AP Physics 2 Premium, 2024-Magnetism and Electromagnetism
1. A charge moves in a circular orbit of radius R due to a uniform magnetic field. If the velocity of the charge is doubled, the orbital radius will become
(A) 2R
(B) R
(C) R/2
(D) 4R
2. Inside a solenoid, the magnetic field
(A) is zero
(B) decreases along the axis
(C) increases along the axis
(D) is uniform
3. An electron crosses a perpendicular magnetic field as shown below. The direction of the induced magnetic force is
(A) to the right
(B) to the left
(C) out of the page
(D) into the page
.png)
4. Three centimeters from a long, straight wire, the magnetic field produced by the current is determined to be equal to 3 × 10−5 T. The current in the wire must be
(A) 2.0 A
(B) 4.5 A
(C) 1.5 A
(D) 3 A
5. Magnetic field lines determine
(A) only the direction of the field
(B) the relative strength of the field
(C) both the relative strength and the direction of the field
(D) only the configuration of the field
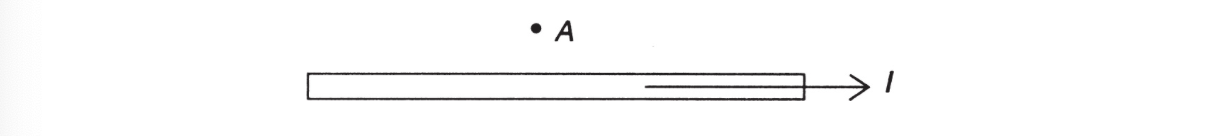
6. What is the direction of the magnetic field at point A above the wire carrying current?
(A) Out of the page
(B) Into the page
(C) Up the page
(D) Down the page
7. A bar magnet is pushed through a flat coil of wire. The induced emf is greatest when
(A) the north pole is pushed through first
(B) the magnet is pushed through quickly
(C) the magnet is pushed through slowly
(D) the south pole is pushed through first
8. The magnetic flux through a wire loop is independent of
(A) the shape of the loop
(B) the area of the loop
(C) the strength of the magnetic flux
(D) the orientation of the magnetic field and the loop
9. A flat, 300-turn coil has a resistance of 3 Ω. The coil covers an area of 15 cm2 in such a way that its axis is parallel to an external magnetic field. At what rate must the magnetic field change in order to induce a current of 0.75 A in the coil?
(A) 0.0075 T/s
(B) 2.5 T/s
(C) 0.0005 T/s
(D) 5 T/s
10. When a loop of wire is turned in a magnetic field, the direction of the induced emf changes every
(A) one-quarter revolution
(B) two revolutions
(C) one revolution
(D) one-half revolution
11. A wire of length 0.15 m is passed through a magnetic field with a strength of 0.2 T. What must be the velocity of the wire if an emf of 0.25 V is to be induced?
(A) 8.3 m/s
(B) 6.7 m/s
(C) 0.0075 m/s
(D) 0.12 m/s
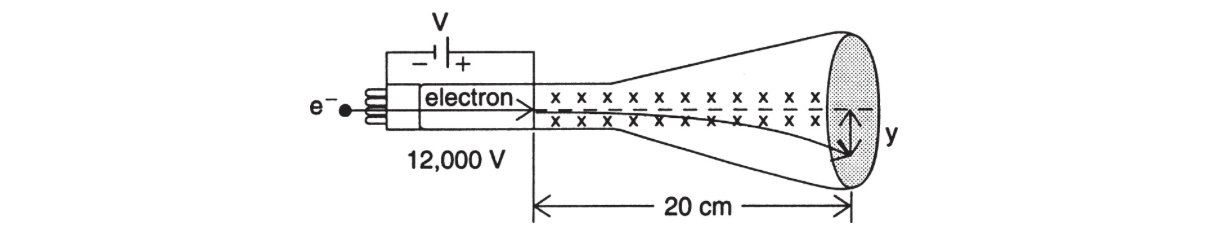
12. An electron is accelerated by a potential difference of 12,000 V as shown in the following diagram. The electron enters a cathode ray tube that is 20 cm in length, and the external magnetic field causes the path to deflect along a vertical screen for a distance y.
(a) What is the kinetic energy of the electron as it enters the cathode ray tube?
(b) What is the velocity of the electron as it enters the cathode ray tube?
(c) If the external magnetic field has a strength of 4 × 10−5 T, what is the value of y? Assume that the field has a negligible effect on the horizontal velocity.
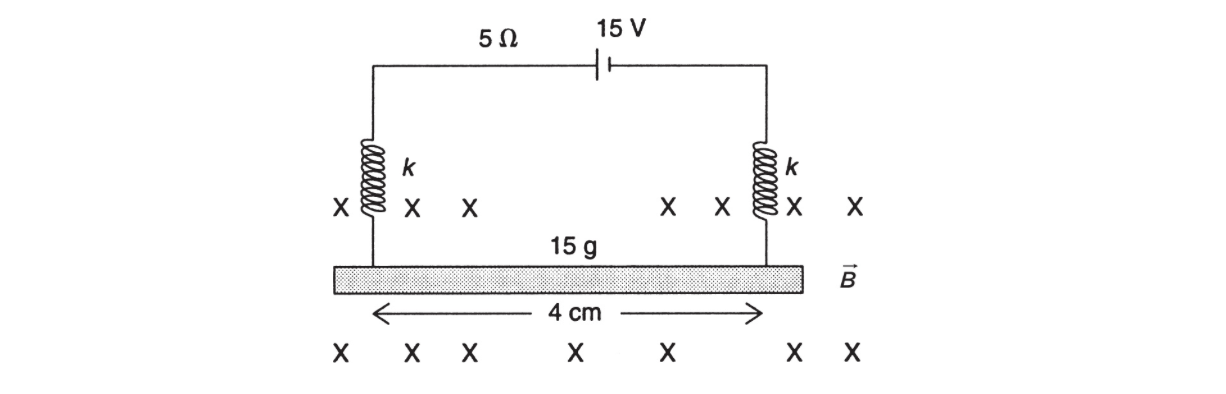
13. A straight conductor has a mass of 15 g and is 4 cm long. It is suspended from two parallel and identical springs as shown below. In this arrangement, the springs stretch a distance of 0.3 cm. The system is attached to a rigid source of potential difference equal to 15 V, and the overall resistance of the circuit is 5 Ω. When current flows through the conductor, an external magnetic field is turned on, and it is observed that the springs stretch an additional 0.1 cm. What is the strength of the magnetic field?
14. Explain why a bar magnet loses its magnetic strength if it is struck too many times.
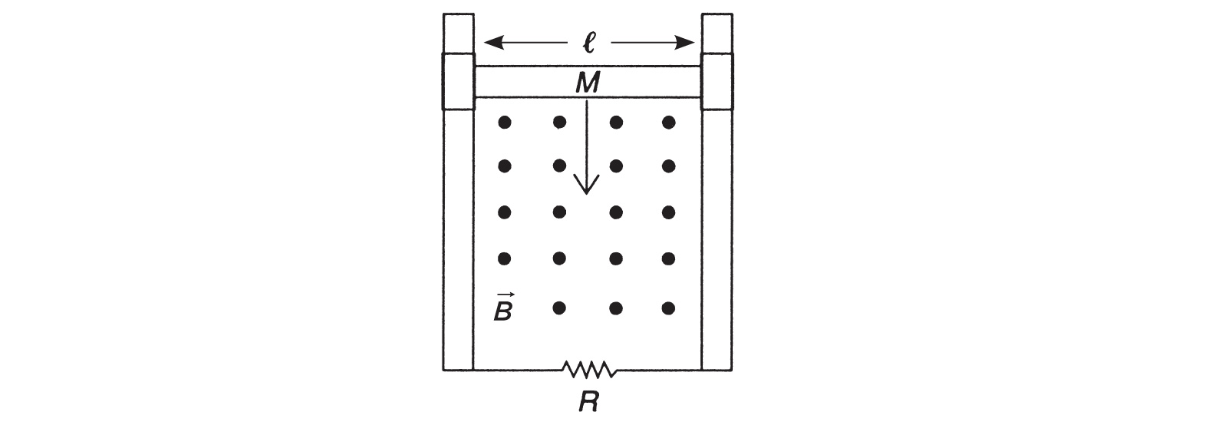
15. A horizontal conducting bar is free to slide along a pair of vertical bars, as shown below. The conductor has length ℓ and mass M. As it slides vertically downward under the influence of gravity, it passes through an outward-directed, uniform magnetic field. The resistance of the entire circuit is R. Find an expression for the terminal velocity of the conductor (neglect any frictional effects due to sliding).
16. A small cylindrical magnet is dropped into a long copper tube. The magnet takes longer to emerge than the predicted free-fall time. Give an explanation for this effect.




