Practice Exercises - Cellular Energetics - AP Biology Premium 2024
Practice Questions
Multiple-Choice
Questions 1–3
Catalase, an enzyme found in aerobic organisms, catalyzes the following reaction:
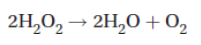
A filter paper disk is saturated with the enzyme catalase and then placed at the bottom of a beaker of H2O2. As the reaction proceeds, oxygen bubbles will cling to the paper and eventually the paper will float to the top of the liquid. By measuring the time it takes for the catalase-saturated disk to float, one can compare the relative rates of decomposition of H2O2 under different experimental conditions.
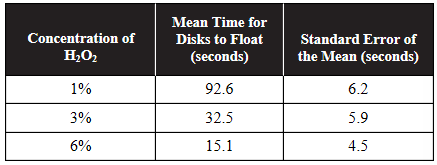
An experiment was performed using catalase extracted from potatoes, with varying concentrations of H2O2. Multiple trials were conducted, and the means and the standard errors of the mean are shown in the following table:
1. Which of the following would be a suitable control for this experiment?
(A) changing the temperature of the H2O2 in one of the beakers
(B) changing the solution the paper disk is soaked in from catalase to water in one of the beakers
(C) changing the source of the catalase from potato to liver
(D) changing the pH of the H2O2 in one of the beakers
2. Predict what would happen if the catalase solution was boiled before performing the experiment, and justify your prediction.
(A) The average time for the disks to float would increase because boiling denatured the enzymes.
(B) The average time for the disks to float would increase because enzyme-catalyzed reactions are always slower at higher temperatures.
(C) The average time for the disks to float would decrease because boiling increased the number of molecular collisions between the enzymes and substrates.
(D) The average time for the disks to float would increase because enzyme-catalyzed reactions are always faster at higher temperatures.
3. A student graphs this data, showing 95% confidence intervals. Based on the 95% confidence intervals, which concentrations of enzyme are least likely to have statistically significant differences?
(A) 1% and 3%
(B) 1% and 6%
(C) 3% and 6%
(D) None of the enzyme concentrations used are likely to have statistically significant differences.
_________________________________________________________________________
(A) adding a cofactor of BCR-ABL
(B) adding a coenzyme of BCR-ABL
(C) adding a competitive inhibitor of BCR-ABL
(D) adding a transcription factor of BCR-ABL
Questions 5–7
Refer to the following figure.
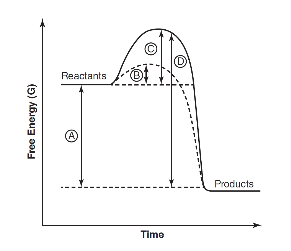
5. Which of the following represents the activation energy of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
6. Which of the following represents the activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
7. Which of the following represents the overall free energy change in the reaction?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
__________________________________________________________________________
(A) Enzymes decrease the overall free energy change of the reaction.
(B) Enzymes decrease the activation energy of the reaction.
(C) Enzymes increase the free energy of the reactants of the reaction.
(D) Enzymes increase the free energy of the products of the reaction.
9. Which of the following correctly describes the differences between competitive inhibitors and noncompetitive inhibitors?
(A) Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of the enzyme; noncompetitive inhibitors bind to the allosteric site of the enzyme.
(B) Competitive inhibitors bind to the substrate; noncompetitive inhibitors bind to the products.
(C) The effects of a noncompetitive inhibitor can be mitigated by adding large amounts of substrate.
(D) Competitive inhibitors increase the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions; noncompetitive inhibitors slow the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
10. Which of the following statements about enzymes is true?
(A) Enzymes can change endergonic reactions into exergonic reactions.
(B) Both proteins and RNA can have catalytic functions.
(C) Enzymes always function optimally at a pH of 7.
(D) Enzymes are consumed during chemical reactions.
Short Free-Response
11. Enzymes are important biological molecules.
(a) Describe how an enzyme interacts with a substrate.
(b) Explain the difference between competitive inhibitors and allosteric inhibitors of enzymes.
(c) An enzyme has its maximum efficiency at an optimum temperature of 25° Celsius. Predict what effect a decrease in temperature to 5° Celsius would have on the enzyme’s efficiency.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
12. The enzyme catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, as shown in this equation:
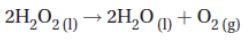
An experiment was performed to measure the amount of oxygen bubbles produced at two different temperatures. The data are shown in the table.
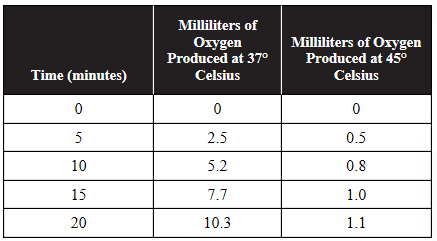
(a) Calculate the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction at both temperatures for the final 10 minutes of the experiment.
(b) Predict which temperature (37°C or 45°C) is closer to the optimum temperature for this enzyme.
(c) Justify your prediction from part (b) using the data provided.
(d) In a follow-up experiment, the reaction was performed at a temperature of 50°C and no oxygen was produced. Explain why the enzyme would not function at 50°C.
Long Free-Response
13. Amylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of amylose into its glucose subunits. The activity of amylase was measured at 37° Celsius and a pH of 7, both of which are optimum conditions for the activity of this enzyme. The production of glucose was measured both with and without the presence of compound X. Data are shown in the following table:
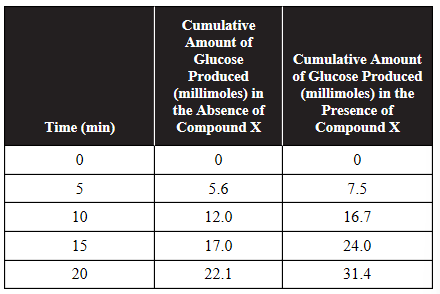
(a) On the axes provided, construct an appropriately labeled graph of this data.
(b) Based on the data and your graph from part (a), identify compound X as either: a cofactor, a competitive inhibitor, or a noncompetitive inhibitor of amylase. Justify your answer with evidence from the data.
(c) Construct an additional line on your graph from part (a) that represents your prediction as to the expected experimental results at a temperature of 10° Celsius in the absence of compound X.
(d) Explain your prediction from part (c), stating why you placed the additional line where you did.
Practice Questions
Multiple-Choice
1. In prokaryotes, where in the cell do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur?
(A) on the thylakoid membrane
(B) on the plasma membrane
(C) in the cytoplasm
(D) in the nucleoid region
Questions 2 and 3
A scientist, who is studying photosynthesis, places a plant in an environment where the oxygen atoms in carbon dioxide are labeled with radioactive 18O but the oxygen atoms in water have nonradioactive 16O.
2. Based on this scenario, predict which product of photosynthesis will contain radioactive 18O.
(A) NADPH
(B) glucose
(C) oxygen gas
(D) ATP
3. Based on this scenario, predict which product of photosynthesis will contain nonradioactive 16O.
(A) NADPH
(B) glucose
(C) oxygen gas
(D) ATP
_____________________________________________________________________________
4. Which of the following lists the three major parts of the light-independent reactions (the Calvin cycle)?
(A) carbon fixation, electron transport chain, reduction
(B) carbon fixation, reduction, production of ATP
(C) carbon fixation, reduction, regeneration of RuBP
(D) reduction, regeneration of RuBP, electron transport chain
5. Which of the following correctly lists the products of the light-dependent reactions?
(A) ADP, NADP+, oxygen
(B) ATP, NADPH, oxygen
(C) G3P, ADP, NADP+
(D) G3P, ATP, NADPH
6. Which of the following correctly lists the products of the Calvin cycle?
(A) ADP, NADP+, oxygen
(B) ATP, NADPH, oxygen
(C) G3P, ADP, NADP+
(D) G3P, ATP, NADPH
7. Which of the following statements correctly identifies the locations of the major parts of photosynthesis in plant cells?
(A) Light-dependent reactions occur in the stroma; light-independent reactions occur in the thylakoid.
(B) Light-dependent reactions occur in the matrix; light-independent reactions occur in the thylakoid.
(C) Light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid; light-independent reactions occur in the matrix.
(D) Light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid; light-independent reactions occur in the stroma.
8. If a thylakoid membrane is punctured so that molecules can freely flow between the thylakoid and the stroma, which of the following processes of photosynthesis will be most directly affected?
(A) the formation of G3P
(B) the generation of a proton gradient
(C) the absorption of light
(D) the fixation of carbon
9.Which of the following best describes a relationship between the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle?
(A) The light-dependent reactions supply the Calvin cycle with oxygen, and the Calvin cycle returns carbon dioxide to the light-dependent reactions.
(B) The light-dependent reactions supply the Calvin cycle with ATP, and the Calvin cycle returns ADP to the light-dependent reactions.
(C) The light-dependent reactions supply the Calvin cycle with carbon dioxide, and the Calvin cycle returns oxygen to the light-dependent reactions.
(D) The light-dependent reactions supply the Calvin cycle with NADP+, and the Calvin cycle returns NADPH to the light-dependent reactions.
10. In the light-dependent reactions, the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is
(A) oxygen.
(B) water.
(C) NAD+.
(D) NADP+.
Short Free-Response
11. The sea slug Elysia crispata eats photosynthetic algae. However, after consuming the algae, the chloroplasts from the algae are incorporated into the sea slug’s own cells, give the sea slug a green color, and remain functional for up to four months. This phenomenon is called kleptoplasty.
(a) Describe the role of photosynthetic algae in ecosystems.
(b) Explain why kleptoplasty would give Elysia crispata a survival advantage.
(c) An oil spill on the surface of the water reduces the intensity of light in Elysia crispata’s habitat. Predict the effect this would have on Elysia crispata’s survival.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
12. The light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis exchange materials and are interdependent, as shown in the following figure.
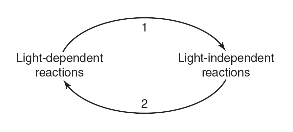
(a) Identify the molecules the light-dependent reactions provide to the light-independent reactions. Label arrow 1 with those molecules.
(b) Identify the molecules the light-independent reactions return to the light-dependent reactions. Label arrow 2 with those molecules.
(c) An inhibitor of the enzyme Rubisco is added to a plant cell. Explain which part of photosynthesis would be most directly affected by this inhibitor.
(d) A student claims that the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis would stop if a plant was kept in the dark for a long period of time. Use your knowledge about photosynthesis to support the student’s claim.
Long Free-Response
13. The following graph shows the absorption spectrum for the pigments chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids.
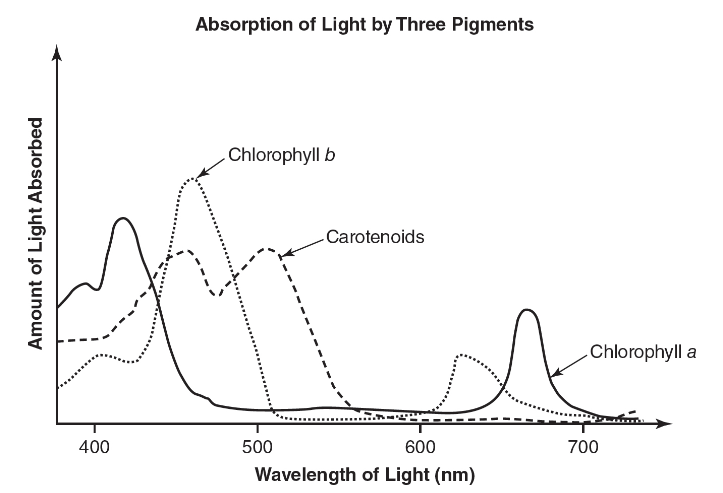
The following table shows the wavelengths of different colors of visible light.
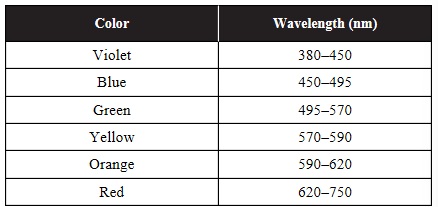
(a) For each of the three pigments, identify the color of light that will be most absorbed by that pigment. Use the graph to justify your answer.
(b) A mutation causes a plant to lose its ability to produce the pigments chlorophyll a and b. A student wants to design an experiment to study the rate of photosynthesis in the plant with this mutation. Identify an appropriate control for the experiment. Identify the independent and dependent variables in the experiment.
(c) The following figure graphs the rate of photosynthesis (as measured by oxygen production) in control plants and in plants with the mutation described in part (b).
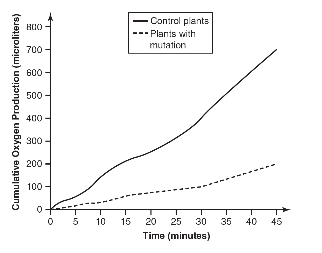
Calculate the rate of photosynthesis in both sets of plants during the first 30 minutes of the experiment.
(d) Plants that use carotenoids as their primary photosynthetic pigment are grown under three different wavelengths of light: 450 nm, 500 nm, and 550 nm. Predict which group of plants will perform the least amount of photosynthesis, and justify your prediction.
Practice Questions
Multiple-Choice
1. What is the primary purpose of fermentation?
(A) to generate ATP
(B) to generate pyruvate
(C) to generate NAD+
(D) to generate carbon dioxide
2. Which of the following processes does NOT release carbon dioxide?
(A) glycolysis
(B) oxidation of pyruvate
(C) Krebs cycle
(D) alcohol fermentation
3. Which of the following statements about glycolysis is NOT correct?
(A) Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol.
(B) Glycolysis can be carried out by all living organisms.
(C) The enzymes of glycolysis are highly conserved.
(D) Glycolysis produces a proton gradient.
4. A mutation in mitochondrial DNA causes the creation of a pore in the mitochondrial membrane through which protons can freely pass. Which of the following processes would most likely be disrupted by this mutation?
(A) glycolysis
(B) Krebs cycle
(C) chemiosmosis
(D) fermentation
5. During oxidative phosphorylation, ____________ is ____________, and oxygen is ____________.
(A) NADH; oxidized; produced
(B) NADH; oxidized; reduced
(C) NAD+; reduced; oxidized
(D) NAD+; reduced; produced
6. Which of the following processes produce ATP?
(A) glycolysis, oxidation of pyruvate, Krebs cycle
(B) glycolysis, Krebs cycle, chemiosmosis
(C) glycolysis, Krebs cycle, fermentation
(D) oxidation of pyruvate, Krebs cycle, fermentation
7. What is the role of oxygen in cellular respiration?
(A) to combine with carbon and electrons to form carbon dioxide
(B) to combine with protons and electrons to form water
(C) to remove carbon from glucose to form pyruvate
(D) to remove carbon from pyruvate to form alcohol
8. Where are the electron transport chain and ATP synthase located?
(A) in the cytosol
(B) on the outer membrane of the mitochondria
(C) on the inner membrane of the mitochondria
(D) in the mitochondrial matrix
9. Which of the following choices correctly describes the flow of electrons in cellular respiration?
(A) glucose → Krebs cycle → oxygen → NAD+
(B) glucose → NAD+ → electron transport chain → oxygen
(C) glucose → electron transport chain → pyruvate → oxygen
(D) glucose → NAD+ → electron transport chain → carbon dioxide
10. Cyanide is a poison that blocks the movement of electrons down the electron transport chain. Which of the following would be the most immediate result of cyanide poisoning?
(A) No pyruvate would be produced.
(B) No NADH would form.
(C) No ATP would be produced.
(D) Chemiosmosis would not occur.
Short Free-Response
11. NAD+ has an important role as an electron carrier in glycolysis.
(a) Identify the process of aerobic cellular respiration during which a cell replenishes its supply of NAD+.
(b) Identify the process of anaerobic respiration during which a cell replenishes its supply of NAD+.
(c) If a cell’s supply of NAD+ ran out, predict the effect that would have on glycolysis within that cell.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
12. In eukaryotes, ATP synthase is found in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. In prokaryotes, which do not have mitochondria, it is found on infoldings of the cell membrane.
(a) Make a claim as to why ATP synthase is found on the cell membrane in prokaryotes.
(b) Justify your claim from part (a) using your knowledge of how ATP synthase works.
(c) Explain why ATP synthase would not be effective if it was found in the cytosol of a cell.
(d) Describe how the structure of the mitochondria allows for the formation of a proton gradient.
Long Free-Response
13. Saccharomyces cerevisiae (also known as baker’s yeast) is a eukaryotic organism. A solution containing 5% yeast and 10% glucose is placed in a transfer pipette. A weight is placed on the transfer pipette, and the apparatus is placed in water in a large test tube, as shown in the following figure.
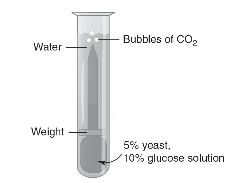
This process is repeated two more times, and each test tube is placed in a beaker of water at different temperatures (5° Celsius, 20° Celsius, and 35° Celsius). To measure the amount of cellular respiration, the cumulative number of bubbles of carbon dioxide released over a 10-minute period is recorded. The data are shown in the following table.
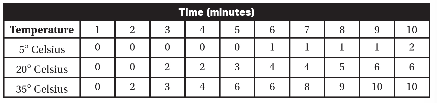
(a) Identify the independent variable and the dependent variable in this experiment.
(b) On the axes provided, construct an appropriately labeled graph of the experimental data.
(c) Calculate the average rate of carbon dioxide production per minute at each temperature.
(d) A fourth experimental apparatus is placed in a beaker of water at a temperature of 10° Celsius. Add a line to your graph from part (b) that predicts the rate of cellular respiration at 10° Celsius. Justify your prediction.




