Practice Exercises - Gases - AP Chemistry Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. Which of the lines on the figure below is the best representation of the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas when all other factors remain constant?
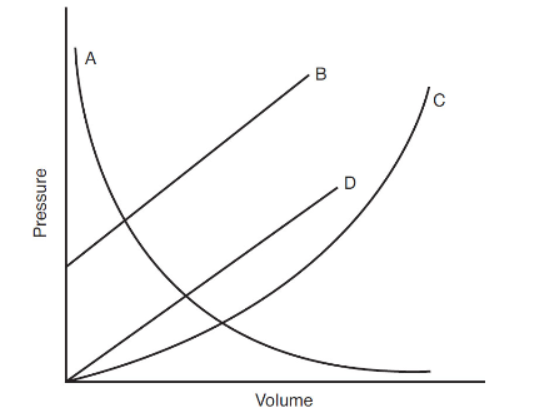
(A) Line A
(B) Line B
(C) Line C
(D) Line D
2. If methane, CH4, rather than ethane, CH3CH3, is the gas used under comparable conditions, there will be an increase in
(A) volume and average kinetic energy
(B) temperature
(C) average kinetic energy and pressure
(D) effusion rate
3. The kinetic molecular theory postulates a direct relationship between
(A) increased volume and increased average kinetic energy
(B) increased temperature and increased average kinetic energy
(C) increased average kinetic energy and increased pressure
(D) increased effusion rate and increased pressure
4. The figure below represents the relative number of gas molecules in separate 2.0 L rigid containers of Cl2, N2, and Ne. The pressure of the container with Cl2 is 6.0 atm. If all three gases are transferred to an evacuated 4.0 L rigid container at constant temperature, what would be the total pressure?
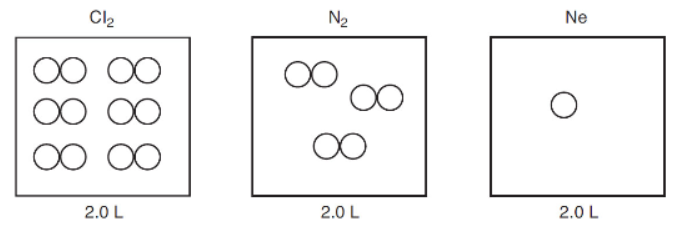
(A) 2.5 atm
(B) 5.0 atm
(C) 7.0 atm
(D) 10. atm
5. A gas will behave more like an ideal gas if we have a _________and a(n) ______________.
(A) large volume, increased temperature
(B) high temperature, high average kinetic energy
(C) high average kinetic energy, high pressure
(D) high effusion rate, high pressure
6. The measured pressure exerted by CO2 gas is less than that predicted by the ideal gas equation when at moderate pressures (5 atm at 298 K). This is mainly because
(A) the attractive intermolecular forces among CO2 molecules is now a factor
(B) CO2 condenses to a liquid at pressures greater than 5 atm at 298 K
(C) the volume of the CO2 molecules becomes significant at high pressures
(D) the gas phase collisions prevent the CO2 molecules from colliding with the walls of the container
7. How many moles of helium are needed to fill a balloon that has a volume of 6.45 L and a pressure of 800 mm Hg at a room temperature of 24 °C? Assume ideal gas behavior.
(A) 0.278 moles
(B) 0.288 moles
(C) 214 moles
(D) 2.65 × 103 moles
8. Which of the following changes will NOT affect the total pressure of gas in a container, assuming all other factors remain constant?
(A) Lowering the average velocity of the molecules
(B) Replacing half of the molecules with an equal number of molecules of a gas with a
different molecular weight
(C) Increasing the frequency of collisions of molecules with the walls
(D) Altering the temperature of the sample
9. A sample of NO has a pressure of 45 mm Hg and a volume of 135 mL. When the NO is quantitatively transferred to an evacuated 1.00 L flask, the pressure of the gas will be
(A) 6080 mm Hg
(B) 374 mm Hg
(C) 111 mm Hg
(D) 6.08 mm Hg
10. At 30 °C a sample of hydrogen is collected over water (PH2O = 31.82 mm Hg at 30 °C) in a 500 mL flask. The total pressure in the collection flask is 745 mm Hg. What will be the percent of error in the amount of hydrogen reported if the correction for the vapor pressure of water is not made?
(A) −4.5%
(B) 0.0%
(C) +4.3%
(D) +4.5%
11. A mixture of gases containing 0.500 atm of chlorine and 0.500 atm of argon is placed into a chamber that is separated from a second chamber by a solid wall with a small pinhole. This allows argon and chlorine to effuse from the first chamber to the second. The temperature is held constant during the experiment. After a short time period, which statement is true?
(A) Only chlorine effuses into the second chamber because its molar mass is 35.5 g/mol.
(B) The second chamber will contain a mixture that has more argon than chlorine because the molar mass of an argon atom is less than that of a chlorine molecule.
(C) The second chamber will contain a mixture that has more chlorine than argon because the molar mass of a chlorine atom is less than that of an argon atom.
(D) Only argon effuses into the second chamber because its molar mass is 40 g/mol.
12. A 0.850-mole sample of nitrous oxide, a gas used as an anesthetic by dentists, has a volume of 20.46 L at 123 °C and 1.35 atm. What would be its volume at 468 °C and 1.35 atm?
(A) 5.38 L
(B) 10.9 L
(C) 19.0 L
(D) 38.3 L
The next two questions involve the figures below. The volume of the box containing argon is twice the volume of the box containing neon. Both gases are at the same temperature.
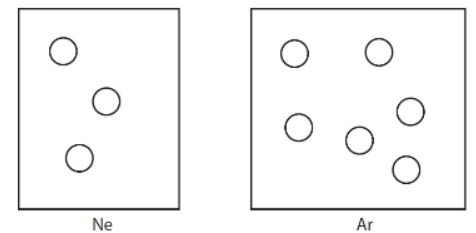
13. When the densities of the two gases were compared, what was found?
(A) The densities of both are equal.
(B) Ar is more dense than Ne.
(C) Ne is more dense than Ar.
(D) Not enough information is given to answer the question.
14. If the neon was transferred to the box containing the argon, what would be the mole fraction of the neon in the mixture?
(A) 4/5
(B) 2/3
(C) 1/2
(D) 1/3
_______________________________________________________________________
15. The effect that increasing the temperature has on the pressure may be explained by the kinetic molecular theory as due to
(A) the increase in force with which the gas molecules collide with the container walls
(B) the increase in rotational energy of the gas molecules
(C) the increase in average velocity of the gas molecules, which causes a corresponding increase in the frequency of collisions with the container walls
(D) a combination of (A) and (C)
16. Hydrogen gas can be prepared by the addition of hydrochloric acid to a sample of zinc. Upon completion of the reaction, 195 mL of gas were collected by water displacement at 25 °C and 753 torr. What mass of the hydrogen gas was collected? Pwater = 24 torr at 25 °C.
(A) 0.00765 g
(B) 0.0154 g
(C) 0.0164 g
(D) 0.159 g
17.Under which conditions will nitrogen behave most like an ideal gas?
(A) Low pressure and high temperature
(B) Low pressure and low temperature
(C) Low volume and high temperature
(D) High pressure and high temperature
18. A compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, and chlorine is allowed to effuse through a pinhole. The rate of effusion for this compound is 0.411 times as fast as neon. What is the correct molecular formula for this compound?
(A) CH2Cl2
(B) C2H2Cl2
(C) C2H3Cl
(D) CHCl3
19. Under identical conditions gaseous CO2 and CCl4 are allowed to diffuse through a pinhole. If the rate of diffusion of the CO2 is 6.3 × 10−2 mol s−1, what is the rate of diffusion of the CCl4?
(A) 1.8 × 10−2 mol s−1
(B) 3.4 × 10−2 mol s−1
(C) 6.3 × 10−2 mol s−1
(D) 2.2 × 10−1 mol s−1
20. A gas has a density, at STP, of 3.48 g L−1. The most reasonable formula for this compound is
(A) C2H6
(B) C6H6
(C) CCl4
(D) CaF2
21. Assuming all other factors remain constant, which of the following changes will NOT affect the total pressure of a gas in a container?
(A) Half of the molecules are replaced by an equal number of molecules of a gas with a different molar mass.
(B) The average velocity of the molecules is lowered.
(C) The frequency of collisions of molecules with the walls is increased.
(D) The temperature of the sample is altered.
22. A gas mixture contains twice as many moles of O2 as N2. Addition of 0.200 mol of argon to this mixture increases the pressure from 0.800 atm to 1.10 atm. How many moles of O2 are in the mixture?
(A) 0.533 mol O2
(B) 0.355 mol O2
(C) 0.200 mol O2
(D) 0.178 mol O2
23. A gas in a 1.50 L container has a pressure of 245 mm Hg. When the gas is transferred completely to a 350. mL container at the same temperature, the pressure will be
(A) 1.05 mm Hg
(B) 1.05 atm
(C) 2.14 mm Hg
(D) 1050 mm Hg
24. At STP a 5.00 L flask filled with air has a mass of 543.251 g. The air in the flask is replaced with another gas, and the mass of the flask is then determined to be 566.107 g. The density of air is 1.290 g L−1. What is the gas that replaced the air?
(A) Ne
(B) O2
(C) Ar
(D) Xe
.png)
25. What volume of hydrogen gas, at STP, will a 0.100 g sample of magnesium (molar mass = 24.31) produce when reacted with an excess of HCl?
(A) 184 mL
(B) 92.1 mL
(C) 46.1 mL
(D) 9.2 mL
Free-Response
Answer the following questions concerning the properties of gases and the theories used to explain their behavior.
(a) Propane gas, C3H8, is used extensively as a fuel for gas grills. The complete combustion of this gas in the presence of oxygen produces carbon dioxide gas, water vapor, and heat.
(i) Write a balanced chemical equation for this combustion reaction.
(ii) Assuming the reaction is proceeding in the presence of excess oxygen, how many liters of carbon dioxide will be produced from a 5.0 L tank at 28 °C and a pressure of 745 mm Hg?
(iii) In some cases, not enough oxygen is present to yield a complete combustion of the gas. So carbon monoxide is produced. Write a balanced equation for the incomplete combustion of propane.
(b) A student performed the decomposition of potassium chlorate, KClO3, to produce oxygen and potassium chloride. In order to collect the oxygen safely, the student used water displacement.
(i) Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
(ii) How much oxygen gas (in mL) did the student collect if 0.25 g of KClO3 were heated at 25 °C and 735 mm Hg? (The vapor pressure of water at 25 °C is 23.8 mm Hg.)
(iii) The theoretical volume of oxygen gas calculated by the student for the gas was 76 mL. Is this number higher or lower than the answer for (ii)? Explain the error the student made in his/her calculation.




