AP Physics 2 Premium, 2024 - Practice Test 1
SECTION I: MULTIPLE-CHOICE
1. Which materials have the highest heat conductivity?
(A) Gases because the individual particles move the fastest
(B) Gases because they are the easiest to ionize
(C) Metals because they are ductile and malleable
(D) Metals because they have conduction layers
2. A gas is not able to do work under which of the following circumstances?
(A) Isobaric because pressure is required for work to be done
(B) Isobaric because constant force will produce no work
(C) Isochoric because constant shape implies no changes in energy
(D) Isochoric because no change in volume implies no displacement
3.Which of the following materials will exert the highest pressure on its bottom surface?
(A) 1 liter of water in a puddle on the ground
(B) 1 liter of water, frozen into a cube on the ground
(C) 1 liter of water in a tall, thin, vertical tube
(D) 1 liter of water, frozen into a cube, floating in liquid water
4. In which of the following situations would the greatest increase in average atomic velocity be required?
(A) Raising the temperature of one million Helium atoms by 100 Kelvin
(B) Raising the temperature of one million Neon atoms by 100 Kelvin
(C) Raising the temperature of one million Helium atoms by 100 degrees Fahrenheit
(D) Raising the temperature of one million Neon atoms by 100 degrees Fahrenheit
QUESTIONS 5 AND 6 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING GRAPHS:
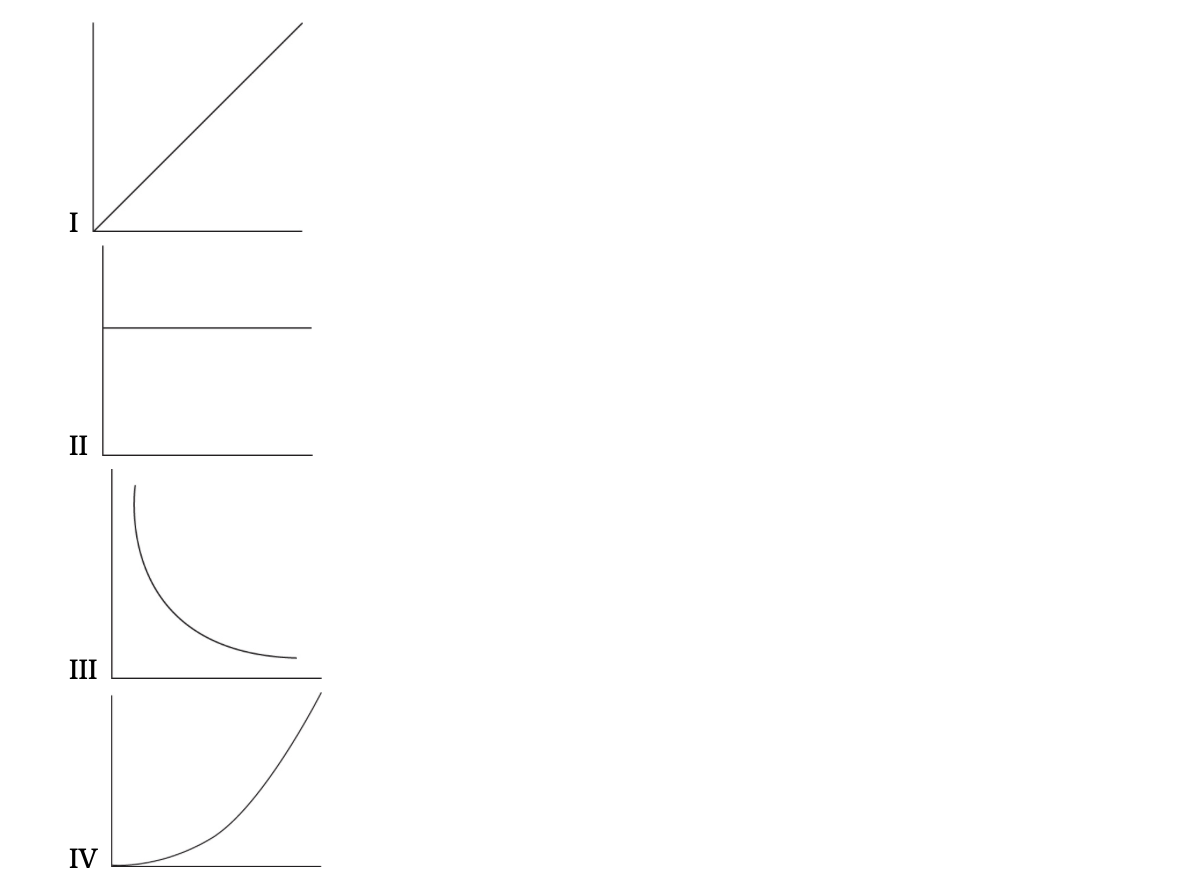

5. Which graph best represents the relationship between pressure and volume for an ideal confined gas at constant temperature?
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
6. Which graph best represents the relationship between the average kinetic energy of the molecules in an ideal gas and its absolute temperature?
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
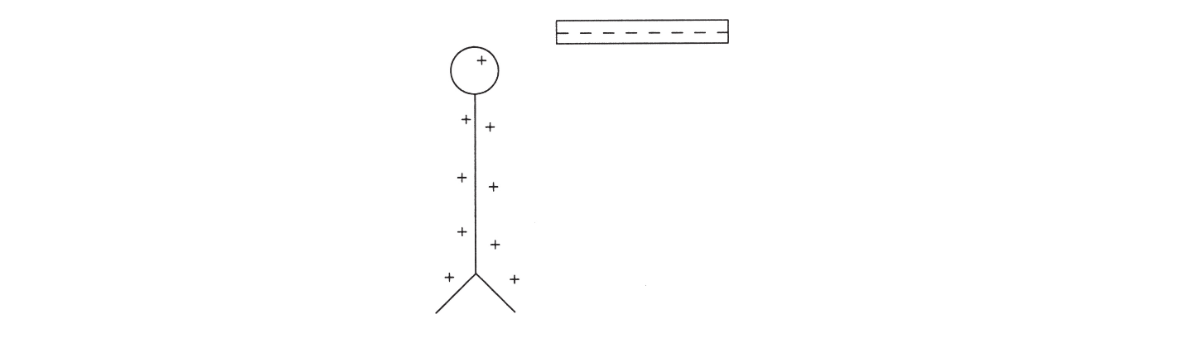
7. The diagram above shows a leaf electroscope that has been charged positively by a negatively charged rod. Which of the following statements is correct?
(A) The electroscope was charged by conduction.
(B) The electroscope was charged by contact.
(C) If the rod is brought closer, protons will move to the top of the electroscope.
(D) If the rod is brought closer, electrons will be repelled from the top of the electro-scope.
QUESTIONS 8 AND 9 ARE BASED ON THE CIRCUIT SHOWN BELOW:
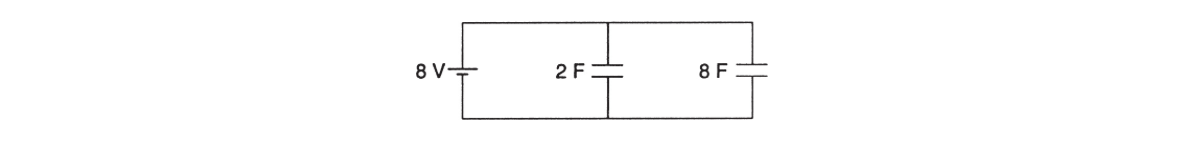
8. What is the maximum charge stored in the 2-farad capacitor?
(A) 4 C
(B) 16 C
(C) 10 C
(D) 8 C
9. What is the maximum energy stored in the 8-farad capacitor?
(A) 64 J
(B) 256 J
(C) 32 J
(D) 128 J
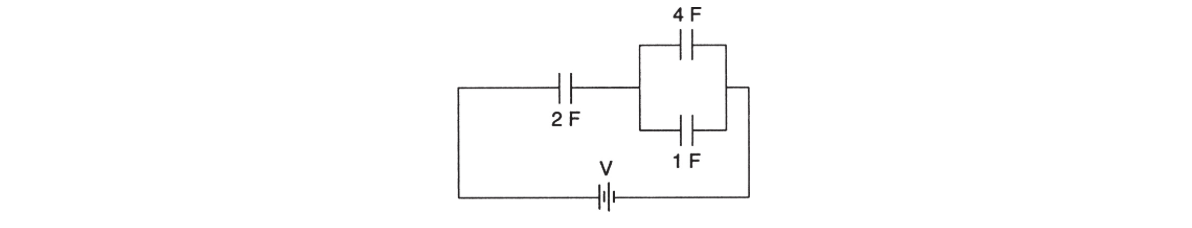
10.What is the equivalent capacitance of the circuit shown above?
(A) 7/10 F
(B) 10/7 F
(C) 7 F
(D) 14/5 F
11. An electron (charge e, mass m) is trapped in a circular path because of a uniform perpendicular magnetic field B. The velocity of the electron is v, and the radius of the path is r. Which of the following expressions represents the angular velocity ω?
(A) (Ber/m)½
(B) (Be/rm)½
(C) Be/m
(D) 2πBe/m
QUESTIONS 12 AND 13 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION AND DIAGRAM:
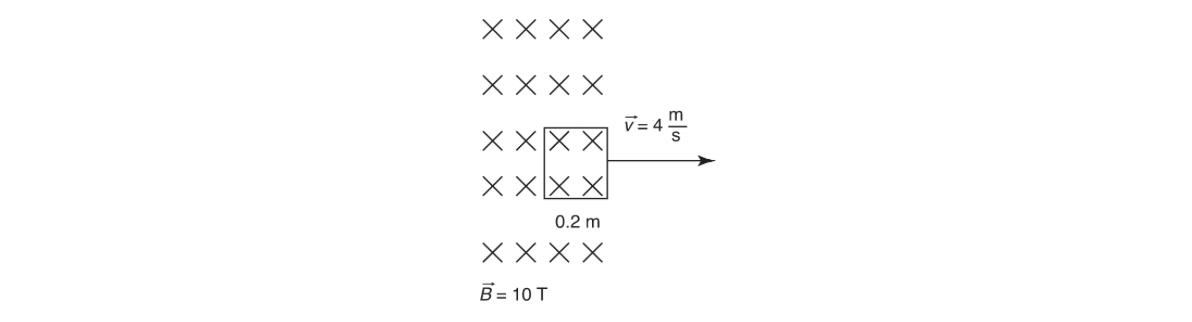
A square wire frame is pulled to the right with a velocity of 4 meters per second across and out of an inward uniform magnetic field of strength 10 teslas. The length of each side of the frame is 0.2 meters.
12. What is the magnitude of the induced motional electromotive force in the wire as it leaves the field?
(A) 40 V
(B) 20 V
(C) 8 V
(D) 16 V
13. As the wire is moved to the right, a force appears to oppose it. This force’s opposing direction is best explained by
(A) Lenz’s law because an opposing force keeps the flux from changing
(B) Faraday’s law because the changing flux induces emf
(C) Lenz’s law because the force must be in the negative direction
(D) Faraday’s law since decreasing flux always produces negative forces
14. A shadow is formed by a point source of light. Upon closer inspection, the edges of the shadow seem to be diffuse and fuzzy. This phenomenon is probably caused by
(A) dispersion as the different wavelengths of light focus at different points
(B) refraction as the rays are bent by their contact with the shadow-forming surface
(C) diffraction as the waves nearest the edge of the shadow-forming surface are sources for waves going into the shadow region
(D) dispersion as the different wavelengths are traveling at slightly different speeds in the new medium
.png)
15. A light ray is incident on a glass-air interface as shown above. Which path will the light ray follow after it enters the air?
(A) A or B
(B) B or C
(C) E
(D) D
16. As the angle of incidence for a ray of light passing from glass to air increases, the critical angle of incidence for the glass
(A) increases
(B) decreases
(C) increases and then decreases
(D) remains the same
17. Which of the following statements about a diverging mirror is correct?
(A) The mirror must be concave in shape.
(B) The images are sometimes larger than the actual objects.
(C) The images are always upright.
(D) The images are sometimes real.
18. Which of the following waves cannot be polarized?
(A) Sound waves because they are longitudinal
(B) Waves on a string because they lack amplitude
(C) X rays because they are too short
(D) Microwaves because they have too low of a frequency
19. The “flapping” of a flag in the wind is best explained using
(A) Bernoulli’s principle due to the difference in pressure at various heights
(B) Bernoulli’s principle due to the difference in pressure for different velocities
(C) Archimedes’ principle due to the difference in pressure at various heights
(D) Archimedes’ principle due to the difference in pressure for different velocities
20. In a photoelectric effect experiment, the emitted electrons could be stopped with a retarding potential of 12 volts. What was the maximum kinetic energy of these electrons?
(A) 1.92 × 10–18 J
(B) 12 J
(C) 1.6 × 10–19 eV
(D) 1.92 × 10–18 eV
21. As a single photon of light enters a new medium with a higher index of refraction, the photon’s energy
(A) decreases as the wave speed is now lower
(B) decreases as its wavelength is now shorter
(C) remains constant because its speed
(D) remains constant because its frequency remains the same
22. If an electron and an alpha particle were moving with the same velocity, which one would have the smaller de Broglie wavelength?
(A)The electron since its charge is negative
(B)The electron since it has only one unit of elementary charge
(C)The alpha particle since it is heavier
(D)The alpha particle since it has two units of elementary charge
QUESTIONS 23 AND 24 ARE BASED ON THE FOLLOWING SIMULATED ENERGY-LEVEL DIAGRAM FOR A MYTHICAL HYDROGEN-LIKE ATOM:
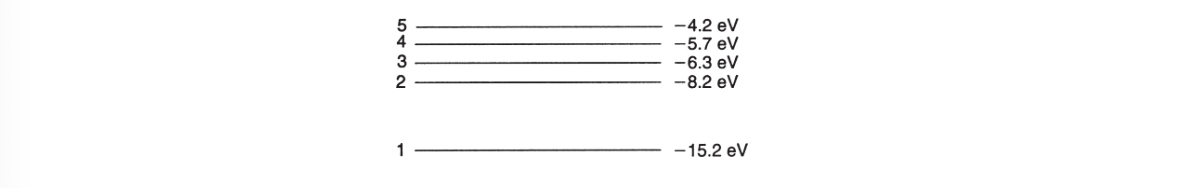
23. How much energy is required to ionize an atom with an electron in level 3?
(A) 8.1 eV
(B) 6.3 eV
(C) 15.2 eV
(D) 2.5 eV
24. Which of the following level transitions will result in the emission of a photon with the highest frequency?
(A) 1 to 3
(B) 5 to 2
(C) 1 to 2
(D) 2 to 1
25. The mass per nucleon in different elemental nuclei changes because
(A) the number of nucleons is different for the different elements
(B) some elements are radioactive, and others are not
(C) the binding energies are different in different nuclei
(D) the mass per nucleon is the same in all elements
26. How many neutrons are contained in the isotope 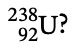
(A) 92
(B) 100
(C) 146
(D) 330
27.In the reaction below, what is the mass number for particle X?
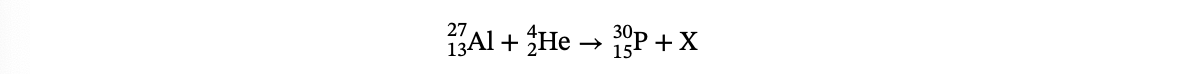
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 0
(D) −1
28. A device that takes mechanical energy and converts it into electrical energy is
(A) a solenoid
(B) an electric motor
(C) a transformer
(D) a generator
29. Radon gas 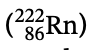 is radioactive with a half-life of four days as it undergoes alpha decay. A sample is sealed in an evacuated tube for more than one week. At that time, the presence of a second gas is detected. This gas is most probably
is radioactive with a half-life of four days as it undergoes alpha decay. A sample is sealed in an evacuated tube for more than one week. At that time, the presence of a second gas is detected. This gas is most probably
(A) hydrogen
(B) helium
(C) nitrogen
(D) argon
30. According to the scale of binding energy per nucleon, which atom has the most stable nuclear isotope?
(A) Hydrogen because it cannot decay into anything
(B) Hydrogen because it can exist with only one nucleon
(C) Iron because its nucleons are the most tightly bound
(D) Iron because it is in the middle of the periodic table
31. The colors observed in thin films like soap bubbles are caused by
(A) reflection and interference
(B) refraction and reflection
(C) diffraction and interference
(D) polarization and reflection
32. As the number of lines per cm on a diffraction grating is increased (or the slit spacing is decreased in a two-slit diffraction pattern),
(A) the spacing between the spectral lines increases
(B) the spacing between the spectral lines decreases
(C) the intensity of the spectral lines increases
(D) the intensity of the spectral lines decreases
33. Which is storing more energy, a 20-microfarad capacitor charged up by a 6-volt source or a 10-microfarad capacitor charged up by a 12-volt source?
(A) They both store the same amount of energy.
(B) Neither is storing energy.
(C) The 20-microfarad capacitor is storing more energy.
(D) The 10-microfarad capacitor is storing more energy.
34. What is the function of a moderator in a fission reactor?
(A) Control the number of neutrons
(B) Act as a source of fissionable material
(C) Control the costs of running the reactor
(D) Control the half-life of the radioactive material
35. Compare the energy and speed of a 30-MHz photon with those of a 15-MHz photon.
(A) They have the same speed and energy.
(B) The 30-MHz photon has higher speed and energy.
(C) The 30-MHz photon has higher energy but the same speed.
(D) The 30-MHz photon has lower energy but the same speed.
36. An electric motor has an effective resistance of 30 ohms, using 4 amperes of current when plugged into a 120-volt outlet. As the motor heats up, its effective resistance increases. Which statement best describes the power consumption of the motor?
(A) It starts off at 480 W and goes down from there as 42R as it heats up.
(B) It starts off at 480 W and goes up from there as 42R as it heats up.
(C) It starts off at 480 W and goes down from there as 1202/R as it heats up.
(D) It starts off at 480 W and goes up from there as 1202/R as it heats up.
37. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long, straight wire?
(A) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(B) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
(C)The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
(D) The field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire.
38. Electrons are being shot into a uniform magnetic field. The angles of the electrons’ velocity vary as they are being shot. A magnetic force will be exerted on all electrons except those that are
(A) perpendicular to the field
(B) parallel to the field
(C) at a 45° angle to the field
(D) either perpendicular or parallel to the field, depending on the strength of the field
39. Your friend asks you to explain where the energy comes from in a demo. This demo shows that as a magnet is thrust quickly into a coil of wire, a current is produced, but when a piece of wood is pushed in just as quickly, there is no current produced.
(A) The energy is actually the same in both situations.
(B) The coil of wire used stored magnetic energy to move the charges.
(C) The energy comes from an application of Faraday’s law to the coil.
(D) The magnet requires more work to be thrust into the coil than the piece of wood.
40. Which of the following statements about the adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas is correct?
(A) The temperature may change during the expansion.
(B) The process must be isothermal.
(C) No change will occur in the internal energy.
(D) The gas cannot do any work during the expansion.
41. Which of the following processes is not involved in an ideal Carnot cycle?
(A) Isothermal expansion
(B) Isobaric expansion
(C) Adiabatic expansion
(D) Adiabatic compression
42. A charged rod attracts a suspended pith ball. The ball remains in contact with the rod for a few seconds and then is visibly repelled. Which of the following statements must be correct?
(A) The pith ball is negatively charged at the end of the process.
(B) The rod is negatively charged.
(C) The pith ball remained neutral throughout the process.
(D) The rod has less charge on it at the end of the process than at the beginning.
43. One material is shown to refract light to a greater degree than a second material. This indicates that
(A) the first material is more opaque than the second
(B) the first material has heavier atoms than the second
(C) the speed of light is slower in the first material
(D) the first material is more magnetic than the second
44. Comparing gravitational fields to electric fields shows that they are very similar. Which of the following is a major difference?
(A) Gravitational fields do not have direction, whereas electric fields do.
(B) Gravitational fields do not have equipotential lines associated with them, whereas electric fields do.
(C) Gravitational field lines show the direction of force for positive mass, whereas electric field lines show the direction for negative charge.
(D) Gravitational field lines do not have sources, whereas electric field lines can be sourced by positive charges.
45. Bernoulli’s equation for fluids is essentially
(A) Newton’s laws for fluids
(B) energy conservation for fluids
(C) momentum conservation for fluids
(D) Bernoulli’s equation is not based on any of these
46. Which of the following transformations could a transformer accomplish? Select two answers.
(A) Increase AC input voltage with decreased AC current output
(B) Decrease AV input voltage with an increase in AC current output
(C) Transform AC to DV with the same current
(D) Decrease DC voltage with an increase in DC current
47. Which of the following are synonyms for voltage? Select two answers.
(A) Electromotive force
(B) Electrical potential energy
(C) Potential difference
(D) amp · hr
48. Which of the following are examples of polarization of waves? Select two answers.

(A) Two instruments play a sound pitches very close together and produce a beat frequency.
(B) A student creates a transverse wave by moving their hand up and down.
(C) Light reflected at the Brewster angle
(D) The alternating dark and light spot patterns on a screen behind two slits illuminated by a laser
49. What energies could be associated with a photon emitted during an overall transition from level 4 to level 2 of the diagram above? Select two answers.
(A) 1.9 eV
(B) 5.7 eV
(C) 2.5 eV
(D) 6.3 eV
50. The electric field near the surfaces of a rectangular solid conducting object with 15 microcoulombs of extra charge can be described as which of the following? Select two answers.
(A) Directed normally outward near the outside surfaces
(B) Uniform in strength near all outside surfaces
(C) Zero on the inside
(D) Directed normally inward near the inside surfaces
45. Bernoulli’s equation for fluids is essentially
(A) Newton’s laws for fluids
(B) energy conservation for fluids
(C) momentum conservation for fluids
(D) Bernoulli’s equation is not based on any of these
46. Which of the following transformations could a transformer accomplish? Select two answers.
(A) Increase AC input voltage with decreased AC current output
(B) Decrease AV input voltage with an increase in AC current output
(C) Transform AC to DV with the same current
(D) Decrease DC voltage with an increase in DC current
47. Which of the following are synonyms for voltage? Select two answers.
(A) Electromotive force
(B) Electrical potential energy
(C) Potential difference
(D) amp · hr
48. Which of the following are examples of polarization of waves? Select two answers.
(A) Two instruments play a sound pitches very close together and produce a beat frequency.
(B) A student creates a transverse wave by moving their hand up and down.
(C) Light reflected at the Brewster angle
(D) The alternating dark and light spot patterns on a screen behind two slits illuminated by a laser
49. What energies could be associated with a photon emitted during an overall transition from level 4 to level 2 of the diagram above? Select two answers.
(A) 1.9 eV
(B) 5.7 eV
(C) 2.5 eV
(D) 6.3 eV
50. The electric field near the surfaces of a rectangular solid conducting object with 15 microcoulombs of extra charge can be described as which of the following? Select two answers.
(A) Directed normally outward near the outside surfaces
(B) Uniform in strength near all outside surfaces
(C) Zero on the inside
(D) Directed normally inward near the inside surfaces
45. Bernoulli’s equation for fluids is essentially
(A) Newton’s laws for fluids
(B) energy conservation for fluids
(C) momentum conservation for fluids
(D) Bernoulli’s equation is not based on any of these
46. Which of the following transformations could a transformer accomplish? Select two answers.
(A) Increase AC input voltage with decreased AC current output
(B) Decrease AV input voltage with an increase in AC current output
(C) Transform AC to DV with the same current
(D) Decrease DC voltage with an increase in DC current
47. Which of the following are synonyms for voltage? Select two answers.
(A) Electromotive force
(B) Electrical potential energy
(C) Potential difference
(D) amp · hr
48. Which of the following are examples of polarization of waves? Select two answers.
(A) Two instruments play a sound pitches very close together and produce a beat frequency.
(B) A student creates a transverse wave by moving their hand up and down.
(C) Light reflected at the Brewster angle
(D) The alternating dark and light spot patterns on a screen behind two slits illuminated by a laser
49. What energies could be associated with a photon emitted during an overall transition from level 4 to level 2 of the diagram above? Select two answers.
(A) 1.9 eV
(B) 5.7 eV
(C) 2.5 eV
(D) 6.3 eV
50. The electric field near the surfaces of a rectangular solid conducting object with 15 microcoulombs of extra charge can be described as which of the following? Select two answers.
(A) Directed normally outward near the outside surfaces
(B) Uniform in strength near all outside surfaces
(C) Zero on the inside
(D) Directed normally inward near the inside surfaces
45. Bernoulli’s equation for fluids is essentially
(A) Newton’s laws for fluids
(B) energy conservation for fluids
(C) momentum conservation for fluids
(D) Bernoulli’s equation is not based on any of these
46. Which of the following transformations could a transformer accomplish? Select two answers.
(A) Increase AC input voltage with decreased AC current output
(B) Decrease AV input voltage with an increase in AC current output
(C) Transform AC to DV with the same current
(D) Decrease DC voltage with an increase in DC current
47. Which of the following are synonyms for voltage? Select two answers.
(A) Electromotive force
(B) Electrical potential energy
(C) Potential difference
(D) amp · hr
48. Which of the following are examples of polarization of waves? Select two answers.
(A) Two instruments play a sound pitches very close together and produce a beat frequency.
(B) A student creates a transverse wave by moving their hand up and down.
(C) Light reflected at the Brewster angle
(D) The alternating dark and light spot patterns on a screen behind two slits illuminated by a laser
49. What energies could be associated with a photon emitted during an overall transition from level 4 to level 2 of the diagram above? Select two answers.
(A) 1.9 eV
(B) 5.7 eV
(C) 2.5 eV
(D) 6.3 eV
50. The electric field near the surfaces of a rectangular solid conducting object with 15 microcoulombs of extra charge can be described as which of the following? Select two answers.
(A) Directed normally outward near the outside surfaces
(B) Uniform in strength near all outside surfaces
(C) Zero on the inside
(D) Directed normally inward near the inside surfaces
SECTION II: FREE-RESPONSE
1. (10 points; ~20 minutes) A laser of unknown wavelength is provided to students along with a screen with two closely spaced slits (1.67 μm) cut in it. Students are also provided with metersticks.
(a) Describe an experimental procedure to determine the wavelength of the laser. You may include a labeled diagram of your setup to help in your description. Indicate what measurements you would take and how you would take them. Include enough detail so that another student could carry out your procedure.
(b) What are the common sources of error or expected deviations from ideal results that might happen during this investigation?
(c) If the wavelength of the laser is 632.8 nm and the two-slit screen indicates spacing of 1.67 μm, determine some reasonable expected measurement a student might make in the procedure outlined above. Estimate a margin of error for each measurement, and justify this margin of error.
2. (12 points; ~25 minutes) Use the electric field drawing below to answer the questions. A, B, and C are physical sources of charge. Points e, d, and f are points within the field.
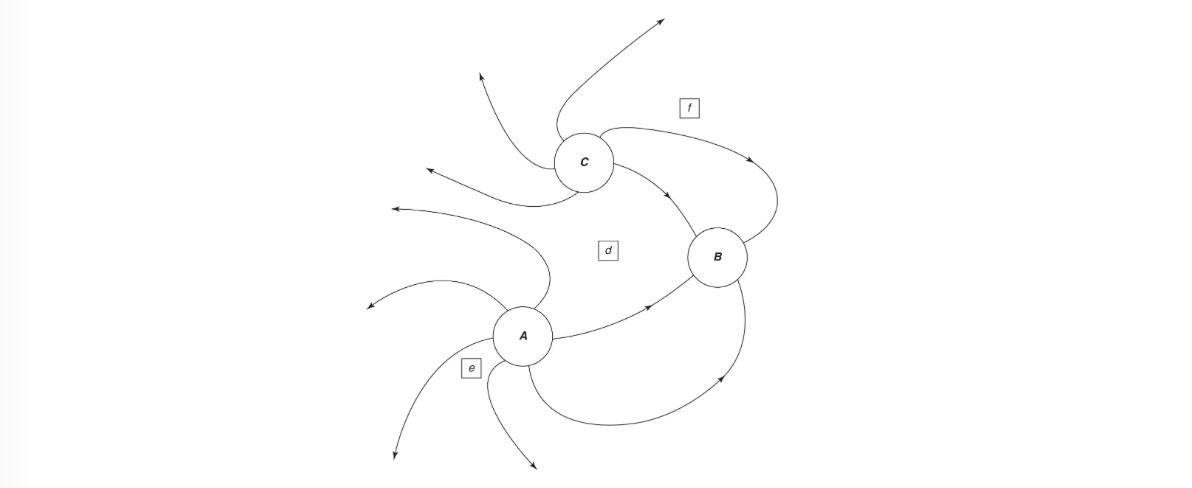
(a) Describe the relative amount of charge and type (positive or negative) at each of locations A, B, and C. Explain your answers.
(b) Rank the relative strength of the net electric field at each of points e, d, and f. Explain your answer.
(c) By extending the existing sketch, sketch out what the field lines would look like from very far away from these charges. Assume no other charges are present.
(d) On the sketch above, draw a single, complete equipotential surface that runs through point f.
(e) How can there always be electric potential at point f and yet the electrical potential energy can sometimes be zero?
(f) If a proton were placed at point f, in what direction (if any) would it experience a force? Would its change in electrical potential energy be negative or positive as it moved in response to this electrical force? Explain your reasoning.
(g) Repeat the answers to the questions in part (f) but for an electron placed at point e.
3. (12 points; ~25 minutes) An ideal gas expands from points A to C along three possible paths.
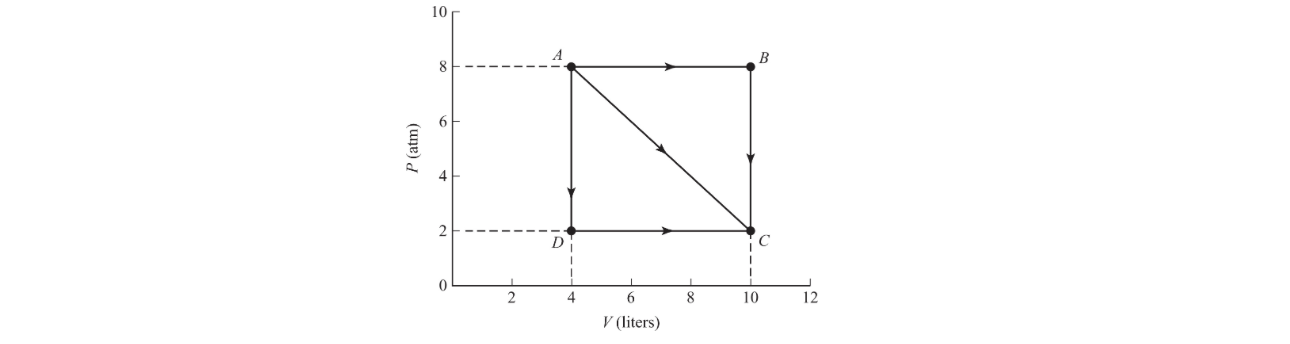
(a) Is it expected that final temperature at point C be path dependent? Justify your answer qualitatively with no calculations.
(b) Discuss and compare the flow of thermal energy along the three paths (AC, ABC, ADC). Indicate the direction of heat for each pathway (into or out of the gas) and the relative amount of thermal energy involved. Justify your answer qualitatively with no calculations.
(c) Calculate the work done along path:
i. ABC
ii. AC
iii. ADC
(d) Is there a way to go from A to C with no thermal energy exchanged with the environment? If so, describe and sketch the path on a P-V diagram.
(e)Is there a way to go from A to C with no temperature change? If so, describe and sketch the path on a P-V diagram.
4. (10 points; ~20 minutes) Given the following information:
Proton mass = 1.0078 u
Neutron mass = 1.0087 u
Mass of 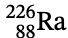 = 226.0244 u
= 226.0244 u
(a) Determine the mass defect for this isotope of radium.
(b) What does this mass defect represent? Explain both qualitatively and quantitatively.
(c) If radium-88 naturally undergoes alpha decay, write down a nuclear reaction for this process. Be sure to show any energy required (Q) or released by this process. If a new element is formed and you are unsure of its symbol, you may use an X to rep“resent that new element. Use the same isotope notation as that given in the information above.
(d) In the reaction in part (c), compare the total mass defects on the reactant side to the mass defect found in part (a):
_____ The reactants have the same mass defect.
_____ The reactants have a larger mass defect.
_____ The reactants have a smaller mass defect.
Justify your choice qualitatively, without using equations.




