AP Physics 2 Premium, 2024 - Quantum, Atomic, and Nuclear Physics
1. How many photons are associated with a beam of light having a frequency of 2 × 1016 Hz and a detectable energy of 6.63 × 10−15 J?
(A) 25
(B) 500
(C) 135
(D) 8
2. A photoelectric experiment reveals a maximum kinetic energy of 2.2 eV for a certain metal. The stopping potential for the emitted electrons is
(A) 1.2 V
(B) 1.75 V
(C) 3.5 V
(D) 2.2 V
3. The work function for a certain metal is 3.7 eV. What is the threshold frequency for this metal?
(A )9 × 1014 Hz
(B) 2 × 1015 Hz
(C) 7 × 1014 Hz
(D) 5 × 1015 Hz
4. In which kind of waves do the photons have the greatest momentum?
(A) Radio waves
(B) Microwaves
(C) Red light
(D) X ray
5. What is the momentum of a photon associated with yellow light that has a wavelength of 5,500 Å?
(A) 1.2 × 10−27 kg · m/s
(B) 1.2 × 10−37 kg · m/s
(C) 1.2 × 10−17 kg · m/s
(D) 1.2 × 10−30 kg · m/s
6. What is the de Broglie wavelength for a proton (m = 1.67 × 10−27 kg) with a velocity of 6 × 107 m/s?
(A) 1.5 × 1014 m
(B) 1.5 × 10−14 m
(C) 4.8 × 10−11 m
(D) 6.6 × 10−15 m
7. Which of the following statements is correct about emission line spectra?
(A) All of the lines are evenly spaced.
(B) All elements in the same chemical family have the same spectra.
(C) Only gases emit emission lines.
(D) All lines result from discrete energy differences.
8. Which electron transition will emit a photon with the greatest frequency?
(A) n = 1 to n = 4
(B) n = 5 to n = 2
(C) n = 3 to n = 1
(D) n = 7 to n = 3
9. An electron in the ground state of a hydrogen atom can absorb a photon with any of the following energies except
(A) 10.2 eV
(B) 12.1 eV
(C) 12.5 eV
(D) 12.75 eV
10. Which of the following statements about the atom is correct?
(A) Orbiting electrons can sharply deflect passing alpha particles.
(B) The nucleus of the atom is electrically neutral.
(C) The nucleus of the atom deflects alpha particles into parabolic trajectories.
(D) The nucleus of the atom contains most of the atomic mass.
11. Which of the following statements about the Bohr theory reflect how it differs from classical predictions about the atom?
I. An electron can orbit without a net force acting.
II. An electron can orbit about a nucleus.
III. An electron can be accelerated without radiating energy.
IV. An orbiting electron has a quantized angular momentum that is proportional to Planck’s constant.
(A) I and II
(B) I and III
(C) III and IV
(D) II and IV
12. An electron makes a transition from a higher energy state to the ground state in a Bohr atom. As a result of this transition,
(A) the total energy of the atom is increased
(B) the force of attraction on the electron is increased
(C) the energy of the ground state is increased
(D) the charge on the electron is increased
13. How many different photon frequencies can be emitted if an electron is in excited state n = 4 in a hydrogen atom?
(A) 1
(B) 3
(C) 5
(D) 6
14. A radioactive atom emits a gamma ray photon. As a result,
(A) the energy of the nucleus is decreased
(B) the charge in the nucleus is decreased
(C) the ground-state energy is decreased
(D) the force on an orbiting electron is decreased
15. How many neutrons are in a nucleus of 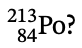 ?
?
(A) 84
(B) 129
(C) 213
(D) 297

17. Which radiation has the greatest ability to penetrate matter
(A) X ray
(B) Alpha particle
(C) Gamma ray
(D) Beta particle
18. In the following nuclear reaction, an isotope of aluminum is bombarded by alpha particles:
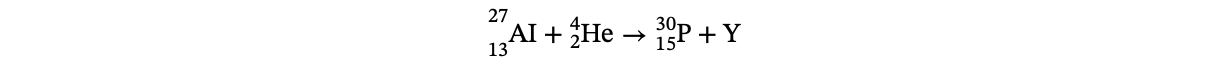
Quantity Y must be
(A) a neutron
(B) an electron
(C) a positron
(D) a photon
19. When a gamma-ray photon is emitted from a radioactive nucleus, which of the following occurs?
(A) The nucleus goes to an excited state.
(B) The nucleus goes to a more stable state.
(C) An electron goes to an excited state.
(D) The atomic number of the nucleus decreases.
20. The threshold frequency for calcium is 7.7 × 1014 Hz.
(a) What is the work function, in joules, for calcium?
(b) If light of wavelength 2.5 × 10−7 m is incident on calcium, what will be the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons?
(c) What is the stopping potential for the electrons emitted under the conditions in part (b)?
21. Explain why electrons are diffracted through a crystal.
22. Explain why increasing the intensity of electromagnetic radiation on a photoemissive surface does not affect the kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectrons. Why is this kinetic energy referred to as the “maximum kinetic energy”?
23. Why don’t we speak of the wavelength nature of large objects such as cars or balls?
24. If a source of light from excited hydrogen gas is moving toward or away from an observer, what changes, if any, are observed in the emission spectral lines?
25. Given the isotope 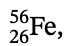 , which has an actual mass of 55.934939 u:
, which has an actual mass of 55.934939 u:
(a) Determine the mass defect of the nucleus in atomic mass units.
(b) Determine the average binding energy per nucleon in units of million electron volts.
26. Why do heavier stable nuclei have more neutrons than protons?
27. Why are the conditions for the fusion of hydrogen into helium favorable inside the core of a star?
28. Explain the radioactive disintegration series of uranium-238 into stable lead-206 in terms of the neutron-proton plot.
29. Albert Einstein, in his special theory of relativity, stated that energy and mass were related by the expression E = mc2. Explain how the concept of binding energy confirms this claim.




