Practice Exercises - Cell Communication and Cell Cycle - AP Psychology Premium 2024
Practice Questions
Multiple-Choice
1. Auxin is a plant hormone that triggers cell division. A mutation occurs that deletes the gene for the auxin receptor. Which of the following is the most likely result of this mutation?
(A) The cells will still divide but at a faster rate.
(B) The cells will not be able to divide.
(C) The cells will develop a new receptor for the signaling molecule.
(D) The cells will not be affected by the lack of the auxin receptor.
2. Cortisol is a hormone produced in response to stress. Hunger is a stressor that can increase cortisol levels. Which of the following is most likely an effect of increased cortisol levels in response to hunger?
(A) increased activation of the immune response
(B) increased storage of calcium in bones
(C) increased reabsorption of water by the kidneys
(D) increased hydrolysis of glycogen to glucose
3. How do small ligands move between plant cells?
(A) Receptor proteins on plant cell membranes transport the ligands.
(B) Ligands pass through plasmodesmata that connect plant cells.
(C) Ligands can pass through the plant cell membrane unassisted.
(D) Active transport transfers ligands across the plant cell wall.
4. How do growth factors stimulate cell division?
(A) Growth factors bind to multiple cells, grouping them in multicellular structures.
(B) Growth factors bind to cyclic AMP, removing it from the cytosol.
(C) Growth factors bind to cell membrane receptors, triggering a signal transduction pathway.
(D) Growth factors bind to cell membrane phospholipids, which results in increased cell division.
5. In some autoimmune disorders, the body produces antibodies that bind to cell surface receptors on target cells, blocking them from interacting with other molecules. Which of the following is the most likely effect of the binding of the antibodies to the receptors?
(A) increased stimulation of the target cell
(B) the target cell’s inability to respond to ligands
(C) no effect on the target cell
(D) stimulation of gene expression in the target cell
6. Which of the following best describes the roles of calcium ions and cyclic AMP in the signal transduction process?
(A) They act as ligands.
(B) They act as receptor proteins.
(C) They act as secondary messengers.
(D) They act as protein kinases.
7. Which of the following removes phosphate groups from other molecules?
(A) cyclic AMP
(B) protein kinase
(C) protein phosphatase
(D) adenylyl cyclase
8. The hormone insulin travels through the circulatory system to reach target cells. Insulin is involved in which type of cell signaling?
(A) autocrine signaling
(B) juxtacrine signaling
(C) paracrine signaling
(D) endocrine signaling
9. Neurotransmitters travel short distances across synapses. This is an example of which type of signaling?
(A) autocrine signaling
(B) juxtacrine signaling
(C) paracrine signaling
(D) endocrine signaling
10. Which of the following is the most likely reason why some cells do not respond to certain ligands?
(A) Nonresponsive cells lack cyclic AMP.
(B) Nonresponsive cells lack receptors for the ligand.
(C) Nonresponsive cells lack the gene for the ligand.
(D) Nonresponsive cells cannot metabolize the ligand.
Short Free-Response
11. The ligands in signal transduction pathways may be hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
(a) Describe where in a cell the receptors for hydrophilic ligands and the receptors for hydrophobic ligands are located.
(b) Explain why hydrophobic ligands can cross the cell membrane unassisted.
(c) A mutation in the gene for adenylyl cyclase renders the enzyme ineffective. Predict the effect this would have on the cell.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
12. An experiment is performed to measure how different cell types respond to a hormone that causes cells to absorb glucose from their environment. Four different cell types (A, B, C, and D) are used. At the start of this experiment, there are eight Petri dishes, each of which contains 100 millimolar glucose solution. Two dishes each contain cell type A, two dishes contain cell type B, two dishes contain cell type C, and the final two dishes contain cell type D, as illustrated in the following figure.
The hormone is added to four of the Petri dishes, one of each cell type. Glucose levels are measured in all eight Petri dishes 30 minutes after the addition of the hormone, and those glucose levels are listed in the following table.
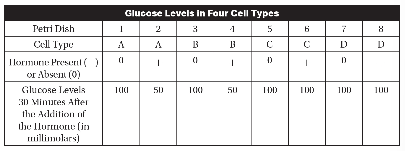
(a) Describe the most likely reason why cell types C and D did not respond to the presence of the hormone.
(b) Identify the function of Petri dishes 1, 3, 5, and 7 in the experimental procedure.
(c) A molecule is added to Petri dish 4 before the hormone is added. This molecule irreversibly binds to this hormone, preventing the hormone from binding to any receptor. The hormone is then added to Petri dish 4. Predict the effect this molecule will have on the glucose concentration in Petri dish 4 at 30 minutes after the addition of the hormone.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
Long Free-Response
13. A signaling pathway for adrenaline is shown in the following diagram.
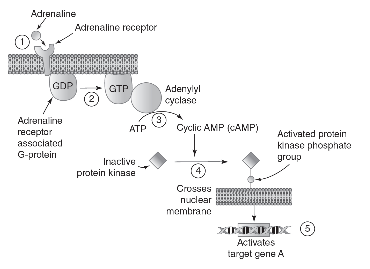
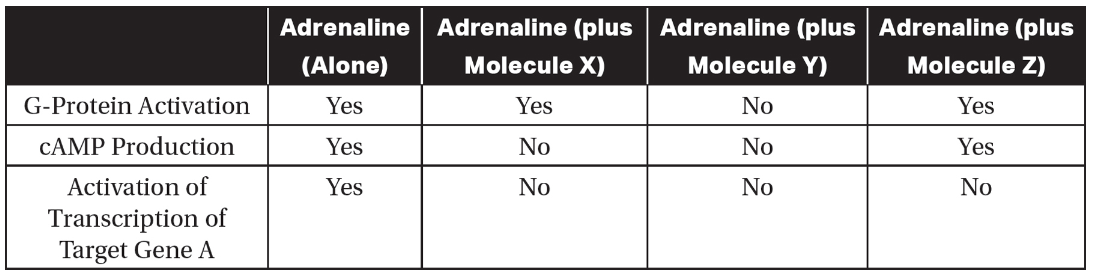
Researchers wanted to measure the effects of three different molecules on the adrenaline signaling pathway. Data are shown in the following table.
(a) Describe the parts of the cell signaling process that are represented in each of the five numbered steps in the diagram.
(b) Identify the control, the independent variable, and the dependent variables in this experimental procedure.
(c) Analyze the data, and identify which molecule(s) most likely interferes with the enzyme adenylyl cyclase.
(d) Cyclic AMP–dependent phosphodiesterase is an enzyme that breaks down cyclic AMP. Predict the numbered step in the diagram that would be most directly affected by adding cAMP-dependent phosphodiesterase to the cell. Justify your prediction.
Practice Questions
Multiple-Choice
1. A chemotherapy drug stops the replication of DNA. During which stage of the cell cycle would this drug have the greatest effect?
(A) G0
(B) G1
(C) G2
(D) S
2. A cell has reached full maturity, is fully differentiated, and no longer divides. Which of the following describes this stage of the cell cycle?
(A) G0
(B) G1
(C) G2
(D) S
3. Which stage of mitosis has twice as many chromosomes at its end as it had at its beginning?
(A) prophase
(B) metaphase
(C) anaphase
(D) telophase
4. During which stage of mitosis do the centromeres of chromosomes attach to spindle fibers and line up in a single column in the center of the cell?
(A) prophase
(B) metaphase
(C) anaphase
(D) telophase
5. A researcher measures the number of cells in each phase of the cell cycle. The data are shown in the following table. Approximately, what percentage of these cells are in interphase?
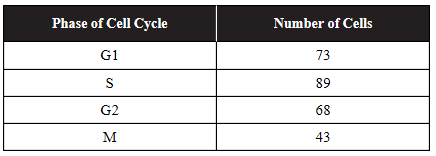
(A) 16%
(B) 33%
(C) 52%
(D) 84%
6. Which process best describes what occurs when soft tissue between the fingers dies during embryonic development?
(A) apoptosis
(B) DNA replication
(C) mitosis
(D) cytokinesis
7. During which process are the cytoplasm (and its cellular contents) divided between daughter cells?
(A) apoptosis
(B) DNA replication
(C) mitosis
(D) cytokinesis
8. Which of the following is a correct statement?
(A) Cancer cells exhibit anchorage dependence.
(B) Somatic cells exhibit density-dependent inhibition.
(C) Somatic cells spend most of their time in mitosis.
(D) Cancer cells exhibit density-dependent inhibition.
9. Which of the following best describes a role of mitosis?
(A) Mitosis distributes cytosol between the daughter cells.
(B) Replication of DNA occurs during mitosis.
(C) Replication of cell organelles occurs during mitosis.
(D) Mitosis distributes genetic material between the daughter cells.
10. During which phase of the cell cycle is a cleavage furrow or cell plate formed?
(A) interphase
(B) mitosis
(C) cytokinesis
(D) G0
Short Free-Response
11. Lectin is a molecule commonly found in legumes. Colchicine is a molecule that inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. An experiment was performed to observe the effects of lectin and colchicine on dividing cells. A total of 300 cells were observed for each treatment. Partial results of the experiment are shown in the following table.
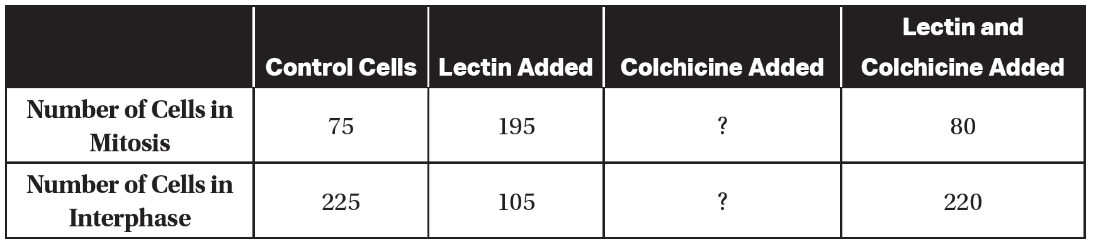
(a) Describe the effect of adding lectin to the cells.
(b) Identify the independent variable and the dependent variable in this experiment.
(c) Based on the data presented, predict the most likely effects of adding only colchicine to the cells.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
12. The following figure represents the concentrations of two different molecules (cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase) during the cell cycle, and the arrow indicates the start of mitosis.
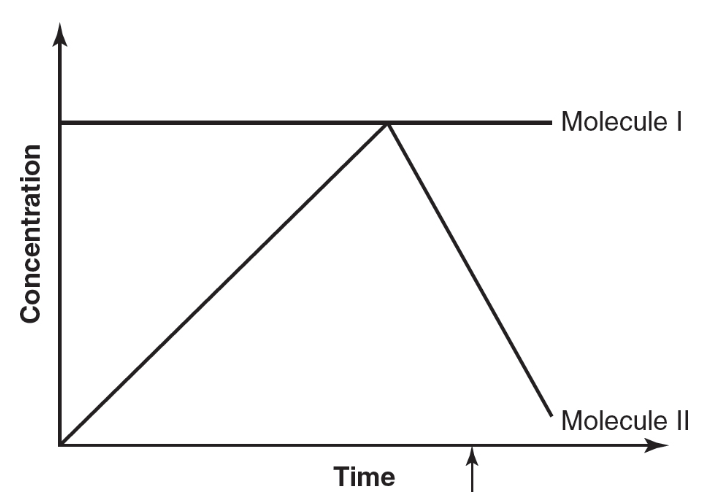
(a) Cell division can be described as having three major events: replication of chromosomes, alignment of chromosomes, and separation of chromosomes. Describe the stages of the cell cycle during which each of these three major events occurs.
(b) In the figure, which molecule (cyclin or cyclin-dependent kinase) is represented by the line labeled “Molecule I”? Which molecule (cyclin or cyclin-dependent kinase) is represented by the line labeled “Molecule II”?
(c) Explain why mitosis starts at the point indicated by the arrow in the figure.
(d) A cancer cell has a mutation that results in the constant production of Molecule II. Explain how the process of mitosis might be affected by this mutation.
Long Free-Response
13. A student wants to test whether treating onion root cells with caffeine will significantly increase the number of cells in mitosis. Two groups of onions are grown: one group received distilled water, and the other received distilled water with caffeine. The root tips of both groups are harvested and stained, and the number of cells in interphase and mitosis in each group is counted. The expected and observed data are shown in the following table.
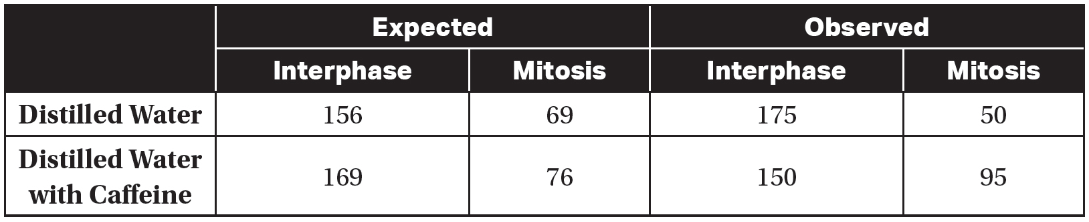
(a) State the null hypothesis for this experiment.
(b) Identify the independent variable and the dependent variable.
(c) Use the chi-square equation and a p-value of 0.05 to analyze the data. Determine if there is a statistically significant difference between the two groups of onions.
(d) Justify your conclusion from part (c).




