Practice Exercises - Acids and Bases - AP Chemistry Premium 2024
Multiple-Choice
1. Which of the following can be made by partially neutralizing an acid?
(A) BaClOH by neutralizing BaCl2
(B) KOH by neutralizing H2O with K2Cr2O7
(C) NaHCO3 by neutralizing H2CO3 with NaOH
(D) MgCO3 by neutralizing H2CO3 with Mg(OH)2
2. A solution containing HF is titrated with KOH. At the end point of the titration, the solution contains
(A) equal amounts of HF and KOH
(B) KF and H2O
(C) K+ and F-
(D) H2O, H+, OH-, K+, F-, and HF
3. A buffer at pH 5.32 is prepared from a weak acid with a pKa = 5.15. If 100 mL of this buffer is diluted to 200 mL with distilled water, what is the pH of the dilute solution?
(A) 5.02
(B) 5.32
(C) 5.62
(D) The identity of the acid is needed to answer the question.
4. When an equal number of moles of each pair is mixed to make an aqueous solution, which of these solutions can be called a buffer?
(A) Cu(OH)2 and CuCl2
(B) KOH and NaHCO3
(C) LiHCO3 and K2CO3
(D) Na2CO3 and H2SO3
5. Which of the following has the highest pH?
(A) 0.100 M HCl
(B) 0.200 M HC2H3O2
(C) 0.100 M Na2CO3
(D) 0.200 M NaCl
6. Which of the following CANNOT occur together in solution?
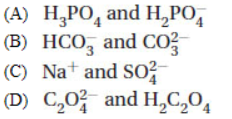
7. When 0.250 mol of NaOH are added to 1.00 L of 0.100 M H3PO4, the solution will contain
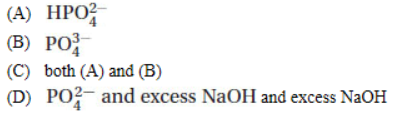
8. A buffer with a pH of 10.0 is needed. Which of the following should be used?
(A) Ethanoic acid with a Ka of 1.8 × 10-5
(B) Ammonia with a Kb of 1.8 × 10-5
(C) Nitrous acid with a Ka of 7.1 × 10-4
(D) 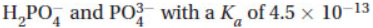
9. pH is equal to pKa
(A) when [conjugate acid] = [conjugate base]
(B) at the end point of a titration
(C) in the buffer region
(D) in the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
10. The pH of a 0.125 M solution of a newly synthesized weak base is 10.45. What is the Kb of this base?
(A) 3.5 × 10-11
(B) 6.4 × 10-7
(C) 2.8 × 10-4
(D) 2.3 × 10-3
11. Which of the following solutions is the acid anhydride of a monoprotic acid?
(A) CaO
(B) SO3
(C) N2O5
(D) CO2
12. Which of the following solutions is expected to result in a solution with the lowest pH? Assume a 0.025 M solution of the nitrate salt of each of these ions.
(A) Ca2+
(B) Ni2+
(C) Fe3+
(D) Na+
13. Which of the following statements is correct?
(A) HClO2 is a stronger acid than HClO3.
(B) HI is a weaker acid than HCl.
(C) CH3COOH is a stronger acid than CH2BrCOOH.
(D) HNO3 is a stronger acid than HNO2.
14. What is the pH of a 0.100 M solution of KH2PO4? (For H3PO4, pK1 = 2.15; pK2 = 7.20; pK3 = 12.35.)
(A) 9.78
(B) 6.67
(C) 4.67
(D) 2.15
15. Which of the following is the correct method for preparing a buffer solution?
(A) Mix the correct amounts of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
(B) Neutralize a weak base partially with strong acid.
(C) Neutralize a weak acid partially with a strong base.
(D) All of the above methods may be used to prepare buffers.
Use the titration curve below to answer questions 16 to 21.
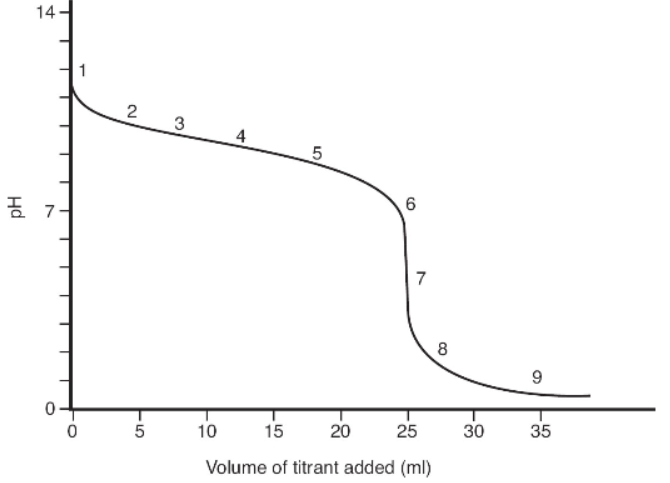
16. What is the titrant and what is the analyte in the experiment that resulted in the titration curve above?
(A) The titrant is a strong acid, and the analyte is a strong base.
(B) The titrant is a weak base, and the analyte is a weak acid.
(C) The titrant is a strong base, and the analyte is a weak acid.
(D) The titrant is a strong acid, and the analyte is a weak base.
17. What is the pH and volume of titrant at the end point?
(A) pH = 7.00; end point = 25.0 mL
(B) pH = 7.0; end point = 12.5 mL
(C) pH = 4.8; end point = 25.0 mL
(D) pH = 5; end point = 25 mL
18. At which point(s) does the analyte flask contain a buffer solution?
(A) At points 2, 3, 4, and 5
(B) At points 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6
(C) Only at point 4
(D) Only at point 7
19. How many moles of analyte were in the analyte flask if the molarity of the titrant was predetermined to be 0.0855 M?
(A) 2.34 mol
(B) 2.13 mol
(C) 0.002138 mol
(D) 0.0021 mol
20. What is true about the the pK of the analyte?
(A) pKa = 9.2
(B) pKb = 9.2
(C) pKb = 4.8
(D) pKa = 11.7
21. What is characteristic of the end point for this type of experiment?
(A) It occurs when a color change occurs.
(B) It occurs at the inflection point of the curve.
(C) It occurs when the first derivative is at a minimum.
(D) It occurs at exactly pH 7.
________________________________________________________________________
22. What is a primary standard used for?
(A) It is used to calibrate a pH meter.
(B) It is used to prepare calibration curves for spectroscopy.
(C) It is used to standardize titrants.
(D) It is the first standard that is prepared.
.png)
23. If 50.0 mL of a 0.0134 M HCl solution is mixed with 24.0 mL of a 0.0250 M NaOH solution, what is the pH of the final mixture?
(A) 1.87
(B) 3.02
(C) 5.29
(D) 12.40
24. If 50.0 g of formic acid (HCHO2, Ka = 1.8 × 10-4) and 30.0 g of sodium formate (NaCHO2) are dissolved to make 500 mL of solution, the pH of this solution is
(A) 4.76
(B) 4.12
(C) 3.76
(D) 3.35
Free-Response
Propanoic acid, CH3CH2COOH, has an acid ionization constant of Ka = 1.3 × 10-5. Ammonia, NH3, has a base ionization constant of Kb = 1.8 × 10-5.
(a) Write the balanced equation for the reaction of propanoic acid, CH3CH2COOH, with ammonia.
(b) Identify the two conjugate acid–base pairs.
(c) Does the equilibrium position lie on the reactant or the product side of the equation when equal moles of propanoic acid and ammonia are mixed? Justify your choice.
(d) Of the two acids in your equation, which is stronger and why?
(e) Of the two bases in your equation, which is stronger and why?
(f) Using appropriate scientific reasoning, state why you would conclude that one binary acid is stronger than another. Give a relevant example.
(g) Using appropriate scientific reasoning, state why you would conclude that one oxoacid is stronger than another. Give a relevant example.




