AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024-Elasticity, Taxation, and Consumer Choice
Multiple-Choice Review Questions
1. When the price elasticity of demand coefficient ratio is 2, demand is
(A) unit elastic.
(B) relatively elastic.
(C) perfectly elastic.
(D) relatively inelastic.
(E) perfectly inelastic.
2. Price times quantity measures
(A) the international trade gap.
(B) the budget deficit.
(C) total revenue.
(D) price elasticity of demand.
(E) price elasticity of supply.
3. A positive sign on cross-price elasticity of demand indicates that the two products are
(A) luxuries.
(B) necessities.
(C) substitutes.
(D) complements.
(E) independent.
4. If the quantity demanded of good X increases 25% while the price decreases 25%, this means the price elasticity of demand is
(A) unit elastic.
(B) relatively elastic.
(C) perfectly elastic.
(D) relatively inelastic.
(E) perfectly inelastic.
5. If an excise tax is imposed on a supplier, the tax incidence will fall more heavily on consumers if
(A) demand and supply are both unit elastic.
(B) the price elasticity of demand is more inelastic than supply.
(C) the price elasticity of supply is more inelastic than demand.
(D) the price elasticity of demand is more elastic than supply.
(E) the price elasticity of supply is perfectly inelastic.
6. Suppose a 10% decrease in the price of ice cream leads to a 15% increase in the quantity demanded of ice cream. What type of elasticity does this show?
(A) Perfectly elastic
(B) Relatively elastic
(C) Unit elastic
(D) Relatively inelastic
(E) Perfectly inelastic
7. A 20% increase in the price of milk leads to a 10% decrease in the quantity of cereal purchased. The cross-price elasticity of demand between milk and cereal is
(A) −0.5 and the two goods are substitutes.
(B) −0.5 and the two goods are complements.
(C) 0.5 and the two goods are complements.
(D) −2 and the two goods are substitutes.
(E) 2 and the two goods are complements.
8. If the cross-price elasticity of demand between goods X and Y is positive and the income elasticity of demand for good Y is negative, which of the following is correct?
(A) Good Y is an inferior good, and good X is a normal good.
(B) Good Y is an inferior good, and goods X and Y are complements.
(C) Good Y is a normal good, and goods X and Y are substitutes.
(D) Good Y is an inferior good, and goods X and Y are substitutes.
(E) Good Y is an inferior good, and goods X and Y are complements.
9. The area above a supply curve, below the equilibrium price“, and left of equilibrium quantity is the
(A) deadweight loss.
(B) consumer surplus.
(C) producer surplus.
(D) price ceiling.
(E) price floor.
10. If the demand for gasoline is price inelastic in a competitive market, an increase in the price of gasoline will
(A) result in a deadweight loss in the gasoline market.
(B) cause an increase in the consumer surplus.
(C) decrease the total revenue of gasoline producers.
(D) increase the total revenue of gasoline producers.
(E) decrease the total spending on gasoline by consumers.
11. A tariff that is imposed on a good that is imported to the United States will result in which of the following to consumer surplus, domestic producer surplus, and tax revenue?

12. Jane is shopping online and is spending $48 on T-shirts and music downloads. Given her budget constraint of $48 she is at her utility-maximization combination of spending. T-shirts cost $10. In addition, her marginal utility of T-shirts is 40 and for music downloads it’s 8. What then is the price of music downloads?
(A) 50¢
(B) $1
(C) $2
(D) $3
(E) $4
Use this chart for questions 13 and 14.
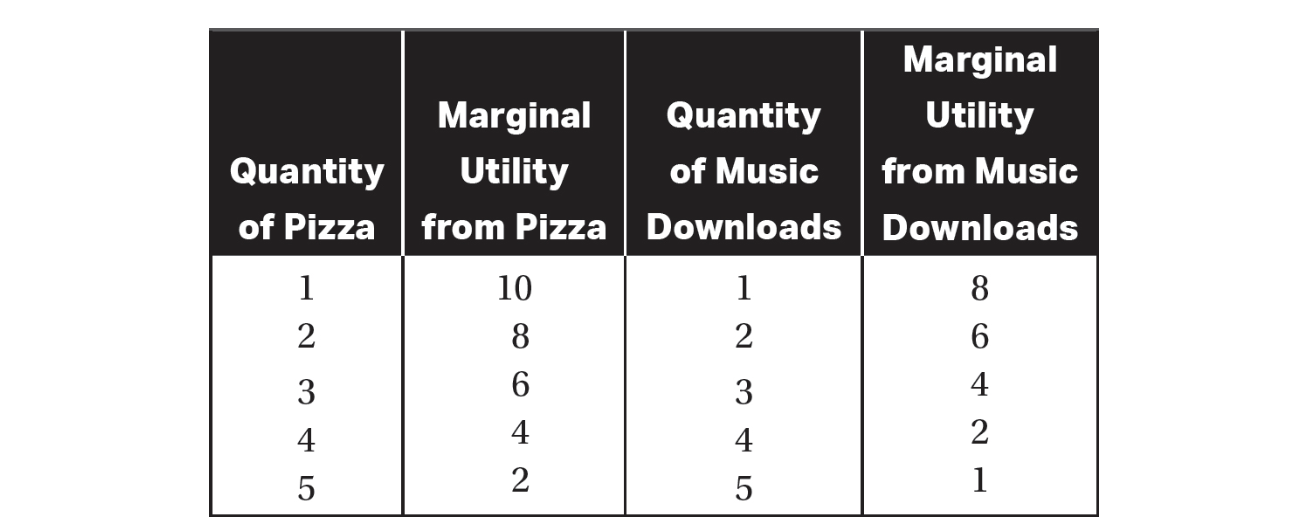
13. Samantha consumes both pizza and music downloads. The table above shows her marginal utility from these. What is her total utility from purchasing four music downloads?
(A) 4
(B) 14
(C) 18
(D) 20
(E) 21
14. Now assume Samantha’s weekly income is $12, the price of a pizza is $2, and the price of a music download is $1. What is the utility-maximization quantity of pizza and music downloads if she spends her entire $12 on these two goods?

15. According to the principle of diminishing marginal utility, as more units of the same good are consumed
(A) marginal utility stays the same.
(B) total utility stays the same.
(C) marginal utility decreases.
(D) marginal utility increases.
(E) marginal utility and total utility both increase.
16. An effective price ceiling is characterized by
(A) a price set below the current (or equilibrium) market price of the good.
(B) a price set above the current (or equilibrium) market price of the good.
(C) a shift of the demand curve.
(D) a shift of the supply curve.
(E) a surplus of the good.
17. Which of the following would cause the price of a good to be fixed above the equilibrium price?
(A) Consumers’ incomes decreased
(B) An effective price ceiling
(C) Taxes for producers increased
(D) The price of a substitute product decreased
(E) An effective price floor
Free-Response Review Questions
1. Analyze the following graph of the sugar market and how a per-unit excise tax affects the following.
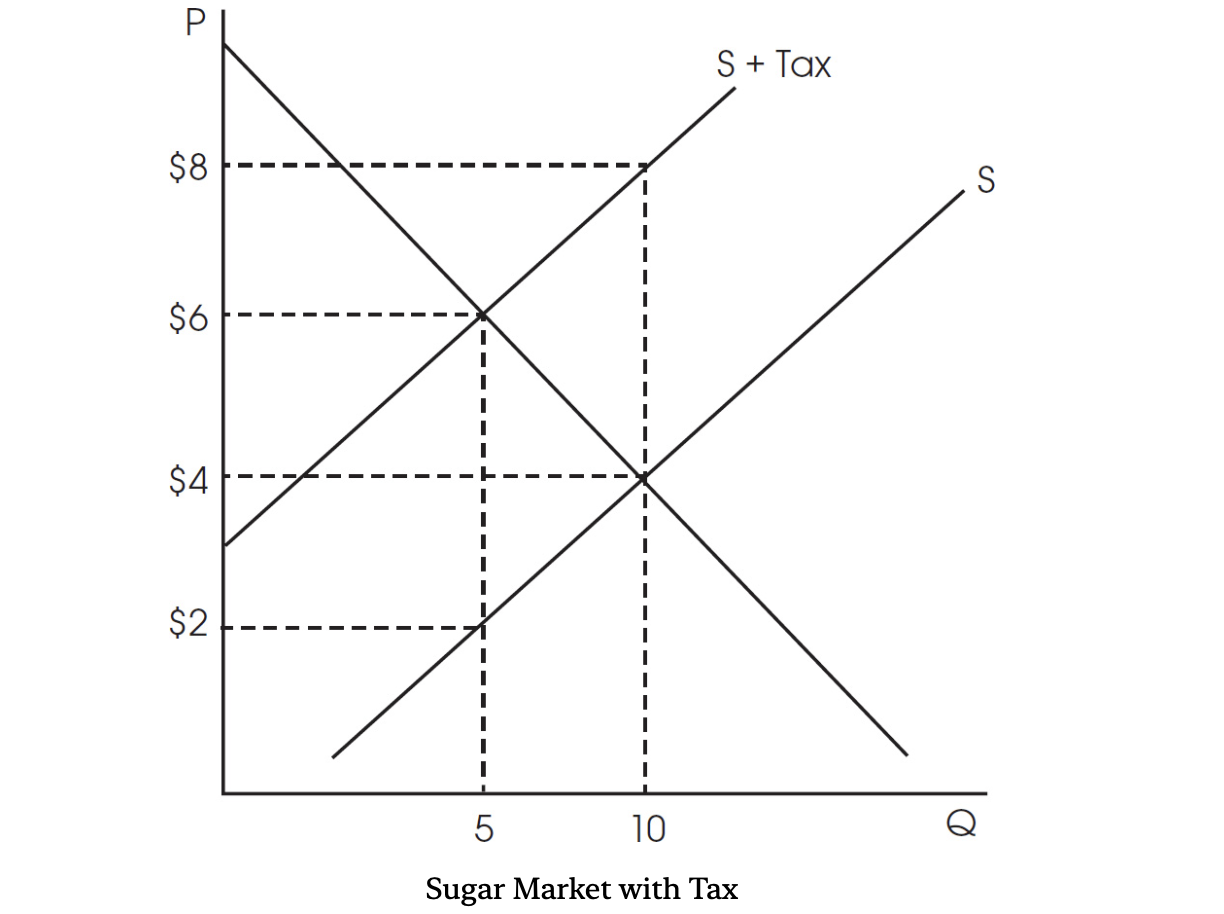
(a) What is the size of the tax per unit on the sugar market?
(b) What is the total amount of tax revenue from the tax?
(i) Is the tax incidence between consumers and producers equal, do consumers pay more of the tax than producers, or do producers pay more of the tax than consumers?
(c) What is the price that consumers pay for sugar after the tax?
(i) What is the after-tax, per-unit price received by producers for each sale?
(d) What was the equilibrium price and quantity before the tax?
(e) Now assume the price elasticity of demand becomes more inelastic while supply remains constant. Who will now pay more of the burden of the tax? Consumers? Producers? Or will the burden of the tax be equal? Explain.
2. Assume Micah spends $14 on burgers and slices of pizza every week. A burger costs $4, and a slice of pizza is $2. Using the chart, answer the following questions.
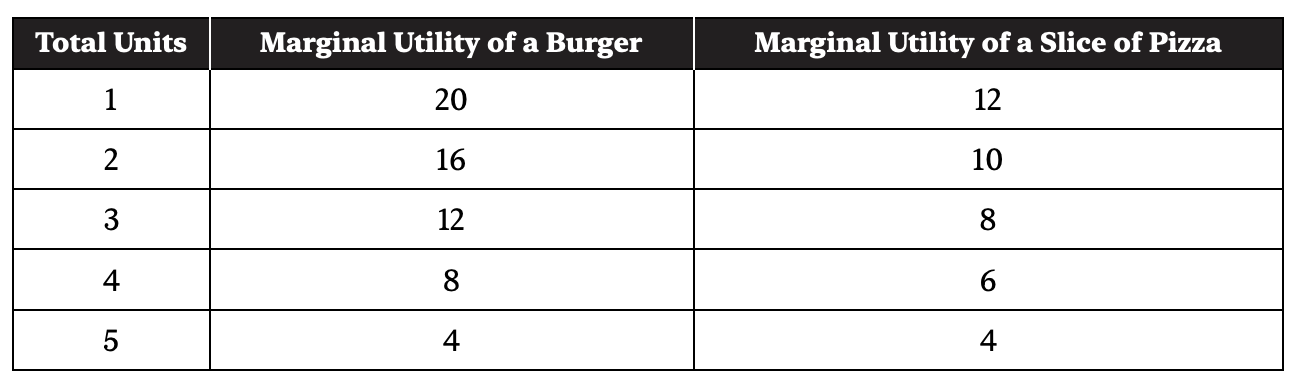
(a) What is the total utility of consuming 4 burgers?
(b) What is the quantity of burgers and slices of pizza that will maximize Micah’s utility given that he spends $14?
(c) Now suppose a 10% increase in the price of a burger leads to a 5% increase in the quantity of slices of pizza purchased. Calculate the cross-price elasticity between burgers and pizza, and note if burgers and pizza are complements, substitutes, or inferior goods. Show your work.
3. Analyze the following graph of the price of sugar in the United States before and after a tariff is imposed.
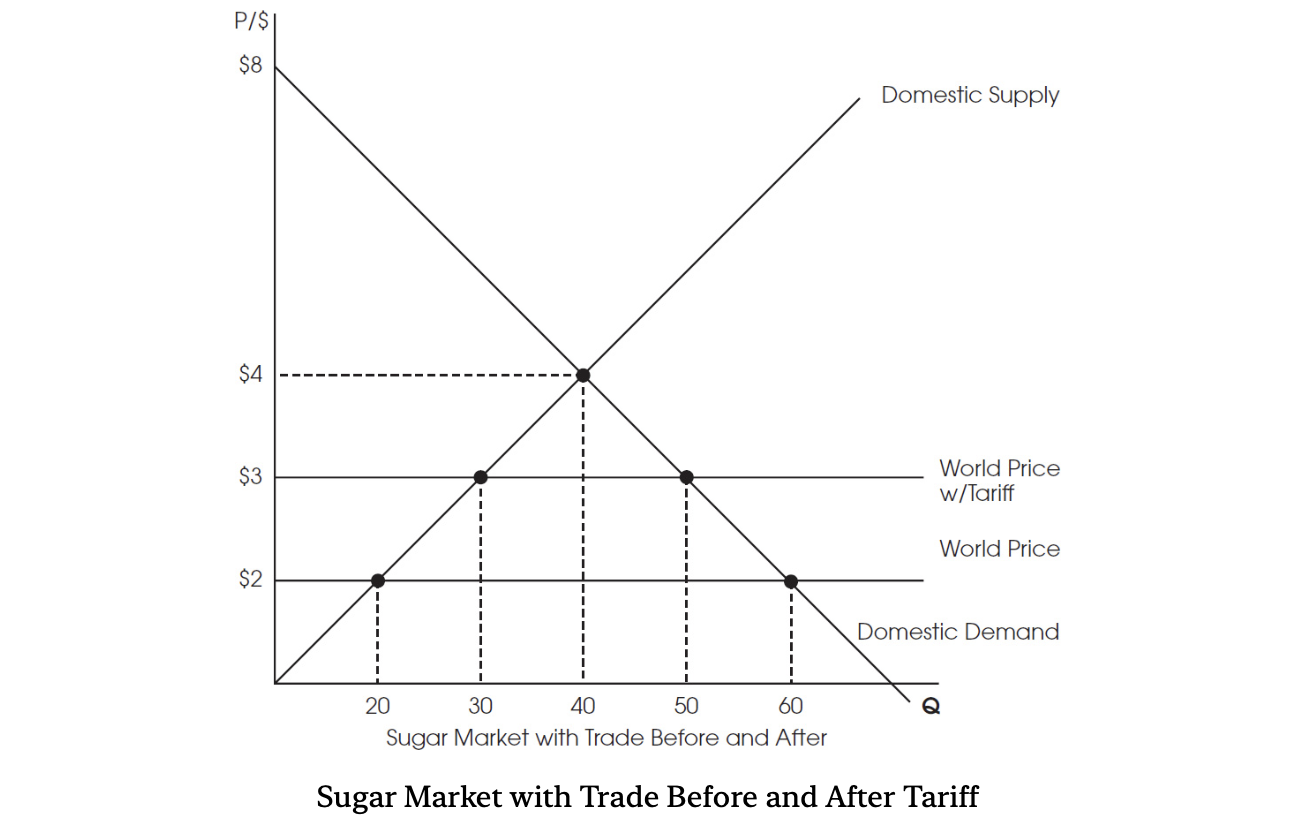
(a) What is the price of sugar if there is no trade?
(b) Calculate the total consumer surplus both without trade and at the world price. Show your work.
(c) Calculate the total tariff revenue at the world price with a tariff. Show your work.
(d) What is the quantity of domestic supply at the world price both with and without a tariff?
4. Assume the market for chicken wings is in equilibrium.
(a) Draw a correctly labeled graph of the chicken wing market, labeling the price PE and the quantity QE at equilibrium.
(b) Assume the government now decides the price of chicken wings is too high and decides to set an effective price ceiling in the market. Draw the price ceiling on the same graph drawn in (a), labeling the new price PC, the new quantity supplied QS, and the new quantity demanded QD.
(c) At the new price, is the chicken wing market in equilibrium, or does it have a shortage or a surplus? Explain.




