Practice Exercises - Kinetics - AP Chemistry Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. Why does an increase in temperature increase the rate of a reaction?
(A) The activation energy of the reaction increases.
(B) The temperature acts as a catalyst in the reaction.
(C) There are more collisions per second that will have the proper energy to exceed the activation energy.
(D) There are a greater proportion of collisions with the correct orientation to be effective.
2. A change in temperature of 10 degrees was found to triple the rate of a particular chemical reaction. How does this change in temperature affect the reacting molecules?
(A) The average velocity of the molecules tripled.
(B) The number of collisions per second tripled.
(C) The number of molecules above the reaction energy threshold tripled.
(D) The average energy of the molecules tripled.
3. In a series of chemical reactions, how do the reaction intermediates differ from the activated complexes?
(A) The intermediates have structures with characteristics of both reactants and products.
(B) The intermediates are unstable and can never be isolated.
(C) The intermediate molecules contain normal bonds rather than partial bonds and can be occasionally isolated.
(D) All reactions involve reaction intermediates, but not all have activated complexes.
4. The rate of a chemical reaction is related to
(A) activation energy and potential energy curve
(B) orientation
(C) activation energy, orientation, and frequency
(D) frequency
Questions 5 and 6 refer to the following proposed mechanism for the reaction of chlorine gas with chloroform, CHCl3, to form carbon tetrachloride.
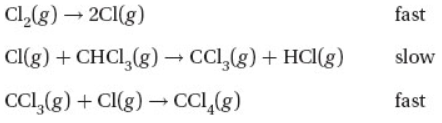
5. What is the overall reaction equation for this mechanism?
(A) Cl(g) + CHCl3(g) → CCl3(g) + HCl(g)
(B) Cl2(g) + CHCl3(g) → HCl(g) + CCl4(g)
(C) CCl3(g) + Cl(g) → CCl4(g)
(D) Cl2(g) + CHCl3(g) + CCl3(g) → HCl(g) + CCl4(g)
6. Which of the following rate laws is consistent with the proposed mechanism?
(A) Rate = k[CHCl3][Cl]
(B) Rate = k[CCl3][Cl]
(C) Rate = k[Cl2]
(D) Rate = k[Cl2][CHCl3]
Questions 7–9 refer to the following diagram:
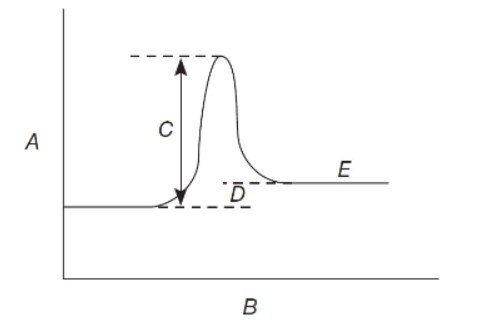
7. In the reaction profile, A, B, and C should be labeled as shown in

8. In the reaction described by the reaction profile,
(A) forward Ea > reverse Ea and ΔH is exothermic
(B) reverse Ea > forward Ea and ΔH is endothermic
(C) forward Ea < reverse Ea and ΔH is exothermic
(D) reverse Ea < forward Ea and ΔH is endothermic
9. Addition of a catalyst to the reaction mixture will affect only
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
10. Given the following mechanism and illustration, what is the rate of reaction for flask B in comparison to flask A?
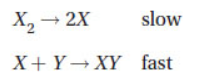
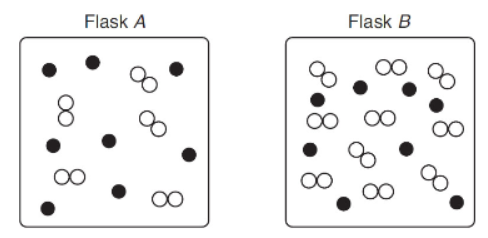
(A) The rate of reaction for flask A is twice as fast as the rate for flask B.
(B) The rate of reaction for flask B is the same as the rate for flask A.
(C) The rate of reaction for flask A is half as fast as the rate for flask B.
(D) The rate of reaction for flask B is half as fast as the rate for flask A.
11. Which of the following rate laws has a rate constant with units of mol L−1 s−1?
(A) Rate = k[A]
(B) Rate = k[A][B]0
(C) Rate = k[A][B]
(D) Rate = k[A]0
12. Which of the following is LEAST effective in increasing the rate of a reaction?
(A) Increasing the pressure by adding an inert gas
(B) Grinding a solid reactant into small particles
(C) Increasing the temperature
(D) Eliminating reverse reactions
13. A first-order reaction has a half-life of 36 min. What is the value of the rate constant?
(A) 3.2 × 10−4 s−1
(B) 1.9 × 10−3 L mol−1 s−1
(C) 1.2 s−1
(D) 0.028 s−1
14. If a reactant’s concentration is doubled and the reaction rate increases by a factor of 8, the exponent for that reactant in the rate law should be
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 3
15. In general, if the temperature of a reaction is raised from 300 K to 320 K, the reaction rate will increase by a factor of approximately
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 4
(D) 2
16. When sucrose is placed into an acid solution, it decomposes to fructose and glucose. A plot of ln [sucrose] vs. time produces a straight line with a slope of -0.25 hr−1.
Which of the following is the correct rate law?
(A) Rate = 0.25 hr−1 [sucrose]2
(B) Rate = 0.063 hr [sucrose]2
(C) Rate = 0.25 hr−1 [sucrose]
(D) Rate = 0.063 hr [sucrose]
17. The rate at which CO2 is produced in the following reaction:
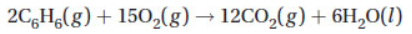
is 2.2 × 10−2 mol L−1 s−1. What is the rate at which O2 is consumed?
(A) 1.8 × 10−3 mol L−1 s−1
(B) 2.2 × 10−2 mol L−1 s−1
(C) 2.8 × 10−2 mol L−1 s−1
(D) 1.3 × 10−1 mol L−1 s−1
.png)
18. Consider the following reaction:
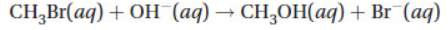
The experimental rate law was found to be first order with respect to both reactants. The rate for this reaction was determined to be 0.0432 M s−1. What is the rate constant for this reaction if the concentration of CH3Br is 0.050 M and the OH− is 0.025 M?
(A) 0.029 M−1 s−1
(B) 0.86 M−1 s−1
(C) 35 M−1 s−1
(D) 69 M−1 s−1
19. Which response identifies the intermediate(s) in the following mechanism?
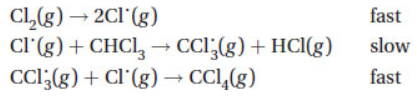
(A) Cl˙
(B) CCl˙3
(C) CHCl3
(D) Both Cl˙ and CCl˙3
20. A first-order reaction has a half-life of 85 s. What fraction of the reactant is left after 255 s?
(A) 1/2
(B) 1/3
(C) 1/4
Questions 21 and 22 refer to the following data. For the reaction
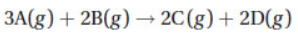
the following data were collected at constant temperature:
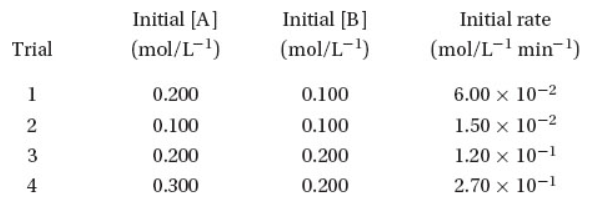
21. What is the correct rate law for this reaction?
(A) Rate = k[A][B]2
(B) Rate = k[A]3[B]2
(C) Rate = k[A]2[B]
(D) Rate = k[A][B]
22. What is the rate constant for this reaction?
(A) 750 M−2 min−1
(B) 30 M−2 min−1
(C) 15 M−2 min−1
(D) 3.0 M−2 min−1
______________________________________________________________________
23. A rate law is found to be
Rate = k[A][B]
Which of the following actions will not change the initial reaction rate?
(A) Halving the concentration of A and doubling the concentration of B
(B) Doubling the concentration of both A and B
(C) Halving the concentration of A and quadrupling the concentration of B
(D) Doubling the concentration of A and halving the concentration of B
24. In an acid solution, sucrose (C12H22O11) will decompose into fructose and glucose. A plot of ln[C12H22O11] versus time yields a straight line with a slope of -0.45 hr−1. What is the rate law for this decomposition reaction?
(A) Rate = 0.45 hr−1 [C12H22O11]2
(B) Rate = -0.45 hr−1 [C12H22O11]0
(C) Rate = 0.45 hr−1 [C12H22O11]
(D) Rate = -0.45 hr−1 [C12H22O11]−1
25. A catalyst will NOT
(A) increase the forward reaction rate
(B) shift the equilibrium to favor the products
(C) alter the reaction pathway
(D) increase the speed at which equilibrium will be achieved
Free-Response
(a) In the gas phase at 500 °C, cyclopropane, C3H6, reacts to form propene in a first-order reaction.
(i) Given the following data, plot the ln[C3H6] versus time on the grid provided.

(ii) How does this plot verify that the reaction is first order? Justify your answer.
(iii) What is the rate constant for this reaction?
(b) You are given the following reaction and the table of data below.
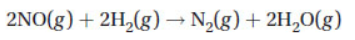
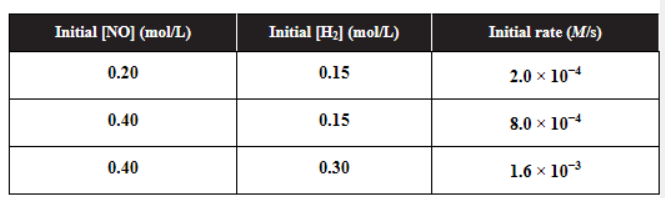
(i) Determine the rate law for this reaction.
(ii) What is the value of the rate constant for this reaction?




