Practice Exercises - Cell Structure and Function - AP Biology Premium 2024
Practice Questions
Multiple-Choice
1. An animal cell that lacks glycolipids and glycoproteins in its plasma membrane would likely be unable to carry out which of the following functions?
(A) cell recognition
(B) maintaining the fluidity of the phospholipid bilayer
(C) endocytosis
(D) creating a membrane potential
2. When some bacteria are exposed to antibiotics, the bacteria use ATP to try to pump the antibiotics out of their cells. Which of the following processes is most likely used to do this?
(A) osmosis
(B) diffusion
(C) active transport
(D) endocytosis
3. Which of the following is NOT a component of the cell membrane?
(A) phospholipids
(B) cellulose
(C) proteins
(D) glycolipids
4. Muscle cells require large amounts of energy to function. Which cellular organelle is most likely found in high concentrations in muscle cells?
(A) lysosome
(B) Golgi complex
(C) amyloplast
(D) mitochondria
5. Niemann-Pick disease is caused by the cell’s inability to break down large lipid molecules. Which cellular organelle is most likely not functioning properly in an individual with Niemann-Pick disease?
(A) rough endoplasmic reticulum
(B) Golgi complex
(C) lysosomes
(D) ribosomes
6. A student has access to four dyes that stain different components of cells, as shown in the following table.
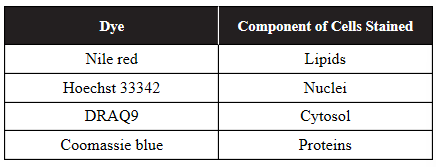
Which dye would be the best choice to use to distinguish prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
(A) Nile red
(B) Hoechst 33342
(C) DRAQ9
(D) Coomassie blue
7. Which types of molecules pass through the cell membrane unassisted most easily?
(A) small and hydrophilic
(B) small and hydrophobic
(C) large and hydrophilic
(D) large and hydrophobic
8. A cell is not able to modify and package proteins for secretion from the cell. Which of the following organelles is most likely not functioning correctly?
(A) ribosomes
(B) lysosomes
(C) vacuoles
(D) Golgi complex
9. Which of the following is NOT evidence that supports the endosymbiosis hypothesis?
(A) Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own circular DNA.
(B) Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own ribosomes.
(C) Mitochondria and chloroplasts reproduce by binary fission.
(D) Mitochondria and chloroplasts are found in all eukaryotic cells.
10. A molecule is moving from an area of higher concentration outside of a cell to an area of lower concentration inside the cell. Which process best describes the movement of this molecule?
(A) active transport
(B) diffusion
(C) endocytosis
(D) exocytosis
Short Free-Response
11. A student conducts an experiment to investigate which cell shape would allow for the most efficient exchange of materials with its environment. Agar blocks (containing bromothymol blue dye) are cut into three different shapes to model three differently shaped cells. The agar blocks are then placed in a vinegar solution. As the vinegar diffuses into the agar models, the acid in the vinegar will turn the bromothymol blue dye yellow. The time required for each agar model to turn completely yellow is measured and is an indication of the efficiency of movement of materials into the agar models. The shape, volume, and surface area of each agar block is shown in the table.
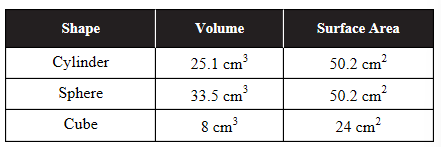
(a) Describe the measurement that would best predict the efficiency of each agar block’s exchange of materials with its environment. Calculate that measurement for each agar block.
(b) Identify the independent variable and the dependent variable in this experiment.
(c) Predict which cell would turn completely yellow first.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
12. Apoptosis is programmed cell death. Apoptosis is often triggered by mutations that could cause a cell to form a tumor if the cell continued to grow and multiply.
(a) Describe the organelle in a eukaryotic cell that is most likely to participate in apoptosis.
(b) Explain other functions the organelle from part (a) would have in the cell besides participating in apoptosis.
(c) A mutation causes the enzymes in the organelle from part (a) to become nonfunctional. Predict what effects this would have on the cell.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
Long Free-Response
13. Two different molecules, A and B, can enter a cell using passive transport. A cell that did not initially contain molecule A or molecule B was placed in a beaker with a solution containing equal concentrations of both molecules for 30 minutes. The cell was removed from the beaker, and the concentration of each molecule inside the cell was measured. The experiment was repeated with different, but equal, starting concentrations of molecules A and B in the beaker. The data are shown in the table.
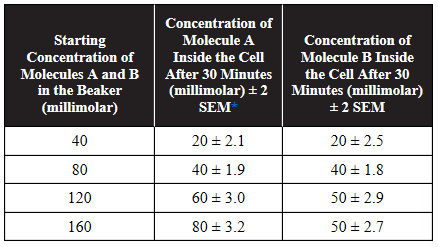
*Standard Error of the Mean
(a) Describe two types of passive transport.
(b) Using the axes provided, construct a graph of this data. Include 95% confidence intervals.
(c) Based on the data, make a claim about which molecule (A or B) uses simple diffusion and which molecule uses facilitated diffusion. Justify your claim with evidence from the data.
(d) This experiment is repeated with the addition of a molecule that irreversibly binds to transport proteins in the cell membrane. Make a prediction about what, if any, changes this would lead to in the data. Justify your prediction.
Practice Questions
Multiple-Choice
1. The solute potential of distilled water is
(A) negative.
(B) zero.
(C) positive.
(D) dependent on the temperature.
2. A solution has a solute concentration of 0.25 moles per liter and is at a temperature of 37°C. The ionization constant of the solute is 1. What is the solute potential of this solution?
(A) –0.64 bars
(B) –0.77 bars
(C) –6.44 bars
(D) –7.70 bars
3. A cell has a solute potential of –5.42 bars and a pressure potential of 0.48 bars. What is its total water potential?
(A) –5.42 bars
(B) –4.94 bars
(C) 0.48 bars
(D) 4.94 bars
4. A blood cell with a water potential of –7.7 bars is placed in distilled water. Which of the following correctly describes what will occur?
(A) Water will flow out of the blood cell because the blood cell has a higher water potential than distilled water.
(B) Water will flow into the blood cell because the blood cell has a higher water potential than distilled water.
(C) Water will flow out of the blood cell because the blood cell has a lower water potential than distilled water.
(D) Water will flow into the blood cell because the blood cell has a lower water potential than distilled water.
5. A plant cell with a solute potential of –4.0 bars and a pressure potential of 0.5 bars is placed into a solution with a water potential of –5.0 bars. What will happen to the plant cell in this solution?
(A) Water will flow into the plant cell because the plant cell has a total water potential that is lower than that of the surrounding solution.
(B) Water will flow into the plant cell because the plant cell has a total water potential that is higher than that of the surrounding solution.
(C) Water will flow out of the plant cell because the plant cell has a total water potential that is lower than that of the surrounding solution.
(D) Water will flow out of the plant cell because the plant cell has a total water potential that is higher than that of the surrounding solution.
6. Four solutions of covalent compounds are in beakers that are open to the atmosphere. Which of the following solutions has the highest water potential?
(A) 0.5 molar glucose at a temperature of 21°C
(B) 0.75 molar fructose at a temperature of 21°C
(C) 1.0 molar sucrose at a temperature of 21°C
(D) 1.25 molar lactose at a temperature of 21°C
7. A freshwater fish is placed in a saltwater aquarium. Predict the most likely effect this will have on the fish, and justify your prediction.
(A) The fish will gain water because it likely has a lower water potential than its new surroundings.
(B) The fish will lose water because it likely has a lower water potential than its new surroundings.
(C) The fish will gain water because it likely has a higher water potential than its new surroundings.
(D) The fish will lose water because it likely has a higher water potential than its new surroundings.
8. Potato slices that are immersed in distilled water for 24 hours become stiff and hard. Potato slices that are immersed in 0.5 molar sucrose solution for 24 hours become limp and soft. Which of the following is the most logical conclusion based on this information?
(A) The potato slices are hypotonic to both distilled water and the 0.5 molar sucrose solution.
(B) The potato slices are hypertonic to both distilled water and the 0.5 molar sucrose solution.
(C) The potato slices are hypotonic to distilled water and hypertonic to the 0.5 molar sucrose solution.
(D) The potato slices are hypertonic to distilled water and hypotonic to the 0.5 molar sucrose solution.
9. Human cells have an approximate NaCl concentration of 0.15 moles per liter. Seawater has an approximate NaCl concentration of 0.45 moles per liter. Which of the following is the most likely effect if a person drank seawater?
(A) The lower water potential in the human cells would cause water to flow out of the human cells into the seawater that was consumed.
(B) The lower water potential in the human cells would cause NaCl to flow out of the human cells into the seawater that was consumed.
(C) The higher water potential in the human cells would cause water to flow out of the human cells into the seawater that was consumed.
(D) The higher water potential in the human cells would cause NaCl to flow out of the human cells into the seawater that was consumed.
10. A dandelion plant is growing in an environment with a temperature of 21°C. The water potential in the root cells of a dandelion plant is –1.2 bars. If a 0.1 molar sodium chloride solution at 21°C was poured on the dandelion roots, what would be the most likely result?
(A) Sodium chloride would move into the dandelion cells, raising the water potential of the dandelion cells.
(B) Water would flow out of the dandelion cells because the water potential in the dandelion cells would be higher than the water potential of the 0.1 molar sodium chloride solution.
(C) There would be no effect on the dandelion cells because they would be open to the atmosphere and have a pressure potential of zero.
(D) Water would flow into the dandelion cells because the water potential in the dandelion cells would be lower than the water potential of the 0.1 molar sodium chloride solution.
Short Free-Response
11. The paramecium Paramecium aurelia has a contractile vacuole, which it uses to pump excess water out of its cell. P. aurelia was placed in four different salt solutions with concentrations of 0.02 molar, 0.04 molar, 0.08 molar, and 0.10 molar salt. The number of contractions of the contractile vacuole per minute was measured over a 10-minute period.
(a) Describe how the water potential of the surrounding solutions would affect the rate of contraction of the contractile vacuole.
(b) Identify the independent variable and dependent variable in this experiment.
(c) As a follow-up experiment, P. aurelia is placed in a beaker that contains distilled water. Predict what effect, if any, this would have on the rate of contraction of the contractile vacuole.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c) using your knowledge of water potential.
12. If a person is in the hospital with severe dehydration, often an intravenous infusion of physiological saline (0.9% saline) will be administered.
(a) Describe how the water potential of a person’s cells would be affected by severe dehydration.
(b) Explain why 0.9% saline is used to rehydrate a person with severe dehydration and why distilled water is not used.
(c) During strenuous exercise under extreme heat, some athletes are advised to consume salt tablets. Predict whether consuming a salt tablet would lead to water loss or water conservation in the athlete’s body cells.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c) using your knowledge of water potential.
Long Free-Response
13. A student conducts an experiment with four different root vegetables (carrots, beets, parsnips, and potatoes). Five cubes of equal sizes and surface areas are cut from each of the vegetables, and their masses are recorded. Each cube is placed in a beaker that contains a 0.35 molar sucrose solution for 24 hours. After 24 hours, the cubes were removed from the solutions and weighed, and the percent change in mass for each cube was calculated. The mean percent change in mass for each vegetable and the standard errors of the mean are shown in the table.
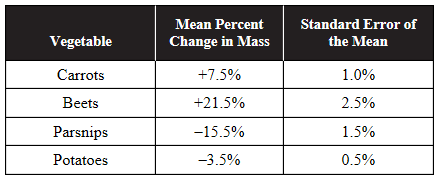
(a) Explain why some of the vegetables would have a positive percent change in mass while others would have a negative percent change in mass during the course of the experiment.
(b) Construct an appropriately labeled graph that shows the mean percent change in mass for each vegetable. Include 95% confidence intervals.
(c) Analyze the data to determine which vegetable has a water potential closest to the water potential of the 0.35 molar sucrose solution used in the experiment. Justify your answer with evidence from the experiment.
(d) It is determined that the sugar content in each vegetable is the major determinant of the vegetable’s water potential. Turnips have a higher sugar content than carrots but a lower sugar content than beets. If the experiment was repeated and included turnip cubes, predict the percent change in mass for the turnip cubes. Justify your prediction with evidence from the experiment.




