AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024- Microeconomics Practice
1. Economics is the study of
(A) business.
(B) government regulation.
(C) central planning.
(D) how societies manage their scarce resources.
(E) society, politics, and government combined.
2. If buyers bid up the price of a good in a capitalist economy, then
(A) sellers will try to bring more of it to market.
(B) sellers will bring less to market, anticipating less demand at the higher price.
(C) fewer resources will be devoted to its production.
(D) they must not want it.
(E) its price will eventually fall back to normal.
3. If a capitalist society demands more coffee, then the relative price of coffee will
(A) decrease.
(B) increase.
(C) not necessarily change.
(D) remain unchanged.
(E) change indeterminately.
4. Which of the following shifts the production possibilities frontier inward?
(A) Exports
(B) Imports
(C) A large wildfire that destroys timber, homes, and factories
(D) Rising prices
(E) An increase in the number of unemployed people
5. ____ has the absolute advantage in guns, and ____ has the absolute advantage in butter.
(A) Cuba; Spain
(B) Cuba; Cuba
(C) Spain; Cuba
(D) Spain; Spain
(E) Spain; neither country

6. According to the law of comparative advantage, Cuba should export ____ and import ____.
(A) butter; neither good
(B) butter; guns
(C) guns; cloth
(D) guns; guns
(E) guns; neither good

7. Which of the following events has no effect on GDP this year?
(A) You buy a 1957 Chevy from a friend.
(B) The Department of Transportation repaves a road.
(C) Your friends make a music CD that does not sell any copies.
(D) A college buys computers.
(E) You buy a bottle of domestic wine.
8. GDP in year 1 is
(A) $100.
(B) $200.
(C) $300.
(D) $400.
(E) $500.
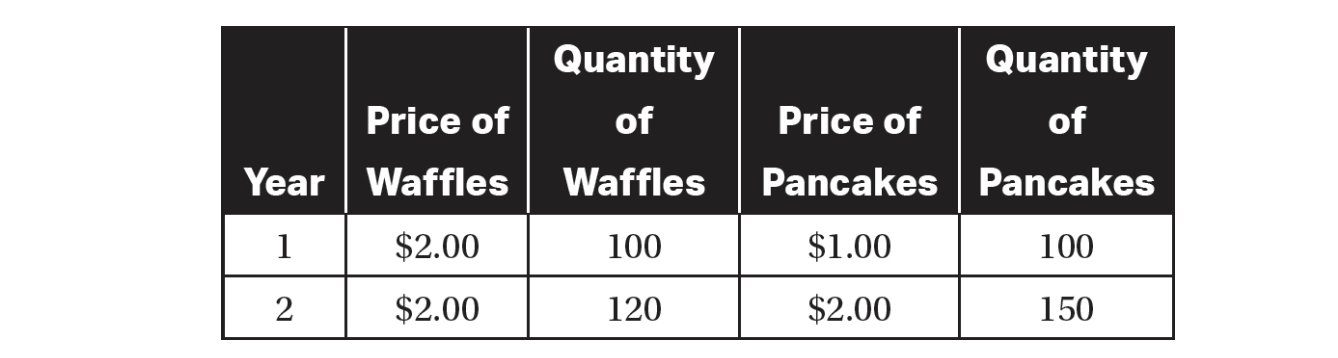
9. Assume the base year is year 1. Real GDP in year 1 is
(A) $100.
(B) $200.
(C) $300.
(D) $400.
(E) $500.
10. The unemployment rate is
(A) 5.5 percent.
(B) 10 percent.
(C) 12.5 percent.
(D) 14.3 percent.
(E) 80 percent.

11. If the consumer price index was 100 in the base year and 107 in the following year, then the inflation rate was
(A) negative 10.7 percent.
(B) 1.07 percent.
(C) 7 percent.
(D) 10.7 percent.
(E) 107 percent.
12. Rising prices are a problem because
(A) households are encouraged to save more.
(B) incomes generally do not rise with prices.
(C) the economy could run out of money.
(D) borrowers have to repay loans with more dollars.
(E) money in household savings accounts can now buy fewer goods and services.
13. A business cycle trough is immediately followed by the
(A) expansion.
(B) peak.
(C) inflexion.
(D) nadir.
(E) contraction.
14. If people save more for retirement, holding all else constant, then the immediate effect is the
(A) aggregate demand curve shifts right.
(B) aggregate demand curve shifts left.
(C) short- and long-run aggregate supply curves shift right.
(D) short- and long-run aggregate supply curves shift left.
(E) short-run aggregate supply curve shifts left.
15. Which of the following shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right?
(A) An increase in the price level
(B) A decrease in the price level
(C) An increase in income taxes
(D) A decrease in income taxes
(E) An increase in the cost of borrowing
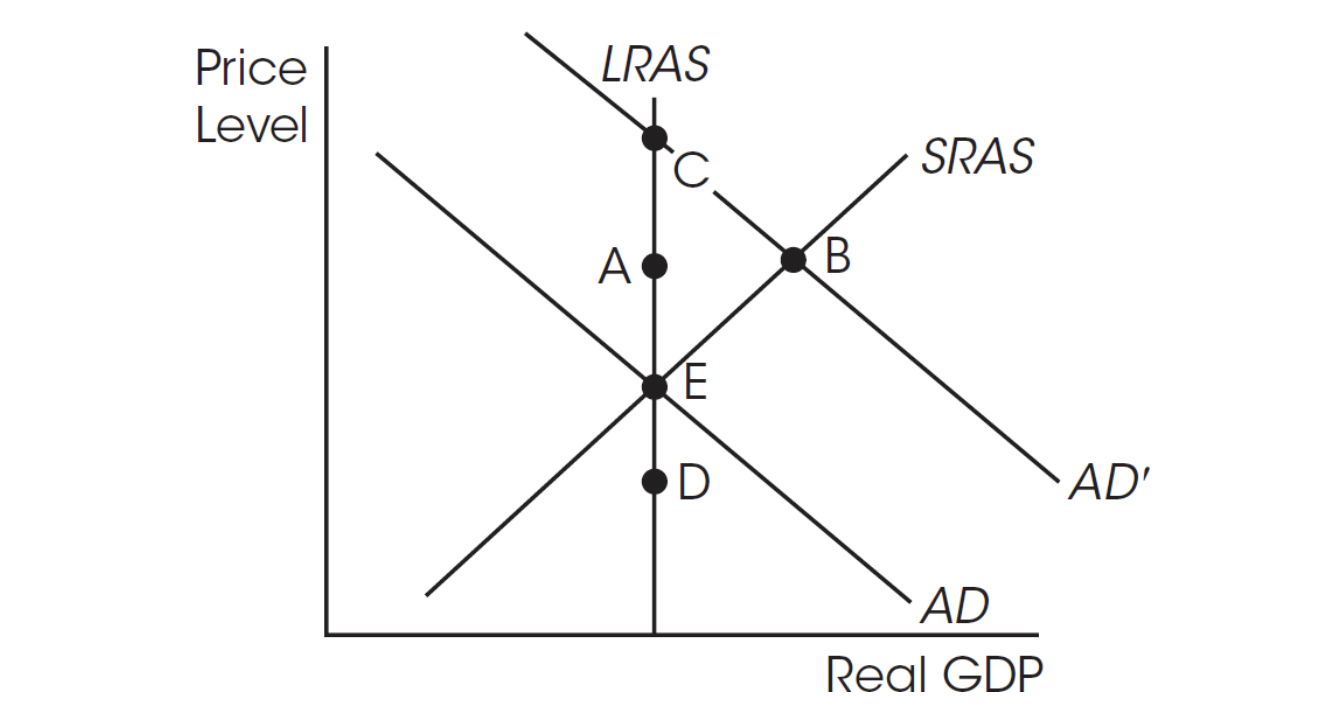
16. If the economy is at A and there is a decrease in aggregate demand, in the short run the economy
(A) stays at A.
(B) moves to B.
(C) moves to C.
(D) moves to D.
(E) experiences an increase in output.
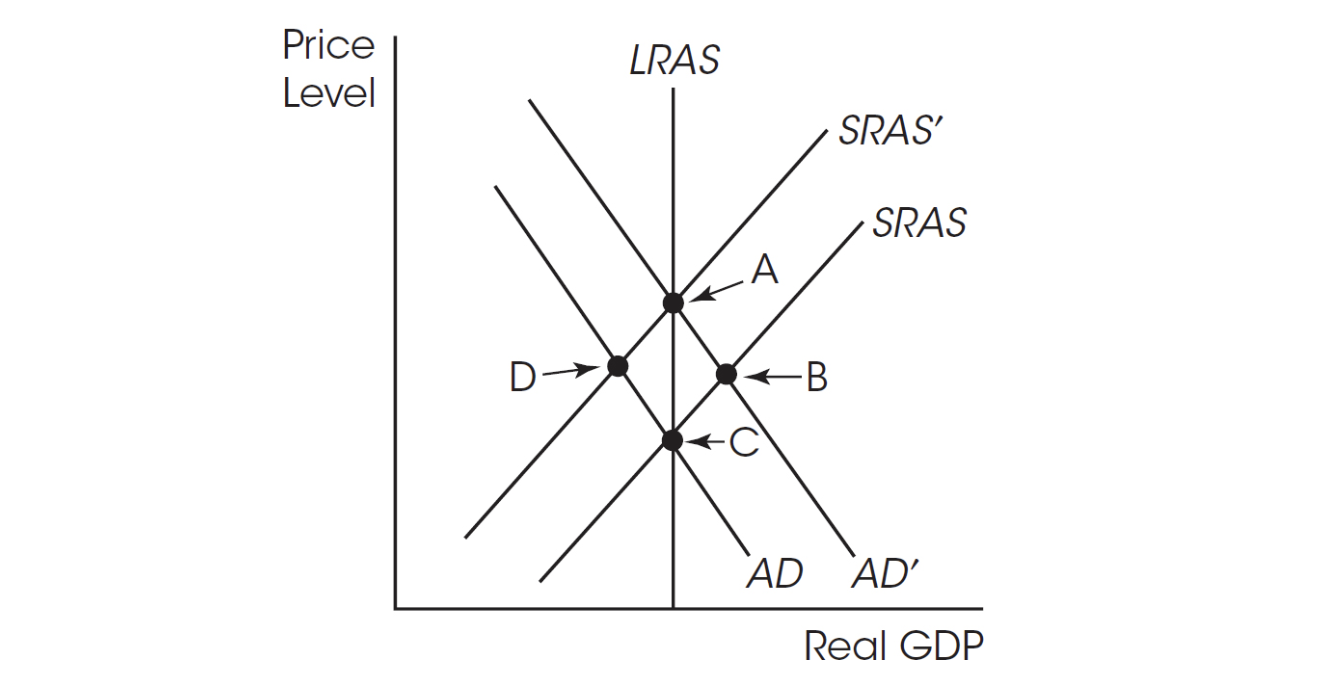
17. What can cause the economy to move from B to A?
(A) An increase in the money supply
(B) A decrease in the money supply
(C) An increase in the nominal wage rate
(D) A decrease in government spending
(E) An increase in immigration from abroad
18. Which of the following shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right?
(A) A fire that destroys a huge timber stand
(B) A technological advance in production methods
(C) A fire wipes out much of the plant and equipment in the economy
(D) Prices are expected to increase in the near future
(E) A decrease in income taxes
19. Which of the following shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right?
(A) An increase in government spending on military equipment
(B) An increase in the labor force
(C) A decrease in unemployment
(D) A decrease in the money supply
(E) An increase in the money supply
20. In the short run, what will happen to the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium quantity of output if short-run aggregate supply increases?
(A) The equilibrium price level increases while the equilibrium quantity of output decreases.
(B) The equilibrium price level decreases while the equilibrium quantity of output increases.
(C) The equilibrium price level and quantity of output increase.
(D) The equilibrium price level and quantity of output decrease.
(E) The equilibrium price level and the equilibrium quantity of output remain unchanged.
21. In the short run, what will happen to the equilibrium price level and equilibrium real GDP if the federal government decreases spending?
(A) The equilibrium price level increases while equilibrium real GDP decreases.
(B) The equilibrium price level decreases while equilibrium real GDP increases.
(C) The equilibrium price level and equilibrium real GDP increase.
(D) The equilibrium price level decreases and equilibrium real GDP is unchanged.
(E) The equilibrium price level and equilibrium real GDP remain unchanged.
22. Imagine an economy on its production possibilities frontier. In the long run, what will happen to the equilibrium price level and equilibrium real GDP if the federal government decreases spending?
(A) The equilibrium price level increases while equilibrium real GDP decreases.
(B) The equilibrium price level decreases while equilibrium real GDP increases.
(C) The equilibrium price level and equilibrium real GDP increase.
(D) The equilibrium price level decreases and equilibrium real GDP is unchanged.
(E) The equilibrium price level and equilibrium real GDP remain unchanged.
23. Assuming the MPC = 0.80 and considering only the multiplier effect, if government spending increases by $40 billion, then national income can potentially increase by
(A) $2 billion.
(B) $8 billion.
(C) $20 billion.
(D) $80 billion.
(E) $200 billion.
24. Assuming the MPC = 0.80 and considering only the multiplier effect, if government taxation increases by $40 billion, then national income can potentially _____ by _____.
(A) increase; $2 billion
(B) decrease; $20 billion
(C) increase; $200 billion
(D) decrease; $8 billion
(E) decrease; $160 billion
25. If the economy is currently in short-run equilibrium at point B and policy makers do nothing, then long-run equilibrium eventually will be achieved at point
(A) A.
(B) B.
(C) C.
(D) D.
(E) E.
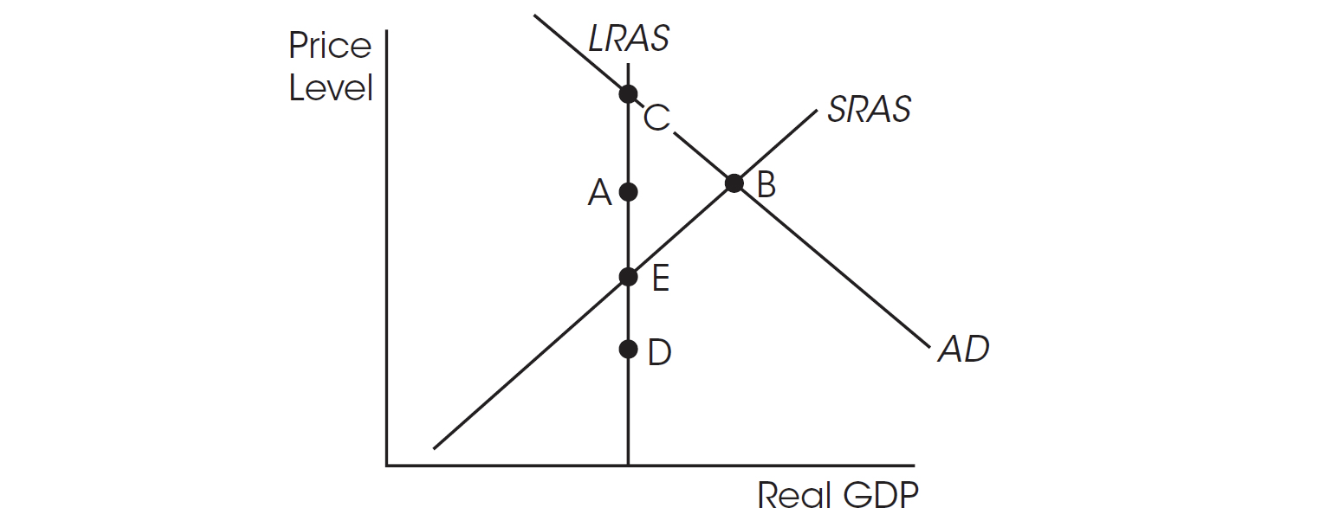
26. If the economy is currently in short-run equilibrium at point E, then an increase in aggregate demand moves the economy to ____ in the short run and ____ in the long run.
(A) D; E
(B) A; E
(C) B; E
(D) B; C
(E) A; C
27. The appropriate fiscal policy to remedy a recession calls for
(A) the federal government to run a deficit.
(B) the federal government to run a surplus.
(C) increased taxes and government spending.
(D) decreased government spending and taxes.
(E) increased taxes and reduced government spending.
28. One drawback of using fiscal policy to remedy a recession is that
(A) unemployment will rise.
(B) taxes will have to be raised.
(C) the equilibrium price level will rise.
(D) government spending on important programs will have to be cut.
(E) equilibrium output will fall.
29. During recessions, automatic stabilizers make government expenditures
(A) and tax collections fall.
(B) and tax collections rise.
(C) rise and tax collections fall.
(D) fall and tax collections rise.
(E) stable.
30. The nominal interest rate is 6 percent, and the inflation rate is 2 percent. What is the implied real interest rate?
(A) Negative 4 percent
(B) 3 percent
(C) 4 percent
(D) 8 percent
(E) 12 percent
31. With a net worth of $2 million, Jim is wealthier than Tim, whose net worth is $1 million. These figures show that money can be used as a
(A) store of value.
(B) medium of exchange.
(C) unit of account.
(D) means of deferred payment.
(E) way to avoid a double coincidence of wants.
32. Which of the following is included in M1?
(A) Currency in a bank’s vault
(B) Credit cards
(C) Small time deposits
(D) Money market mutual funds
(E) Deposits in savings accounts
33. If the reserve requirement is 2 percent, then the money multiplier is
(A) 5.
(B) 5 percent.
(C) 50.
(D) 50 percent.
(E) one-half.
34. According to the quantity equation, if P = 2, Q = 6, and M = 4, then V =
(A) 1.3.
(B) 2.
(C) 3.
(D) 4.
(E) 12.
35. An increase in the supply of money moves the economy from point D to point ____. The equilibrium nominal interest rate ____.
(A) A; decreases
(B) C; decreases
(C) C; increases
(D) B; increases
(E) B; decreases
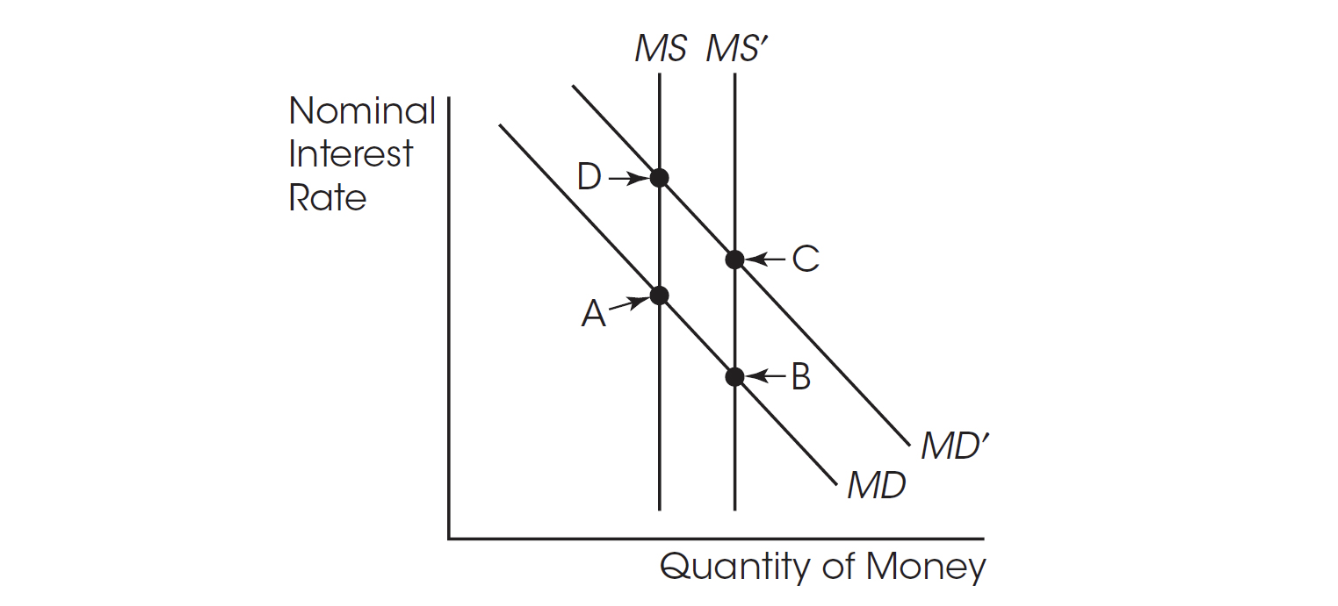
36. If the discount rate is lowered, banks
(A) borrow more from the Fed so bank reserves increase.
(B) borrow less from the Fed so bank reserves increase.
(C) borrow more from the Fed so bank reserves decrease.
(D) borrow less from the Fed so bank reserves decrease.
(E) conduct open market purchases.
37. In the short run, a decrease in the supply of money
(A) decreases interest rates, decreases borrowing, and thereby decreases aggregate demand.
(B) increases interest rates, increases borrowing, and thereby increases aggregate demand.
(C) increases interest rates, decreases borrowing, and thereby decreases aggregate demand.
(D) decreases interest rates, increases borrowing, and thereby increases aggregate demand.
(E) decreases interest rates, increases borrowing, and thereby decreases aggregate demand.
38. Open market operations are when the Fed buys or sells
(A) loans to banks.
(B) Federal Reserve Notes to banks.
(C) Federal Reserve Notes to the public.
(D) Federal Reserve Notes to the U.S. Treasury.
(E) U.S. Treasury securities in the secondary market.
39. If the federal funds rate is above the Fed’s target and banks hold limited reserves, the Fed should
(A) buy bonds to increase the money supply.
(B) buy bonds to decrease the money supply.
(C) sell bonds to increase the money supply.
(D) sell bonds to decrease the money supply.
(E) raise the reserve requirement to decrease the money supply.
40. If the demand for loanable funds increases, then the equilibrium real interest rate
(A) increases but the equilibrium quantity of funds remains unchanged.
(B) increases and the equilibrium quantity of funds increases.
(C) increases and the equilibrium quantity of funds decreases.
(D) decreases and the equilibrium quantity of funds decreases.
(E) decreases and the equilibrium quantity of funds increases.
41. An increase in the money supply _____ the price level in the short run and _____ it in the long run.
(A) increases; decreases
(B) increases; increases
(C) decreases; decreases
(D) decreases; increases
(E) increases; does not affect
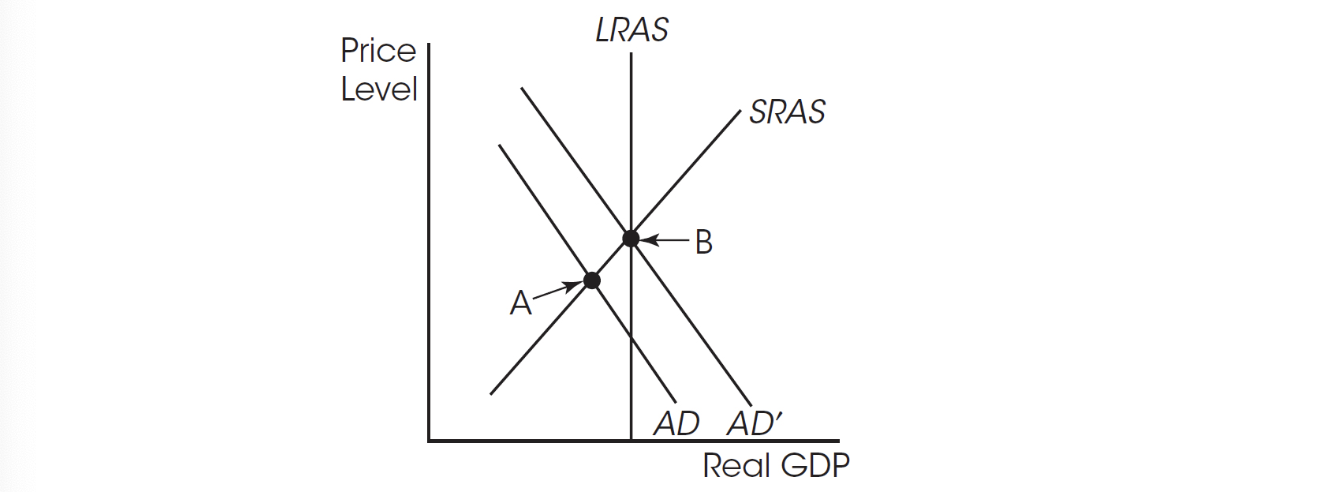
42. What is the appropriate monetary policy to move the economy from point A to point B?
(A) Increase in tax collections
(B) Decrease in tax collections
(C) Increase the federal funds rate
(D) Increase the money supply
(E) Increase the discount rate
43. Monetary and fiscal policy
(A) are not used in command economies.
(B) are not used in capitalist economies.
(C) affect only long-run aggregate supply.
(D) are less effective in an open economy.
(E) shift the long- and short-run aggregate supply curves.
44. To reduce the inflation rate
(A) the federal government should deficit spend.
(B) taxes should be reduced.
(C) government spending should be increased.
(D) long- and short-run aggregate supply should be shifted left.
(E) the growth rates of M1 and M2 should be decreased.
45. A reduction in the income tax rate shifts the aggregate demand curve to the
(A) right, and the economy slides up the Phillips curve.
(B) left, and the economy slides down the Phillips curve.
(C) right, and the economy slides down the Phillips curve.
(D) left, and the economy slides up the Phillips curve.
(E) left, but the Phillips curve is unaffected.
46. In the long run
(A) prices are independent of the money supply.
(B) prices move in the opposite direction as the money supply.
(C) the GDP deflator is independent of the money supply.
(D) inflation is always the result of shortages.
(E) inflation rates parallel money supply growth rates.
47. The federal _____ is the amount the U.S. government owes to all its creditors. The federal _____ is the amount by which federal spending exceeds federal tax revenues in any given year.
(A) budget; account
(B) account; budget
(C) deficit; debt
(D) debt; deficit
(E) deficit; excess
48. Which of the following correctly explains the crowding-out effect?
(A) A decrease in the federal deficit decreases interest rates and so increases investment spending.
(B) A decrease in the federal deficit increases interest rates and so decreases investment spending.
(C) An increase in the federal deficit increases interest rates and so decreases investment spending.
(D) An increase in the federal deficit decreases interest rates and so decreases investment spending.
(E) An increase in the federal deficit increases the interest rate and employment.
49. An increase in ____ promotes economic growth.
(A) the price level
(B) the real interest rate
(C) the nominal interest rate
(D) the labor force
(E) consumer spending
50. Economic growth is most likely to be promoted by an increase in
(A) the price level.
(B) the real interest rate.
(C) government spending on higher education.
(D) the money supply.
(E) consumer spending.




