Diagnostic Test - AP Physics 1 Premium 2024
Section I: Multiple-Choice

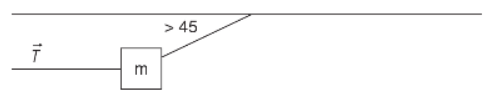
1. A mass is suspended from the ceiling by one rope at an angle as indicated. The mass is held in place by a second, horizontal rope. Without knowing the exact angle from the ceiling, except that it is greater than 45 degrees, which statement best represents the possible value for tension in the horizontal line?
(A) T > m
(B) T = mg
(C) T < mg
(D) cannot be determined without knowing the angle
2. Pushing on a mass of 15 kg with a sideways force of 120 N is not enough to get the mass to start sliding across the floor. Which of the following best describes the coefficient of static friction between the floor and the mass?
(A) μ = 0.8
(B) μ > 0.8
(C) μ < 0.8
(D) μ = 1.25
3. While standing on an elevator and experiencing a downward acceleration of 4.9 m/s2, what is the force between the floor and your feet? The variable m is your mass.
(A) mg
(B) 0.5mg
(C) 1.5mg
(D) 4.9mg
4. After throwing a ball at an upward angle, the reason the ball continues to go horizontally while falling due to gravity is that
(A) the ball’s inertia keeps it going
(B) the force of the throw keeps it going
(C) the energy from gravitational potential keeps replenishing the lost energy
(D) air pressure keeps the ball from falling too quickly
5. Consider the situation in which your hand is pushing a book across a rough desktop with lots of friction. Of the many forces involved, consider only these two individual forces: the force on your hand from the book and the force the book is experiencing from your hand. While the book is accelerating from rest to its final velocity, which statement best compares the force experienced by your hand compared with that experienced by the book?
(A) Force on book > force on hand
(B) Force on hand > force on book
(C) Force on hand = force on book
(D) The relationship between these two forces depends on the frictional force.
6. A puck comes to a stop on a level floor in 20 meters after an initial speed of 10 m/s. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the puck and the floor?
(A) The mass is required to calculate this answer.
(B) 0.25
(C) 0.5
(D) 0.025
7. A rock is dropped from an extremely high cliff and experiences free-fall conditions. Which of the following statements is NOT true about the rock’s velocity, acceleration, or displacement between the 3rd and 4th seconds of falling?
(A) The rock will fall an additional 4.9 meters.
(B) The rock will speed up by 9.8 m/s.
(C) The rock’s acceleration will remain 9.8 m/s2.
(D) The rock’s displacement, velocity, and acceleration vectors are all directed downward.
8. When using the kinematics equation x = x0 + vx0t + ½axt2, which of the following is always assumed to be true?
(A) ax = zero
(B) x > x0
(C) Vx0 is positive.
(D) ax is constant.
9. Consider a projectile launched at 30 degrees above a flat surface. The projectile experiences no air resistance and lands at the same height from which it was launched. Compare the initial and final conditions of the following vector components:
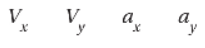
(A) They are all the same at both instances.
(B) They are all different from their initial values.
(C) Vx and Vy have changed, but ax and ay are constant.
(D) They are all the same except for Vy.
10. A physics teacher is swirling a bucket around in a vertical circle. If the bucket slips out of his hand when it is directly overhead, the bucket will
(A) fly upward initially
(B) drop straight down
(C) fly out horizontally initially
(D) fly out up and at an angle initially
11. If the Moon was twice as far from the center of Earth as it is currently, how would its orbital period change?
(A) The Moon’s orbital period would double.
(B) The Moon’s orbital period would increase by a factor of 4.
(C) The Moon’s orbital period would increase by a factor of 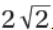 .
.
(D) The Moon’s orbital period would decrease by a factor of 2.
12. If you went to another planet, which of the following would be true?
(A) Your mass would be the same, but your weight would change.
(B) Your mass would change, but your weight would be the same.
(C) Your mass would be the same, and your weight would be the same.
(D) Your mass would change, and your weight would change.
13. You lift a heavy suitcase twice. Each time you lift it to the same height, but the second time you do it in half the time. Compare the work done to and power delivered to the suitcase.
(A) Same work, same power
(B) Twice the work, twice the power
(C) Twice the work, same power
(D) Same work, twice the power
14. A constant horizontal force of 12 N is applied for 5 meters to move an initially stationary mass of 5 kg. The friction between the floor and the mass does a total of −40 joules of work to the mass. The final speed (in m/s) of the object is
(A) 2(6)½
(B) 2(2)½
(C) 2(10)½
(D) 4
15. A skier begins a downhill run at a height of 9 meters and a speed of 2 m/s. If you ignore friction, what will be her speed when she is 3 meters from the bottom of the slope?
(A) 6.0 m/s
(B) 12.8 m/s
(C) 11.1 m/s
(D) 7.7 m/s
16. A rubber ball (m = 0.250 kg) strikes a wall horizontally at 3.50 m/s and rebounds elastically. What is the magnitude of impulse delivered to the wall in N ⋅ s?
(A) 0.875
(B) 1.75
(C) 2.50
(D) 8.75
17. A running back (m = 85 kg) running at 1.5 m/s is tackled from the side by another player (m = 75 kg) running perpendicularly to the running back’s original heading at 1.75 m/s. What is the resulting speed of the two entangled players just after the tackle?
(A) 2.2 m/s
(B) 0.25 m/s
(C) 1.6 m/
(D) 1.1 m/s

18. Which of the following ranks the torques applied by the three equal forces A, B, and C to the long thin rod about its fixed axis as indicated?
(A) τC > τB > τA
(B) τA = τB > τC
(C) τB = τC > τA
(D) τB > τA > τC
19. A large spherical cloud of dust in deep space that is spinning slowly collapses under its own gravitational force into a spherical cloud 10 times smaller in diameter. How does its rotational speed change?
(A) The rotational speed does not change.
(B) The rotational speed increases by a factor of 10.
(C) The rotational speed decreases by a factor of 10.
(D) The rotational speed increases by a factor of 100.
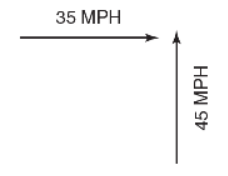
20. Two cars approach an intersection at right angles, as pictured above. What is their relative speed to each other?
(A) 10 mph
(B) 45 mph
(C) 57 mph
(D) 80 mph
21. Which of the following statements are true regarding collisions? Select two answers.
(A) An elastic collision conserves both net momentum and net kinetic energy.
(B) An inelastic collision conserves mechanical energy but not net momentum.
(C) An elastic collision between two objects has equal but opposite impulses delivered.
(D) An inelastic collision between two objects is one in which both objects come to rest during the collision.
Section II: Free-Response
1. A static, nonuniform wedge-shaped mass, m (with center of mass x as indicated), with a base length of L (shown below) is supported at two points. The first support point is at the bottom left corner of the wedge. The second support point is located at a point ¾ of the length of the wedge away from that corner.
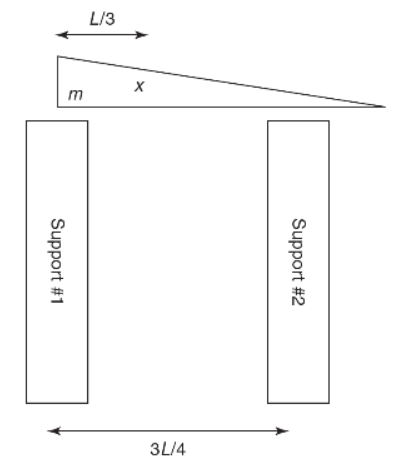
(a) Using as givens m, L, and g (the gravitational field strength), solve for the two unknown contact forces at the points of support (F1 and F2).
(b) Support #2 is removed. The wedge begins to fall by rotating around support #1 with an angular acceleration of 2 rad/s2. If the mass of the wedge is 3.8 kg and L = 75 cm, determine the moment of inertia of the nonuniform wedge about the top of support #1.
(c) As the wedge continues to rotate clockwise but remains in contact with support #1:
(i) Does the angular acceleration increase, decrease, or remain the same? Justify your response.
(ii) Does the moment of inertia of the wedge increase, decrease, or remain the same? Justify your response.
2. An object of unknown mass is fired at an unknown angle with an initial speed of 25 m/s. Ignore frictional effects. If only 45 percent of its initial kinetic energy is still present as kinetic energy at the projectile’s highest point, determine the time in flight for the projectile.




