AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024-Perfect Competition
Multiple-Choice Review Questions
1. The individual firm, operating under perfect competition, is characterized as:
(A) a price maker.
(B) one of a few sellers.
(C) a price strategist.
(D) a price taker.
(E) interdependent.
2. Firms maximize their profits by producing a level of output at which
(A) MC = AFC.
(B) MC = MR.
(C) P = ATC.
(D) MR = AVC.
(E) P = AVC.
3. In the short run, a firm should shut down if
(A) price > ATC.
(B) price < AVC.
(C) price < ATC.
(D) price = ATC.
(E) MR = MC.
4. The demand curve for the firm operating under perfect competition is
(A) upward sloping to the right.
(B) downward sloping to the right.
(C) a perfectly vertical line.
(D) a perfectly horizontal line.
(E) concave to origin.
5. Which of the following is not correct for a perfectly competitive firm, in long-run equilibrium?
(A) Price = minimum average total cost.
(B) Price = marginal revenue.
(C) Price = minimum average variable cost.
(D) Price = marginal cost.
(E) Normal profits.
6. All of the following are true about a perfectly competitive firm in long-run equilibrium except
(A) economic profit = zero.
(B) P > ATC.
(C) P = minimum ATC.
(D) P > AVC.
(E) P = MC.
7. Which of the following is true about this profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm?
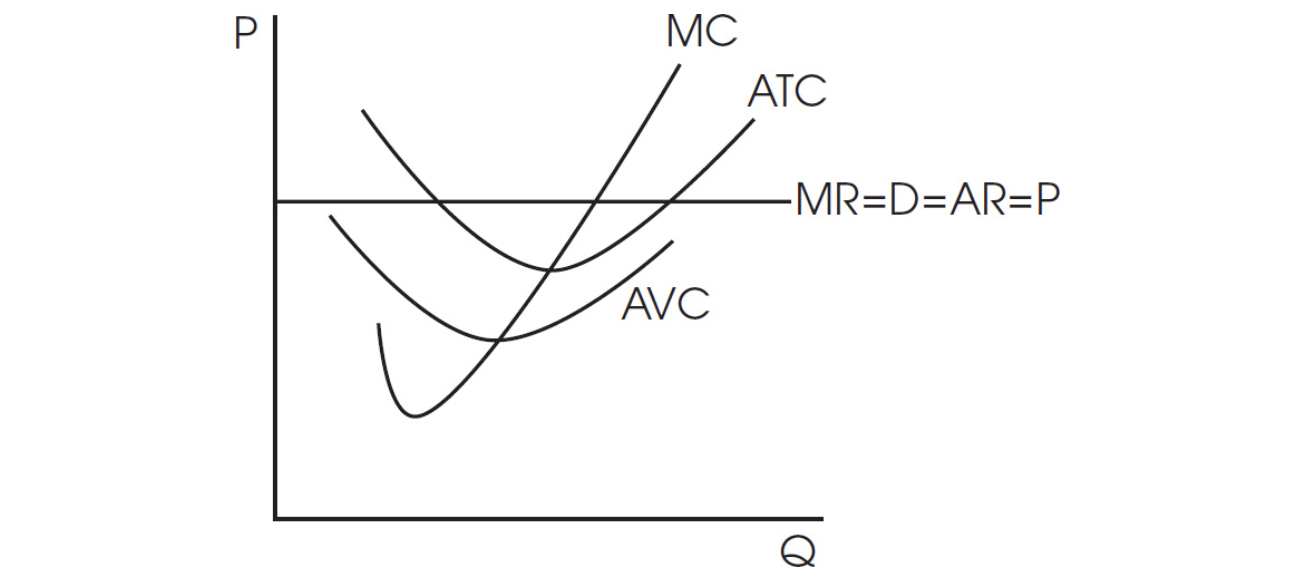
(A) The firm should shut down as P < AVC.
(B) The firm is covering AVC but not ATC.
(C) The firm is incurring economic losses, and firms will enter the industry in the long run.
(D) The firm is incurring economic losses, and firms will leave the industry in the long run.
(E) The firm is earning economic profits, and firms will enter the industry in the long run.
8. A profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm is producing where marginal revenue is greater than the marginal cost. What actions should this firm take?
(A) Increase the quantity they are producing
(B) Decrease the quantity they are producing
(C) Increase their marginal cost
(D) Leave the industry
(E) Increase production so that MC > MR
9. Assume the market for grapes is perfectly competitive. Now assume there is an increase in demand for grapes in the global market. How will this affect a firm currently producing grapes in the short run?
(A) Economic profits will decrease due to increased production costs.
(B) Average total costs will decrease.
(C) The firm’s demand curves will shift up, leading to economic profits.
(D) The firm’s demand curves will shift down, leading to economic losses.
(E) The firm’s demand curve will shift up, but the firm will not make economic profits.
Free-Response Review Question
1. Assume the market for soybeans is perfectly competitive and in long-run equilibrium, and Sam’s Soybeans is a small farm in the market.
(a) Draw correctly labeled side-by-side graphs of both the market for soybeans and the firm, labeling the market equilibrium PM and QM and labeling Sam’s Soybeans equilibrium PF and qF.
(b) Is Sam’s Soybeans earning economic profits, economic losses, or a normal profit?
(c) Now assume that in the soybean market there is a huge drought that ruins the soybean harvest of thousands of farmers (but not Sam’s). Show on the same graph as above what would happen to the new equilibrium price and quantity in both the market and firm, labeling the firm PM2 and QM2 and Sam’s Soybeans PF2 and qF2.
(d) Shade in the area of economic profit or loss for Sam’s Soybeans at the new equilibrium.




