AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024-Resource Markets with Applications to Labor
Multiple-Choice Review Questions
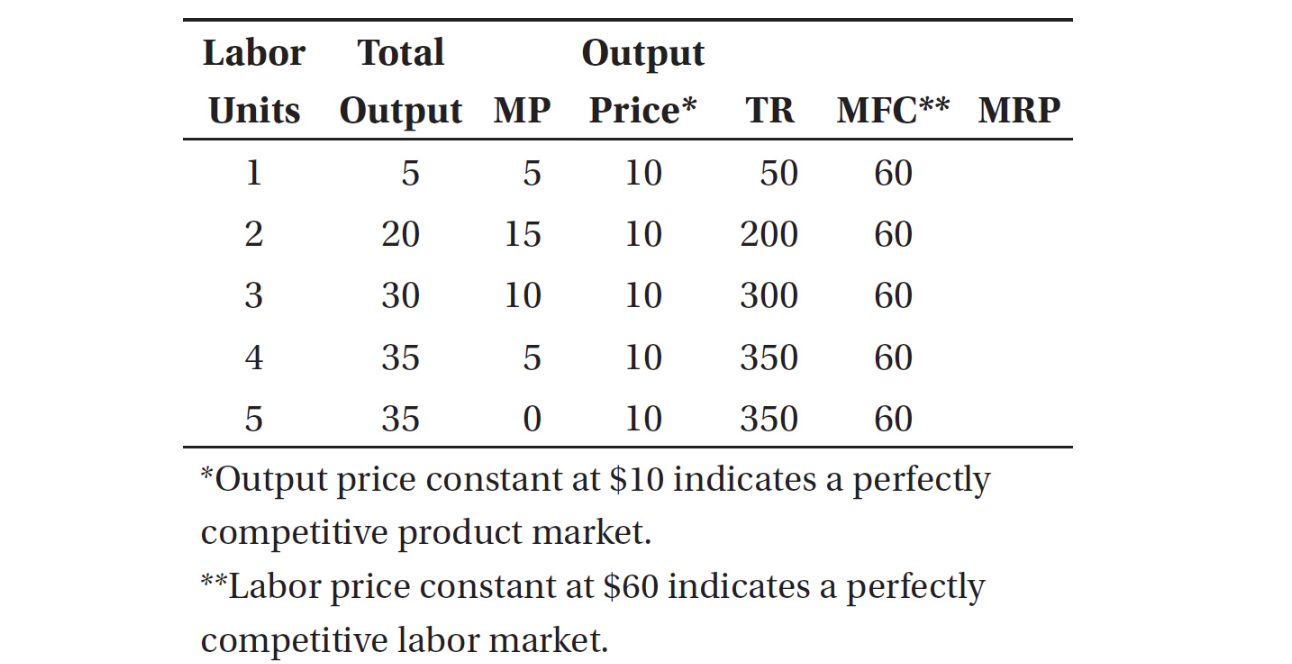
1. With the data in the table above, how many units of labor would the employer hire?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
2. If for two resources, labor (L) and capital (K), the ratios of their marginal physical products are
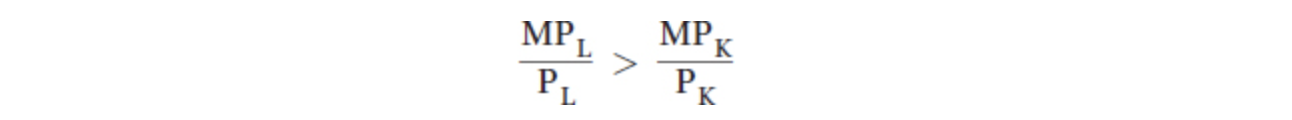
the firm should:
(A) increase capital (K) use and hire less labor until the ratios are equal.
(B) hire more labor (L) and use less capital until the ratios are equal.
(C) lower the price of capital (PK).
(D) lower the price of labor (PL).
(E) seek union membership for labor (L).
3. Which of the following will NOT cause a decrease in labor demand?
(A) A decrease in the price of the product being produced
(B) A decrease in the price of machinery of the good being produced
(C) A decrease in the technical progress used in producing the good
(D) A decrease in supply of the good
(E) A decrease in the demand of the good
Use this chart for question 4.
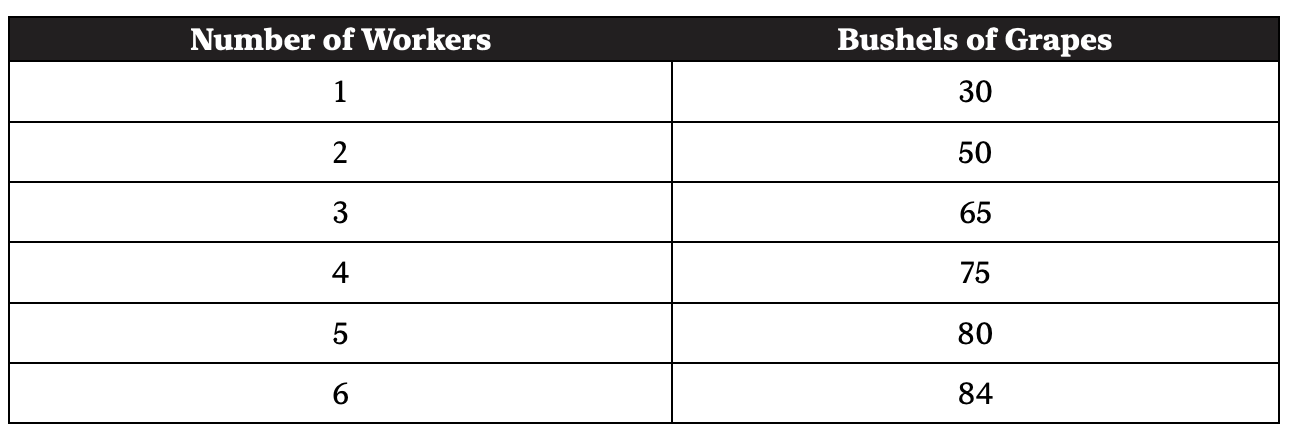
4. In perfectly competitive product and labor markets, if a bushel of grapes sells for $5 and each worker hired costs $25, how many workers should be hired?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
5. An increase in the demand for fidget spinners will likely cause which of the following?
(A) A decrease in the wages of fidget spinner producers
(B) An increase in the demand for the workers who produce fidget spinners
(C) A decrease in the price of the capital used to produce fidget spinners
(D) A decrease in the price of substitute goods for fidget spinners
(E) All of the above
6. When compared to a perfectly competitive labor market, a monopsony will
(A) pay more but hire fewer workers than a perfectly competitive market.
(B) pay less but hire more workers than a perfectly competitive market.
(C) pay more and hire more workers than a perfectly competitive market.
(D) pay less and hire fewer workers than a perfectly competitive market.
(E) pay the same and hire the same amount of workers as a perfectly competitive market.
7. Assume the marginal product of robots is 10,000 and the price of a robot is $1,000, while the marginal product of labor is 81 and the price of labor is $9. What should the firm do?
(A) Make no changes to the amount of capital and labor used
(B) Decrease the amount of capital and decrease labor
(C) Decrease the amount of capital and increase labor
(D) Increase the amount of capital and increase labor
(E) Increase the amount of capital and decrease labor
Use the figure below to answer question 8.
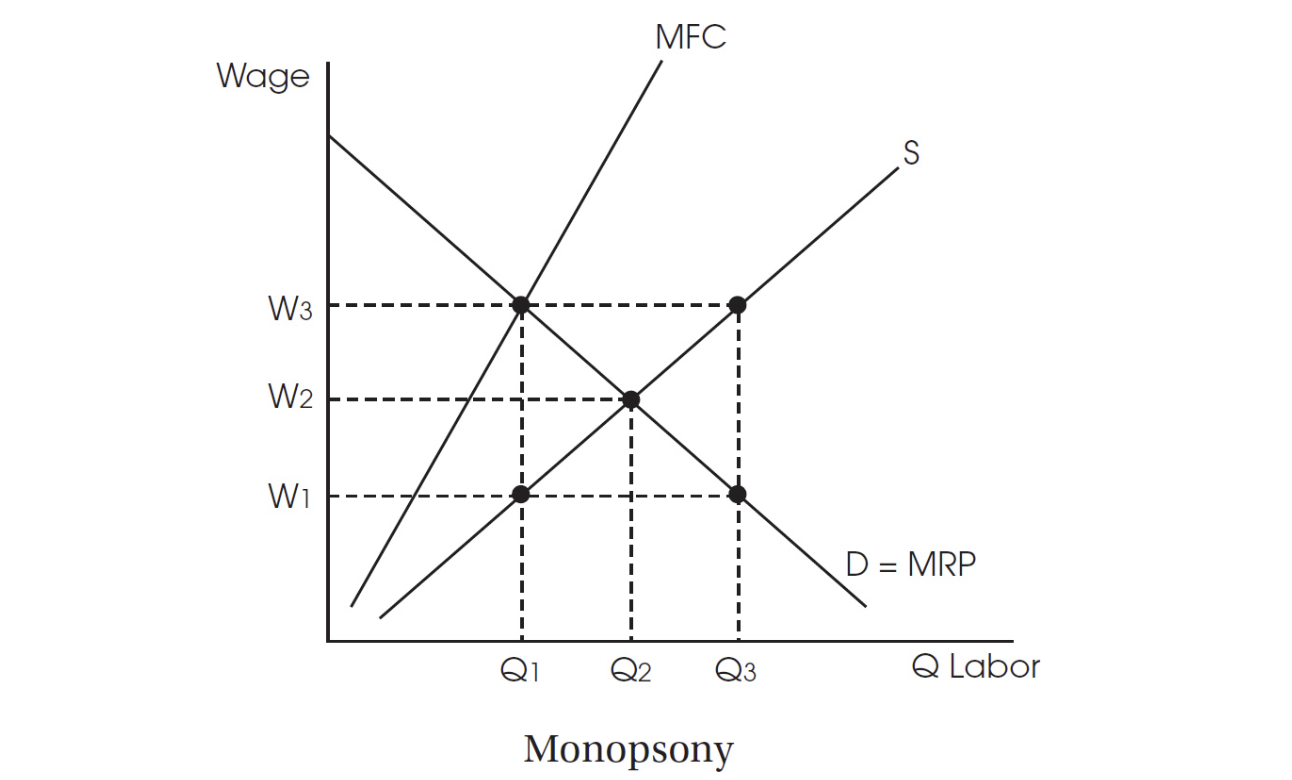
8. Based on the figure, what is the wage and quantity of labor hired for the monopsony?
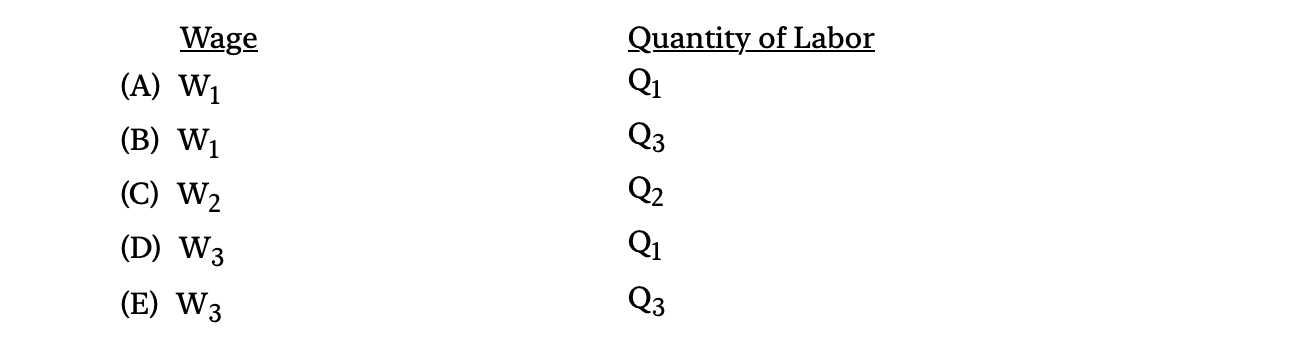
Free-Response Review Questions
1. The I. M. Green Company is a profit-maximizing firm that produces and sells avocados in perfectly competitive product and labor markets. Each avocado sells for $2, and the wage rate is $20 per day. See the short-run production table for avocados below.
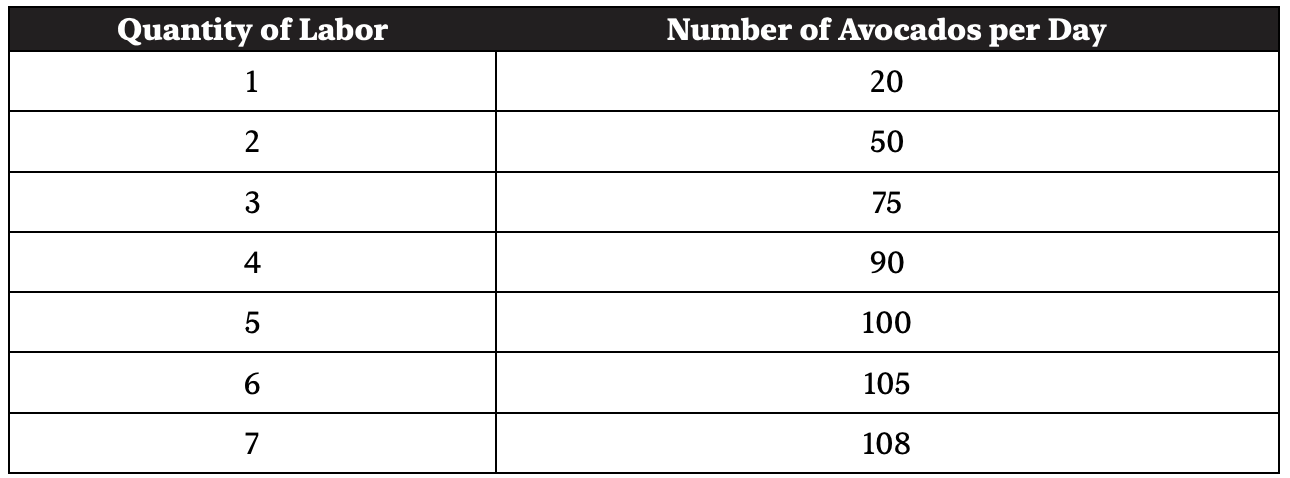
(a) What is the marginal revenue product of the 2nd worker?
(b) After which worker hired do diminishing marginal returns begin?
(c) What is the marginal product of the 4th worker?
(d) How many workers will be hired at a wage of $20 a day?
(e) If fixed costs are $30 and 5 labor units are hired, what is the economic profit or loss?
(f) Now assume the wage rate increases to $30. How many workers will now be hired?
2. Abby’s Apple Farm is a firm that operates in both perfectly competitive product and labor markets.
(a) Using side-by-side graphs for the labor market and Abby’s Apples, label the Farm Labor Market’s equilibrium wage and quantity WM and QM, and Abby’s Apples equilibrium wage and quantity of labor hired WF and QF.
(b) Now assume that there is a significant increase in the number of farm laborers in the market willing to work. What will happen to the following?
(i) Will the wage for workers in the Farm Labor Market increase, decrease, or remain the same?
(ii) Will the quantity of labor hired at Abby’s Apples increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain.
(c) Abby’s Apples is minimizing its costs with the cost-minimizing input combination. Assume each apple-picking robot harvests 1,000 apples per hour and rents for $50 an hour, and each farm laborer costs $10 an hour. How many apples does each apple farm laborer harvest per hour? Show your work.




