Practice Exercises - Chemical Equilibrium - AP Chemistry Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. The effect of changing the temperature on a chemical system is best determined using
(A) Ka, Q, and the enthalpy of reaction
(B) Ksp and Le Châtelier’s principle
(C) Le Châtelier’s principle and the enthalpy of reaction
(D) Kc and Le Châtelier’s principle
2. How can you determine if a system has come to equilibrium?
(A) By calculating Q and the direction toward equilibrium
(B) If Ksp is equal to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
(C) By comparing Keq to Q
(D) By comparing to see if Kc = Kp
3. The term(s) most useful in determining the solubility of a substance is (are)
(A) Ka and Q
(B) Ksp
(C) Q and Le Châtelier’s principle
(D) Kc and the enthalpy of reaction
4. A chemical system in equilibrium will
(A) have the same concentrations of all products and reactants
(B) form more products if the temperature is increased
(C) have a specific ratio of product to reactant concentrations
(D) not have any precipitates
5. Using logical estimates, in which of the following expressions can the variable x be assumed to be either much smaller than or much larger than the other term(s) to simplify the mathematics?
(A) x[C]
(B) [C] − x
(C) [C]/x
(D) ax2 − bx + c
6. Note the following reaction:
heat + 2NO2 (g) ⇌ N2O4(g)
Which change will not be effective in increasing the amount of N2O4(g)?
(A) Decreasing the volume of the reaction vessel
(B) Increasing the temperature
(C) Adding N2 to increase the pressure
(D) Absorbing the N2O4(g) with a solid absorbant
7. The reaction
2 NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4 (g)
has an equilibrium constant of 4.5 × 103 at a certain temperature. What is the equilibrium constant of
2N2O4 (g) ⇌ 4NO2 (g)?
(A) 9.0 × 106
(B) 4.5 × 103
(C) 2.2 × 10−4
(D) 4.9 × 10−8
8. The correct form of the solubility product for silver sulfate, Ag2SO4, is
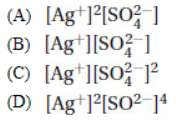
9. In the following concentration versus time curve, at what time has this reaction reached equilibrium?
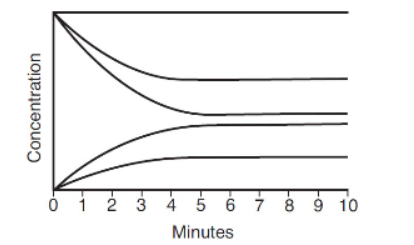
(A) Before 1 minute
(B) Between 1 and 3 minutes
(C) Around 3−4 minutes
(D) After 6 minutes
10. Which is an appropriate formulation of the equilibrium expression for the reaction
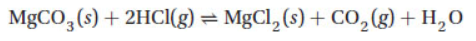
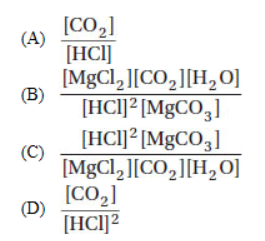
11. In the reaction
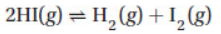
the equilibrium constant is 0.020. If 0.200 mol of HI are placed in a 10.0-L flask, how many moles of I2(g) will be in the flask when equilibrium is reached?
(A) 0.0022 mol
(B) 0.022 mol
(C) 0.025 mol
(D) 2.2 mol
12. For the reaction
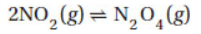
Kp = 8.8 when pressures are measured in atmospheres. Under which of the following conditions will the reaction proceed in the forward direction?
13. The solubility product of PbI2 is 7.9 × 10−9. What is the molar solubility of PbI2 in a solution that has 2.0 × 10−3 molar KI?
(A) 2.0 × 10−3M
(B) 4.0 × 10−6M
(C) 5.0 × 10−4M
(D) 8.9 × 10−5M
14. Consider the concentration versus time curve in question 9. If we call the reactants A and B and the products X and Y, what is the most reasonable chemical equation to describe this reaction?
(A) 2A + 2B ⇄ X + Y
(B) 2A + 3B ⇄ X + 2Y
(C) 2A + B ⇄ 3X + 2Y
(D) A + 2B ⇄ X + 2Y
15. When pure liquids and/or solids are part of a chemical equation, they are not included in the equilibrium expression for that equation. Why?
(A) The concentrations of all pure liquids and solids are defined as 1.00.
(B) Pure substances react very slowly unless ground to a fine powder.
(C) This happens for the same reason that pure substances do not need to be balanced in a chemical equation.
(D) The concentration of a solid or of a liquid at a given temperature and pressure is always a constant no matter how much of the substance is present.
16. Look at questions 9 and 14. Estimate the equilibrium constant for that reaction if the concentration at equilibrium of the bottom line in the graph represents 0.10 M.
(A) 3.7
(B) 0.27
(C) 0.037
(D) 1.0 × 10−2
17. In which of the following cases is the reaction expected to be endothermic?
(A) Increasing the pressure increases the amount of product formed.
(B) Increasing the amount of reactants increases the amount of product formed.
(C) Increasing the temperature increases the amount of product formed.
(D) Increasing the volume decreases the amount of product formed.
18. A reaction has a very large equilibrium constant of 3.3 × 1013. Which statement is NOT true about this reaction?
(A) The reaction is very fast.
(B) The reaction is essentially complete.
(C) The reaction is thermodynamically favored.
(D) The equilibrium constant will change if the temperature is changed.
19. The Ksp of AgCl is 1.8 × 10−10, and the Ksp of AgI is 8.3 × 10−17. A solution is 0.100 M in I− and Cl−. When a silver nitrate solution is slowly added to this mixture, what is the molarity of iodide ions when AgCl just starts to precipitate?
(A) 1.0 × 10−5M
(B) 8.3 × 10−7M
(C) 4.6 × 10−8M
(D) 9.1 × 10−9M
20. A certain reaction is known to be endothermic. A temperature jump experiment is run where the system at equilibrium is rapidly heated a few degrees Celsius and then allowed to cool back to room temperature. The concentrations of the reactants and products are monitored. The following concentration versus time graphs were obtained for all species in the mixture.
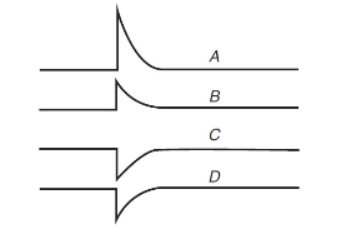
What is the chemical reaction?
(A) A + B ⇄ C + D
(B) 2A + B ⇄ C + D
(C) C + 2B ⇄ 2A + B
(D) C + D ⇄ 2A + B
.png)
21. The equilibrium constant for the reaction
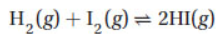
must be determined. If 1.00 g of HI is placed in a 2.00-L flask, which of the following is LEAST important in determining the equilibrium constant?
(A) The temperature must remain constant at the desired value.
(B) Several measurements must be made to assure that the reaction is at equilibrium.
(C) Only one of the three concentrations needs to be accurately determined.
(D) All three concentrations must be accurately measured.
22. In an experiment 0.00300 mol each of SO3(g), SO2(g), and O2(g) were placed in a 10.0 L flask at a certain temperature. When the reaction came to equilibrium, the concentration of SO2(g) in the flask was 3.50 × 10−5M. What is Kc for the reaction
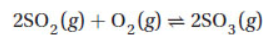
(A) 1.9 × 107
(B) 3.5 × 10−5
(C) 5.2 × 10−8
(D) 1.2 × 10−9
23. The weak acid H2A ionizes in two steps with these equilibrium constants:
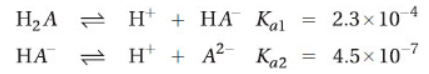
What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction:
H2A ⇌ 2H+ + A2−
(A) 6.8 × 10−11
(B) 1.0 × 10−10
(C) 2.3045 × 10−4
(D) 2.0 × 10−3
Free-Response
Use the principles and techniques of chemical equilibrium to answer the following questions.
1. When performing equilibrium calculations, it is possible to make simplifying assumptions. These assumptions are based in one case on the mathematical principles behind using significant figures in calculations. In a second case, the assumptions are based on an experimental principle of making a measurement.
(a) Explain how an understanding of significant figures allows you to make a simplification and give an example.
(b) Explain how the simplifying assumption often relates to an understanding of a measurement process.
2. (a) The solubility product of HgI2 is 1.1 × 10−28.
(i) What is the molar solubility of HgI2?
(ii) What is the molar solubility if HgI2 is dissolved in 0.000250 molar NaI solution?
(b) At a certain temperature the reaction of hydrogen and chlorine to produce hydrogen chloride, all in the gas phase, has an equilibrium constant of 265. If 25.0 g of HCl are placed in a 150 L vessel and allowed to come to equilibrium, what will the concentrations of all species be?
(c) The gas-phase reaction between oxygen and sulfur dioxide has an equilibrium constant of 8.8 × 1014 at a certain temperature. If 23.4 g of sulfur trioxide are placed in a 20.0 L vessel, calculate the concentration of all species at equilibrium.




