Practice Exercises - Impacts and Linear Momentum - AP Physics 1 Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. Which of the following expressions, where p represents the linear momentum of the particle, is equivalent to the kinetic energy of a moving particle?
(A) mp2
(B) m2/2p
(C) 2p/m
(D) p2/2m
2. Two carts having masses 1.5 kg and 0.7 kg, respectively, are initially at rest and are held together by a compressed massless spring. When released, the 1.5-kg cart moves to the left with a velocity of 7 m/s. What is the velocity and direction of the 0.7-kg cart?
(A) 15 m/s right
(B) 15 m/s left
(C) 7 m/s left
(D) 7 m/s right
3. The product of an object’s instantaneous momentum and its acceleration is equal to its
(A) applied force
(B) kinetic energy
(C) power output
(D) net force
4. A ball with a mass of 0.15 kg has a velocity of 5 m/s. It strikes a wall perpendicularly and bounces off straight back with a velocity of 3 m/s. The ball underwent a change in momentum equal to
(A) 0.30 kg · m/s
(B) 1.20 kg · m/s
(C) 0.15 kg · m/s
(D) 5 kg · m/s
5. What braking force is supplied to a 3,000-kg car traveling with a velocity of 35 m/s that is stopped in 12 s?
(A) 29,400 N
(B) 3,000 N
(C) 8,750 N
(D) 105,000 N
6. A 0.1-kg baseball is thrown with a velocity of 35 m/s. The batter hits it straight back with a velocity of 60 m/s. What is the magnitude of the average impulse exerted on the ball by the bat?
(A) 3.5 N · s
(B) 2.5 N · s
(C) 7.5 N · s
(D) 9.5 N · s
7. A 1-kg object is moving with a velocity of 6 m/s to the right. It collides and sticks to a 2-kg object moving with a velocity of 3 m/s in the same direction. How much kinetic energy was lost in the collision?
(A) 1.5 J
(B) 2 J
(C) 2.5 J
(D) 3 J
8. A 2-kg mass moving with a velocity of 7 m/s collides elastically with a 4-kg mass moving in the opposite direction at 4 m/s. The 2-kg mass reverses direction after the collision and has a new velocity of 3 m/s. What is the new velocity of the 4-kg mass?
(A) −1 m/s
(B) 1 m/s
(C) 6 m/s
(D) 4 m/s
9. A mass m is attached to a massless spring with a force constant k. The mass rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The system is compressed a distance x from the spring’s initial position and then released. The momentum of the mass when the spring passes its equilibrium position is given by
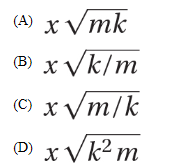
10. During an inelastic collision between two balls, which of the following statements is correct?
(A) Both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved.
(B) Momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy is not conserved.
(C) Momentum is not conserved, but kinetic energy is conserved.
(D) Neither momentum nor kinetic energy is conserved.
Free-Response
1. Two blocks with masses 1 kg and 4 kg, respectively, are moving on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The 1-kg block has a velocity of 12 m/s, and the 4-kg block is ahead of it, moving at 4 m/s, as shown in the diagram below. The 4-kg block has a massless spring attached to the end facing the 1-kg block. The spring has a force constant k equal to 1,000 N/m.
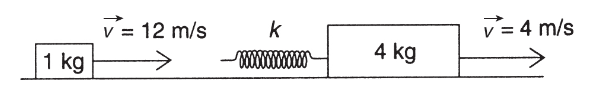
(a) What is the maximum compression of the spring after the collision?
(b) What are the final velocities of the blocks after the collision has taken place?
2. A 0.4-kg disk is initially at rest on a frictionless, horizontal surface. It is hit by a 0.1-kg disk moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 m/s. After the collision, the 0.1-kg disk has a velocity of 2 m/s at an angle of 43° to the positive x-axis.
(a) Determine the velocity and direction of the 0.4-kg disk after the collision.
(b) Determine the amount of kinetic energy lost in the collision.
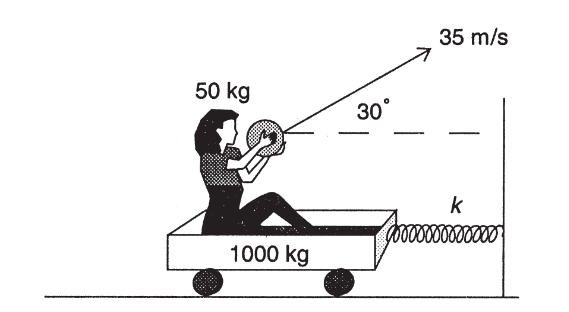
3. A 50-kg girl stands on a platform with wheels on a frictionless, horizontal surface as shown below. The platform has a total mass of 1,000 kg and is attached to a massless spring with a force constant k equal to 1,000 N/m. The girl throws a 1-kg ball with an initial velocity of 35 m/s at an angle of 30° to the horizontal.
(a) What is the recoil velocity of the platform-girl system?
(b) What is the elongation of the spring?
4. (a) Can an object have energy without having momentum? Explain.
(b) Can an object have momentum without having energy? Explain.
5. Explain why there is more danger when you fall and bounce as opposed to falling without bouncing.
6. A cart of mass M is moving with a constant velocity v to the right. A mass m is dropped vertically onto it, and it is observed that the new velocity is less than the original velocity. Explain what has happened in terms of energy, forces, and conservation of momentum (as viewed from different frames of reference).




