AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024-Imperfect Competition: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
Multiple-Choice Review Questions
1. Which of the following is a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
(A) P > MC
(B) Efficiency
(C) D = MR
(D) P = MR
(E) Homogeneous or similar products
2. Which of the following is not a characteristic of oligopolies?
(A) Price takers
(B) Deadweight loss
(C) Strong barriers to entry
(D) Few firms
(E) Interdependence
3. Which of the following is a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
(A) Economically efficient in the long run
(B) Pricing at minimum ATC in the long run
(C) Excess capacity
(D) Very few competitors
(E) Price taker
Use the figure below to answer questions 4 and 5. The game theory matrix below shows the daily profits for both Firm A and Firm B. Firm A’s profits are underlined, and Firm B’s are circled.
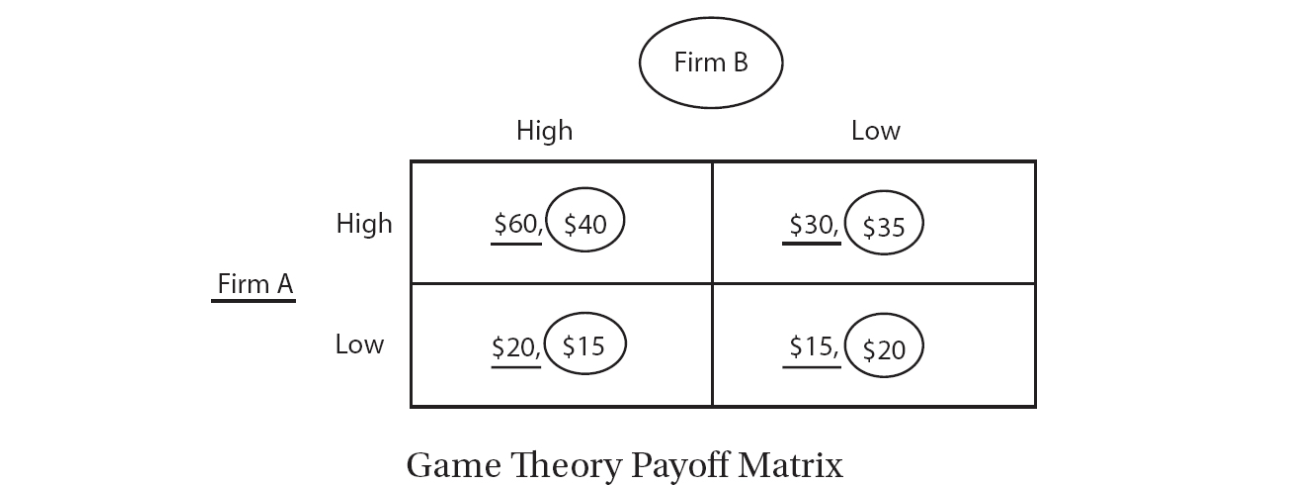
4. Given the data in the game theory matrix, what are both firms’ dominant pricing strategies?

5. Given the data in the game theory matrix, if both firms know all of the information in the matrix and cooperate in their pricing, what will each firm choose?

6. Which of the following is true of oligopolies?
I. They make strategic decisions considering competitors’ actions.
II. There are low barriers to entry.
III. They are neither allocatively nor productively efficient.
IV. They are “price takers” in the market.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I, II, and IV only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, III, and IV only
7. In this market structure, short-run profits attract new competition, causing the demand curve to shift to the left and decrease for existing firms in the market, resulting in zero economic profit in long-run equilibrium.
(A) Perfect competition
(B) Monopoly
(C) Monopolistic competition
(D) Oligopoly
(E) All of these
8. In game theory, this is the best choice for one player regardless of what the other player chooses.
(A) Nash equilibrium
(B) Dominant strategy
(C) Prisoner’s dilemma
(D) Interdependence
(E) Collusion
9. If a lump-sum tax is imposed on a monopolistically competitive firm, which of the following will happen to the price and quantity sold in the market?
(A) Price will increase and quantity will increase.
(B) Price will decrease and quantity will increase.
(C) Price will increase and quantity will decrease.
(D) Price will decrease and quantity will decrease.
(E) Price and quantity will remain unchanged.
Free-Response Review Questions
1. Assume Carly’s Cafe is a coffee shop that is operating in a monopolistically competitive industry. Carly’s Cafe is earning economic profits.
(a) Draw a correctly labeled graph of Carly’s Cafe, and include the following on the graph:
(i) The profit-maximizing price and quantity, labeled PM and QM
(ii) The area of economic profits, shaded in
(iii) The productively efficient output level, QP
(iv) The quantity of excess capacity
(b) What will happen to the number of firms in this monopolistically competitive industry in the long run? Explain.
2. In a remote town, there are only two indoor entertainment complexes, Fields’ Fun House and Amazing Jake’s. The figure below shows the profits for each firm if they price tickets high or low. Analyze the matrix, and answer the following questions. Fields’ Fun House is the first number in each cell, and Amazing Jake’s is the second number.
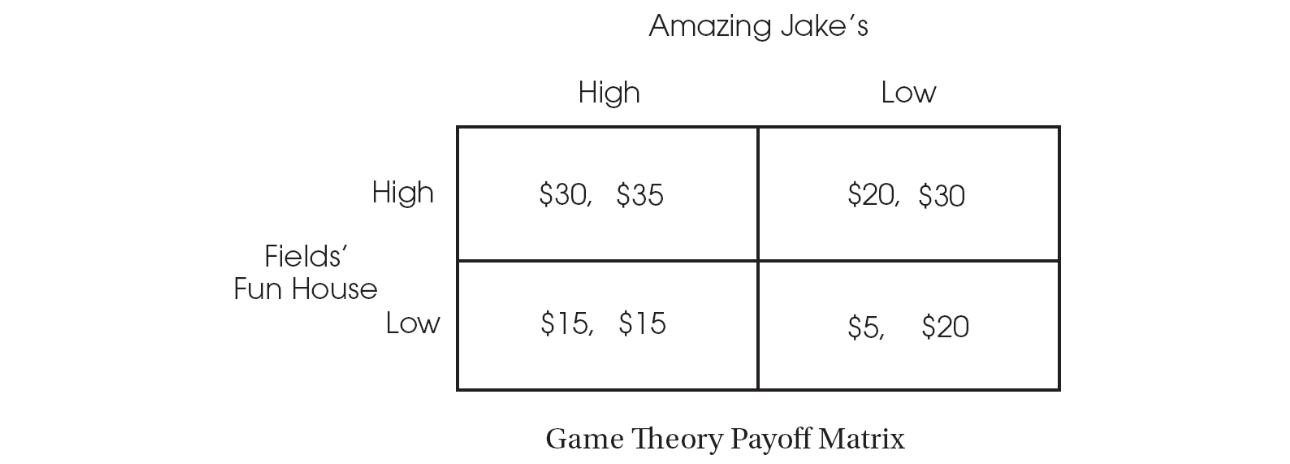
(a) What type of market structure do these two firms operate in?
(b) Is there a dominant strategy for Amazing Jake’s? Explain.
(c) If Field’s goes low, where will Jake’s go?
(d) What is the game’s Nash equilibrium?




