AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024-The Discipline of Economics
Multiple-Choice Review Questions
1. Economics is a social science that
(A) is primarily concerned with money.
(B) is primarily concerned with how resources are used.
(C) relies solely on the scientific method for analysis.
(D) is primarily concerned with maximizing spiritual well-being.
(E) is purely normative.
2. Macroeconomics focuses on
(A) government and its laws that affect commerce.
(B) individuals and their resource use.
(C) corporations and their production levels.
(D) the resource use of the entire nation.
(E) money.
3. Given the table below, what is the opportunity cost of wheat in France?

(A) ½ cloth
(B) ½ wheat
(C) 2 cloth
(D) 2 wheat
(E) ½ cloth
4. Given the table below, which statement is true?

(A) England has the absolute advantage in both products.
(B) France should specialize in and export wheat while England should specialize in and export cloth.
(C) France has the comparative advantage in cloth.
(D) England has the comparative advantage in wheat.
(E) France has the absolute advantage in wheat while England has the absolute advantage in cloth.
5. Which of the following statements is positive?
(A) An economy that produces more butter than guns is better off than an economy that produces more guns than butter.
(B) Nations should concentrate their resources on producing wholesome consumer goods as opposed to the weapons of war.
(C) The production possibilities frontier is concave to the origin because of the law of increasing costs.
(D) Nations ought to devote at least some of their resources to national defense.
(E) Nations would do better by producing toward the middle of their production possibilities frontiers as opposed to the extreme points near the axes.
6. The primary focus of microeconomics is
(A) families and how they make money.
(B) firms and how they make profits.
(C) individual units within the overall economy.
(D) government.
(E) small countries.
7. Economists use the term “capital” to mean
(A) money.
(B) plant and equipment.
(C) where the central government is located.
(D) the center of the economy.
(E) a major idea.
8. What you give up to pursue another alternative is known as
(A) capital.
(B) land.
(C) money cost.
(D) the price of the product.
(E) opportunity cost.
9. Given the following table (combinations that can be produced using resources fully and efficiently)

the opportunity cost of apples is
(A) 10/7 oranges.
(B) 7/10 oranges.
(C) 10/7 apples.
(D) 7/10apples.
(E) 70 percent.
10. Given the following table (combinations that can be produced using resources fully and efficiently),

the opportunity cost of soup is
(A) 5 nuts.
(B) 5 soup.
(C) 20 percent.
(D) 500 percent.
(E) not constant.
11. Production possibilities frontiers are concave to the origin because
(A) of inefficiencies in the economy.
(B) of opportunity cost.
(C) of the law of increasing costs.
(D) of constant opportunity costs.
(E) the extreme points are not as well established.
12. When opportunity cost is constant across all production levels, the production possibilities frontier is
(A) concave to the origin.
(B) convex to the origin.
(C) undefined.
(D) shifted.
(E) a straight diagonal line sloping downward from left to right.
13. When an economy produces a combination of goods that lies on the production possibilities frontier,
(A) resources are being used fully and efficiently.
(B) prices are constant.
(C) opportunity cost is constant.
(D) resources will never be depleted.
(E) prices will rise.
14. The law of increasing costs
(A) does not apply to guns and butter.
(B) is the result of resources not being perfectly adaptable between the production of two goods.
(C) implies that prices will rise when the costs of making a good rise.
(D) causes the production possibilities frontier to be a straight line.
(E) implies that opportunity costs will rise as production levels fall.
15. Land refers to
(A) all productive resources.
(B) all natural resources.
(C) farmland only.
(D) real estate.
(E) chattels.
Free-Response Review Questions
1. Someone claims that air is not a scarce resource since it is all around us. Classify air as land, labor, or capital and explain why it could be considered scarce.
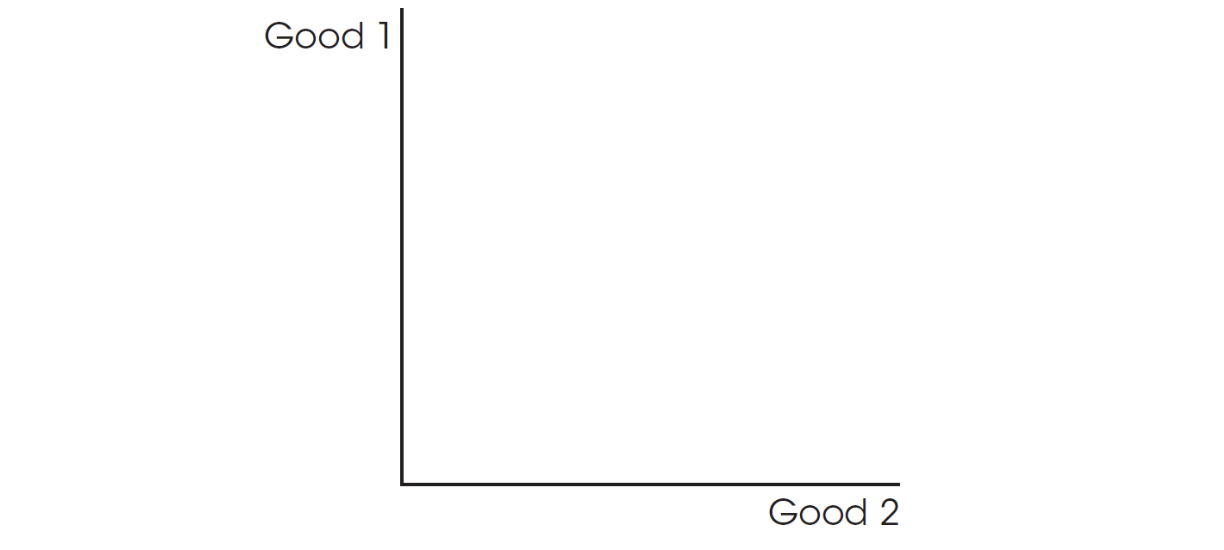
2. In the space below, draw a production possibilities frontier that reflects constant opportunity costs between Good 1 and Good 2. Now suppose the economy’s labor force grows larger. Draw the new production possibilities frontier.
3. Explain why a nation that does not produce any good or service more efficiently can still be a valued trading partner.




