -0.486 V, not thermodynamically favored
(B) 0.154 V, thermodynamically favored
(C) 0.486 V, thermodynamically favored
(D) -0.154 V, not thermodynamically favored
21. Which of the following statements is FALSE?
(A) Reduction involves a gain of electrons.
(B) Batteries are galvanic cells.
(C) A thermodynamically favored reaction always has a positive E°cell.
(D) Electrolysis reactions always produce a gas at least at one electrode.
Free-Response
A galvanic cell can be constructed by using the substances in the following half-reactions:
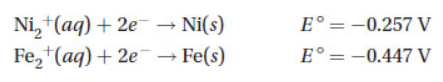
(a) What is the .png) for this reaction?
for this reaction?
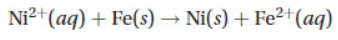
(b) Which reaction takes place at the anode? At the cathode?
(c) Sketch a galvanic cell in which this reaction takes place. Show the direction of electron flow and the directional flow of the ions in the salt bridge.
(d) Calculate the Keq for this reaction. Is this reaction thermodynamically favored?




