AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024- Macroeconomics Practice Test
Section I—Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Consider an economy at full employment equilibrium. In the long run an increase in the money supply results in
(A) a proportional increase in the quantity of output.
(B) stagflation.
(C) an increase in the real rate of interest.
(D) an economic expansion.
(E) a proportional increase in the price level.
2. You buy 100 shares in XYZ Corporation on the Internet, and your broker charges you $29.95.
(A) This will increase the investment component of GDP and therefore overall GDP.
(B) This has no effect on GDP.
(C) This will increase GDP by $29.95.
(D) This will increase GDP by the cost of the shares minus $29.95.
(E) This will increase GDP by the cost of the shares plus $29.95.
Use the following graph for question 3.
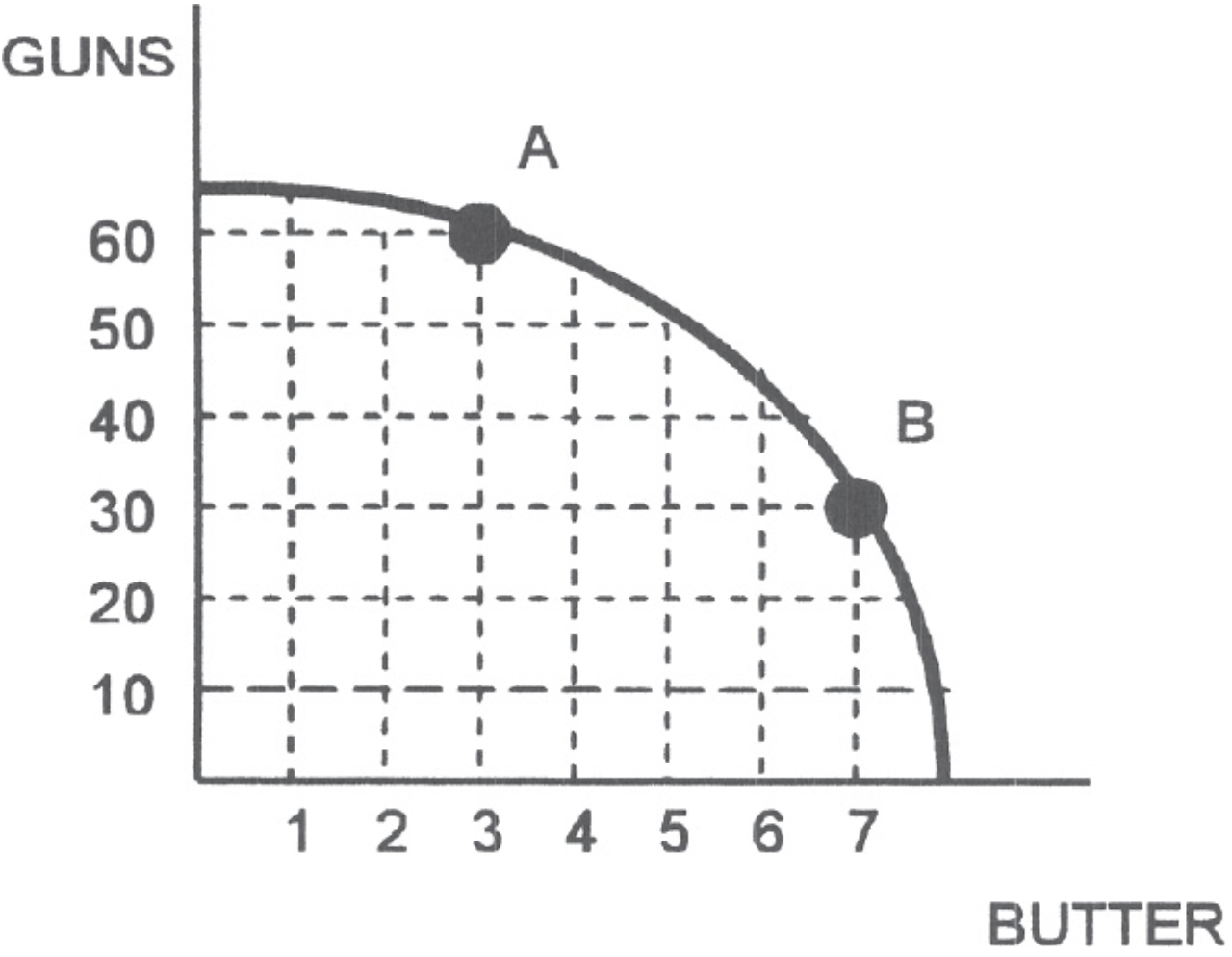
3. Given the graph above, the opportunity cost of 4 additional units of butter as the economy moves from A to B is
(A) 7 units of butter.
(B) 30 units of guns.
(C) 60 units of guns.
(D) unobtainable.
(E) indeterminant.
4. In the short run, contractionary monetary policy causes aggregate demand to ______, output to ______, and the price level to ______.
5. Assume bank reserves are limited and the reserve requirement is 5 percent. If the Fed sells $10 million worth of government securities in an open market operation, then the money supply can potentially
(A) increase by $200 million.
(B) decrease by $200 million.
(C) increase by $50 million.
(D) decrease by $50 million.
(E) increase by $150 million.
6. Given the table below, which statement is true?
Labor hours needed to produce a unit of:

(A) France has the absolute advantage in both products.
(B) France should specialize in and export wine, while Belgium should specialize in and export cheese.
(C) France has the comparative advantage in cheese.
(D) France has the absolute advantage in cheese.
(E) Belgium has the comparative advantage in both products.
Use the following graph for question 7.
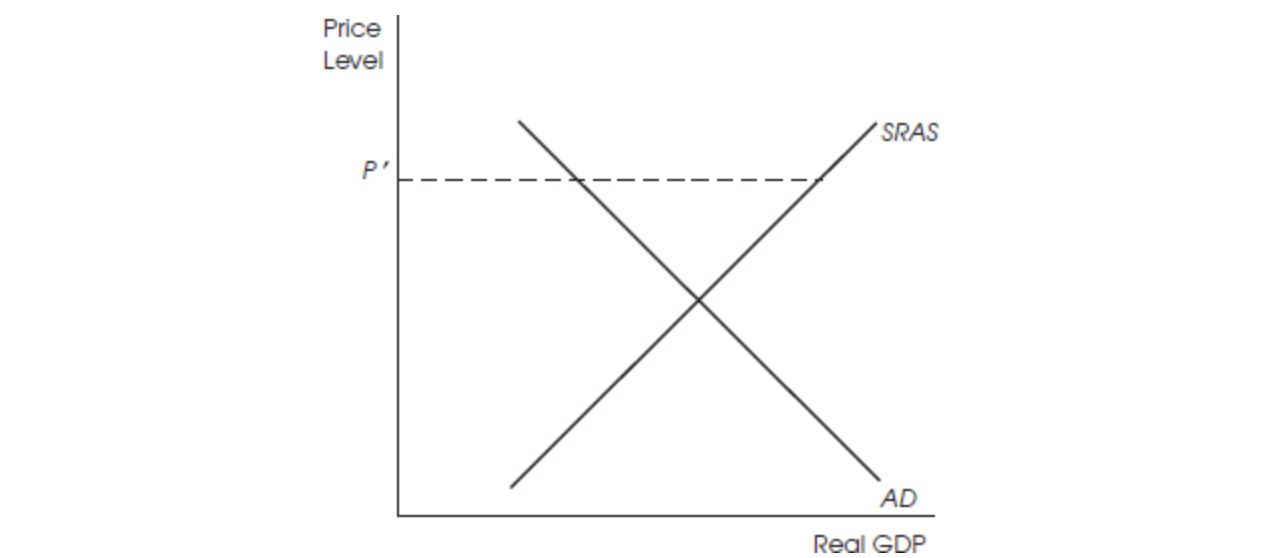
7. At P′ in the diagram above,
(A) inventories will be unintentionally drawn down, and the price level will fall.
(B) inventories will be unintentionally increased, and the price level will fall.
(C) inventories will be unintentionally drawn down, and the price level will rise.
(D) inventories will be unintentionally increased, and the price level will rise.
(E) inventories will be unintentionally drawn down, but prices will not be affected.
8. Suppose taxes are cut in an economy that is in equilibrium at full employment. In the long run the tax cut will
(A) raise real output and raise the price level.
(B) lower real output and raise the price level.
(C) raise real output and lower the price level.
(D) lower real output and lower the price level.
(E) raise the price level.
9. As a result of automatic stabilizers, during economic expansions government expenditures
(A) and taxes fall.
(B) and taxes rise.
(C) rise and taxes fall.
(D) fall and taxes rise.
(E) remain stable.
Use the following graph for question 10.
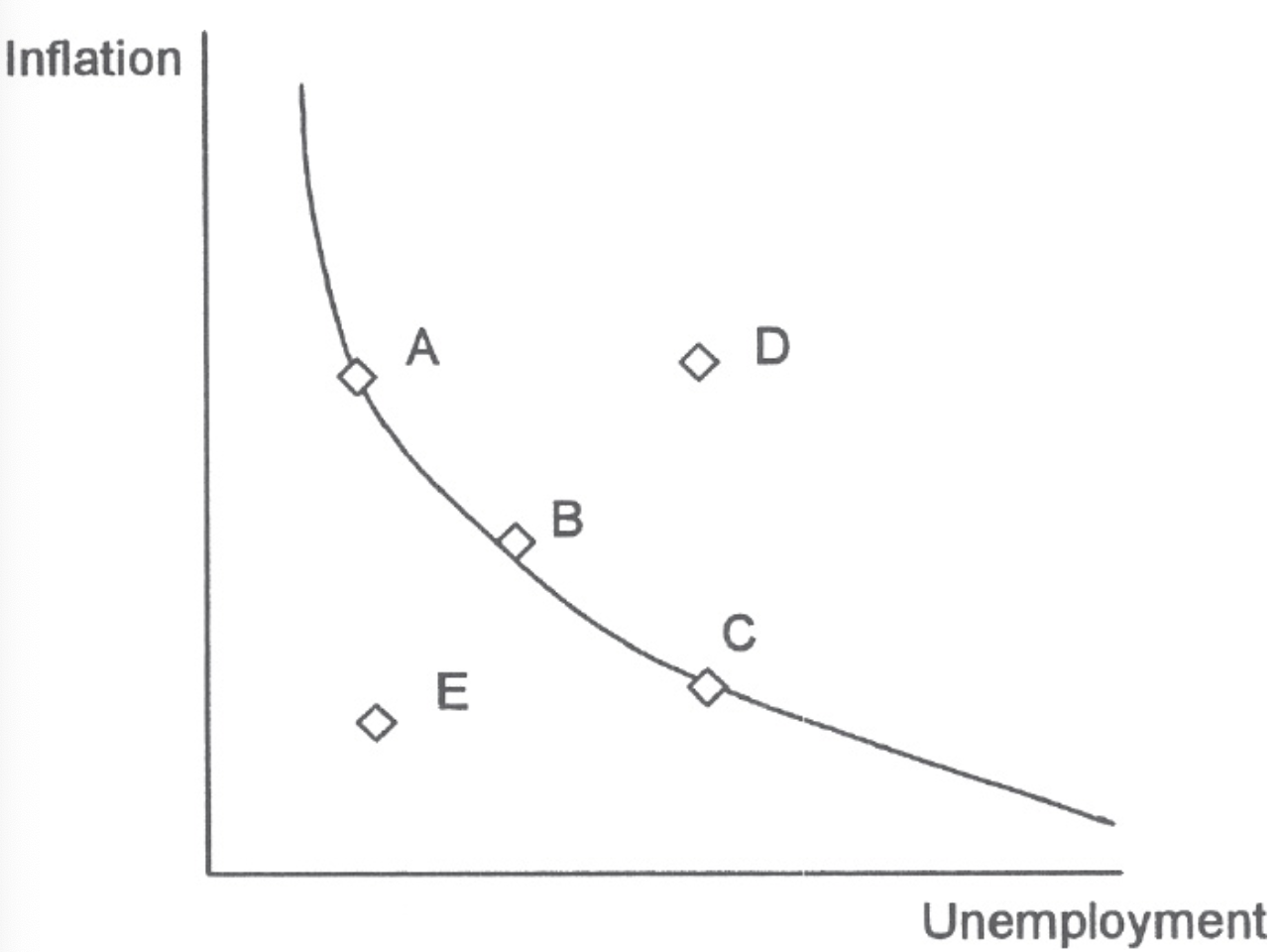
10. Consider the diagram above. In the short run, stagflation will move the economy from point B to
(A) point A.
(B) point A and then back to point B.
(C) point C.
(D) point D.
(E) point E.
11. Which of the following shifts the production possibilities frontier outward?
(A) A decrease in the price level
(B) An increase in labor productivity
(C) An increase in the money supply
(D) A decrease in the unemployment rate
(E) A decrease in the minimum wage
12. In the circular-flow diagram households send ________ to firms in return for ________.
(A) resources; spending
(B) spending; resources
(C) resources; wages and profits
(D) goods and services; wages
(E) goods and services; spending
13. An Italian company opens a shoe factory in the U.S. The production from this shoe factory is included in
(A) the Italian GDP.
(B) the U.S. GDP.
(C) both the Italian and U.S. GDP.
(D) both the Italian and U.S. GDP split 50/50.
(E) neither the Italian nor U.S. GDP.
14. Which of the following is NOT included in GDP?
(A) Federal government purchases of goods and services
(B) Imports
(C) State and local government purchases of goods and services
(D) Exports
(E) The change in business inventories
15. In the short run, an increase in the price level reduces the quantity of goods and services demanded in the economy because
I. consumers’ incomes cannot go as “ar now that prices have risen.
II. foreigners buy less.
III. higher prices result in higher interest rates, which reduce spending.
(A) Only I is correct.
(B) Only I and II are correct.
(C) Only I and III are correct.
(D) Only II and III are correct.
(E) I, II, and III are correct.
16. Suppose real GDP increases. We can conclude without a doubt that
(A) prices are higher.
(B) there has been a technological advance.
(C) production is higher.
(D) prices and output are greater.
(E) the price level is lower.
17. An appropriate fiscal policy to remedy a recession is to
(A) increase government spending and taxes.
(B) reduce government spending and taxes.
(C) increase government spending and reduce taxes.
(D) decrease government spending and increase taxes.
(E) increase the money supply.
18. Which of the following would lead to a decrease in the money in a banking system with limited reserves?
(A) The central bank lowers the discount rate.
(B) The central bank sells government securities in the secondary market.
(C) The federal government spends less money.
(D) The central bank lowers reserve requirements.
(E) The interest rate the central bank pays on bank reserves is decreased.
19. If interest rates rise relatively more in country A than in country B, then the value of country A’s currency will
(A) appreciate.
(B) depreciate.
(C) remain unchanged.
(D) change indeterminately.
(E) depreciate by the difference in interest rates.
20. If the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.75 and government spending increases by $100 million, then overall real GDP can be expected to
(A) decrease by $133.33 million.
(B) increase by $133.33 million.
(C) decrease by $400 million.
(D) increase by $400 million.
(E) increase by $75 million.
21. Inflation
(A) hurts creditors who do not anticipate it.
(B) hurts creditors who anticipate it.
(C) hurts debtors.
(D) benefits debtors who do not anticipate it.
(E) both A and D are correct.
22. Which of the following persons is (are) considered to be unemployed?
I. Mary, who has quit her job to look for another
II. John, who fulfilled his dream by retiring from work at age 45
III. Diane, who works part-time but would like to work full-time
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III
(D) I and III
(E) II and III
Use the following graph for question 23.
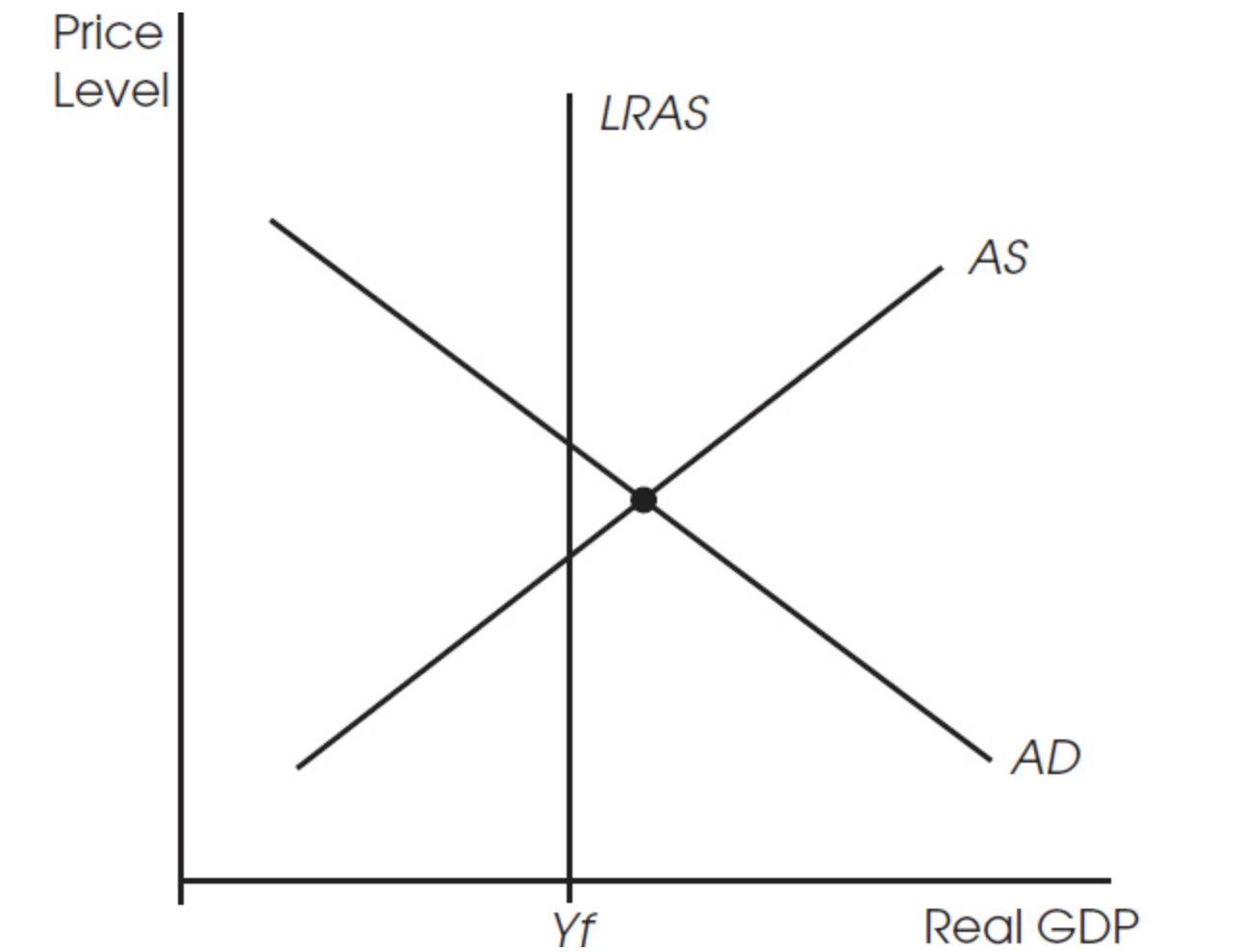
23. The economy depicted in the figure above is experiencing ________. In the absence of monetary or fiscal policy, the economy will eventually move to a point where the price level is ________.
(A) a recession; higher
(B) a recession; lower
(C) extremely high production; higher
(D) extremely high production; lower
(E) extremely high production; unchanged
24. The population of country X is exactly the same as country Y, but country X produces twice as much output as country Y. We can conclude that
(A) the people of country X are smarter than the people of country Y.
(B) the people of country X enjoy a standard of living twice as much as country Y.
(C) the people of country Y enjoy a standard of living twice as much as country X.
(D) the people of country Y work twice as hard as the people of country X.
(E) country X is bigger than country Y.
25. If the government of country Z increases spending by $12 million and raises tax collections by the same amount, then what will be the overall impact of these moves on real GDP in country Z?
(A) Real GDP will increase by $6 million.
(B) Real GDP will decrease by $6 million.
(C) Real GDP will remain unchanged.
(D)Real GDP will increase by $12 million.
(E) Real GDP will decrease by $12 million.
26. Suppose you observe an economy where prices are falling and real GDP is rising. This may have been caused by
(A) stagflation.
(B) an advance in technology.
(C) an increase in government spending.
(D) a decrease in government spending.
(E) a decrease in the money supply.
27. Which of the following would reduce economic growth?
(A) A decline in investment
(B) An increase in immigration from abroad
(C) A technological advance
(D) An increase in the labor force
(E)An increase in the savings rate
28.Currency held by the public
(A) is not part of the money supply, but currency held by banks is.
(B) is part of M1 but not M2.
(C) is part of the money supply, but currency held by banks is not.
(D) and by banks is part of the money supply.
(E) or banks is not part of the money supply since it is not included in M1.
29. The equation of exchange demonstrates the neutrality of money only if the
(A) velocity of money supply and the quantity of output are constant.
(B) money supply and its velocity are equal.
(C) velocity of money supply equals the speed of transactions.
(D) money supply and its velocity are inversely related.
(E) money supply and the exchange rate are inversely related.
30. Economy X is an open economy. Economy Y is closed. Expansionary monetary policy is
(A) more effective in X because the policy will increase net exports.
(B) more effective in X because the policy will decrease net exports.
(C) equally effective in X and Y.
(D) less effective in X because the policy will increase net exports.
(E) less effective in X because the policy will decrease net exports.
31. An increase in the price of forklifts imported into the United States from Belgium will
(A) increase the consumer price index and the GDP deflator.
(B) increase the consumer price index but not the GDP deflator.
(C) increase the GDP deflator but not the consumer price index.
(D) increase the GDP deflator and the producer price index.
(E) have no effect on the consumer price index or the GDP deflator.
32. An increase in the demand for money in the economy could result from
(A) a recession.
(B) a higher price level.
(C) higher interest rates.
(D) expected future inflation.
(E) a decrease in the supply of money.
33. The international value of the dollar will appreciate if
(A) American income falls relative to the rest of the world.
(B) American interest rates fall relative to interest rates in other countries.
(C) American prices rise.
(D) foreigners boycott American products.
(E) speculators expect the value of the dollar to depreciate.
34. The impact of an open market operation will be diminished if
(A) the public prefers to hold less cash.
(B) the velocity of money falls.
(C) depository institutions decide to hold more excess reserves.
(D) the marginal propensity to consume falls.
(E) the international value of the dollar falls.
35. An increase in the federal deficit may affect the demand for loanable funds and therefore the real interest rate and investment spending. Which of the following gives the correct direction of these effects?
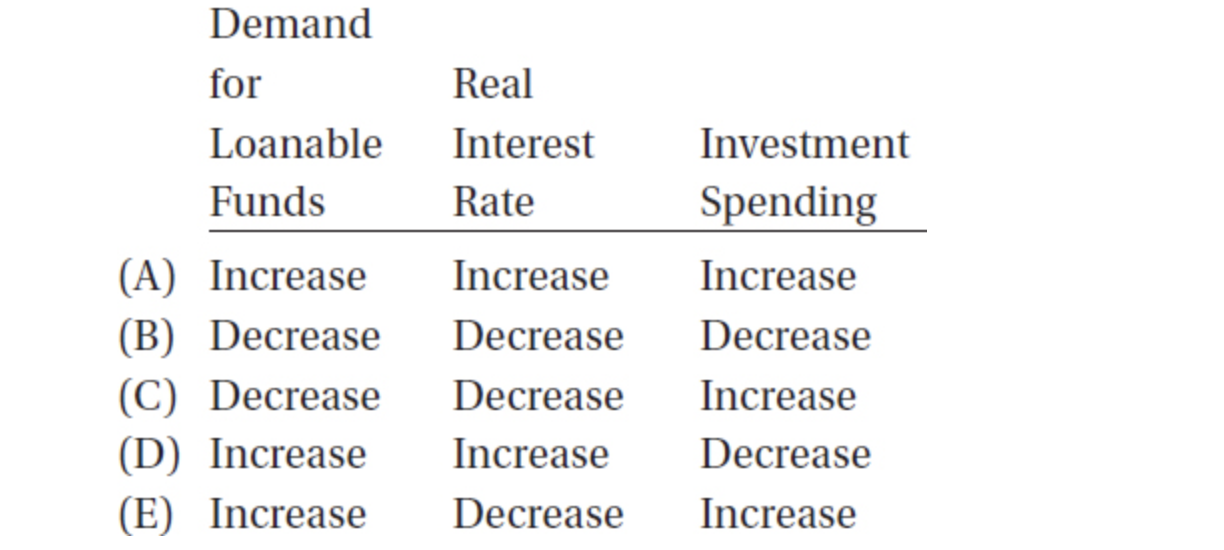
36. If the inflation rate is expected to increase in the immediate future, then
(A) consumers will begin saving more now.
(B) the velocity of money will fall.
(C) this will put upward pressure on the nominal interest rate.
(D) this will put downward pressure on the real interest rate.
(E) the international value of the dollar will rise.
37. If the economy is in disequilibrium where the price level is such that the aggregate quantity of products demanded exceeds the aggregate quantity of products supplied, then
(A) prices will be driven upward to restore equilibrium.
(B) supply will increase.
(C) demand will decrease.
(D) supply will decrease.
(E) a recession is inevitable.
38. If 200 computers with a retail value of $100,000 are domestically produced in 2005 but not sold until 2006, then GDP in 2005 is
(A) $100,000 higher because of the computers.
(B) 200 higher because of the computers.
(C) unaffected until 2006 when the computers are sold and the figure for GDP in 2005 is revised upward by $100,000.
(D) higher by the wholesale value of the computers.
(E) unaffected because the computers are counted in GDP for 2006.
39. Appropriate fiscal and monetary polices during the contractionary phase of the business cycle include
(A) budget surpluses and higher discount rates.
(B) tax reductions and open market purchases.
(C) budget surpluses and lower discount rates.
(D) increases in government spending and higher discount rates.
(E) decreases in government spending and lower discount rates.
40. A change in government spending will have a greater short-run impact on real output when
(A) the marginal propensity to consume is lower.
(B) the velocity of money is lower.
(C) the velocity of money is higher.
(D) the marginal propensity to consume is larger.
(E) interest rates rise.
41. Suppose a country produces only two goods, pizza and soda. Given the information in the table below, nominal GDP, real GDP, and the GDP deflator in 2005 are (assume 2004 is the base year):
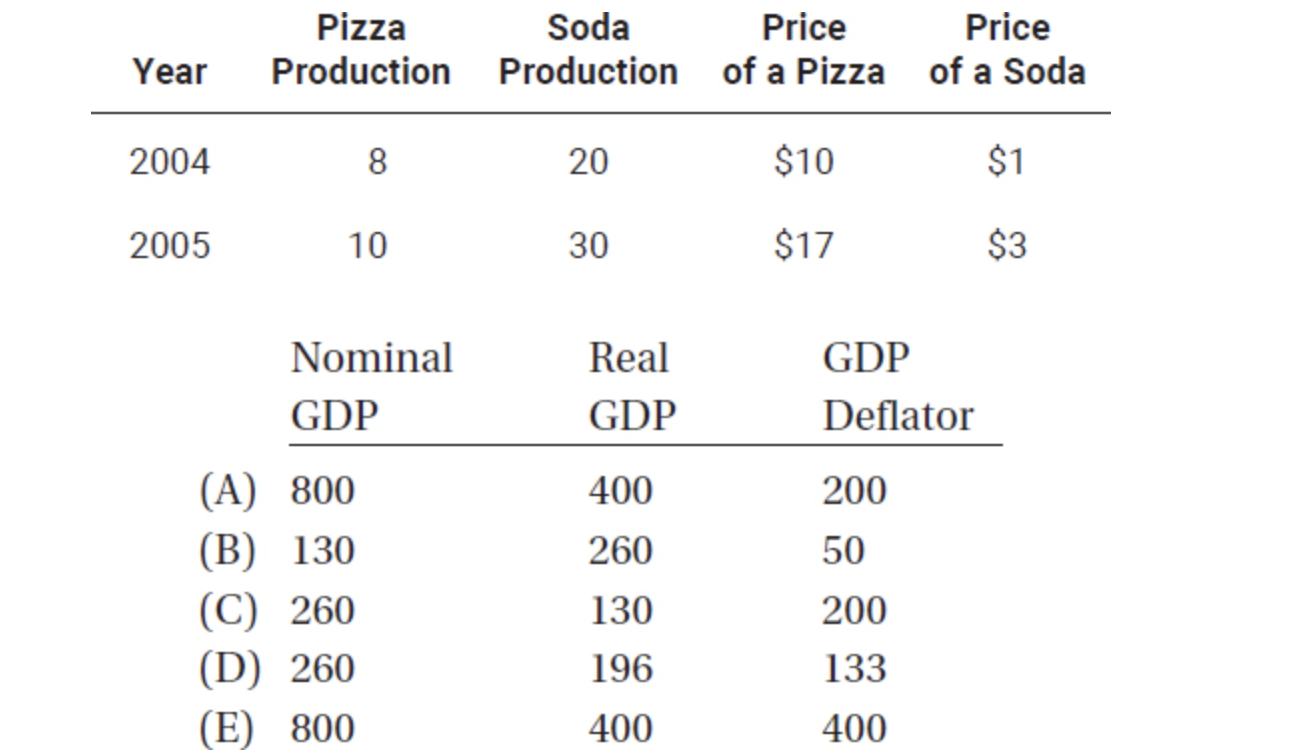
42. If the economy experienced a decrease in real GDP and price level, this could best be explained by
(A) a decline in labor productivity.
(B) a technological advance.
(C) a decline in investment.
(D) an uptick in net exports.
(E) a reduction in interest rates.
Use the following graph for question 43.
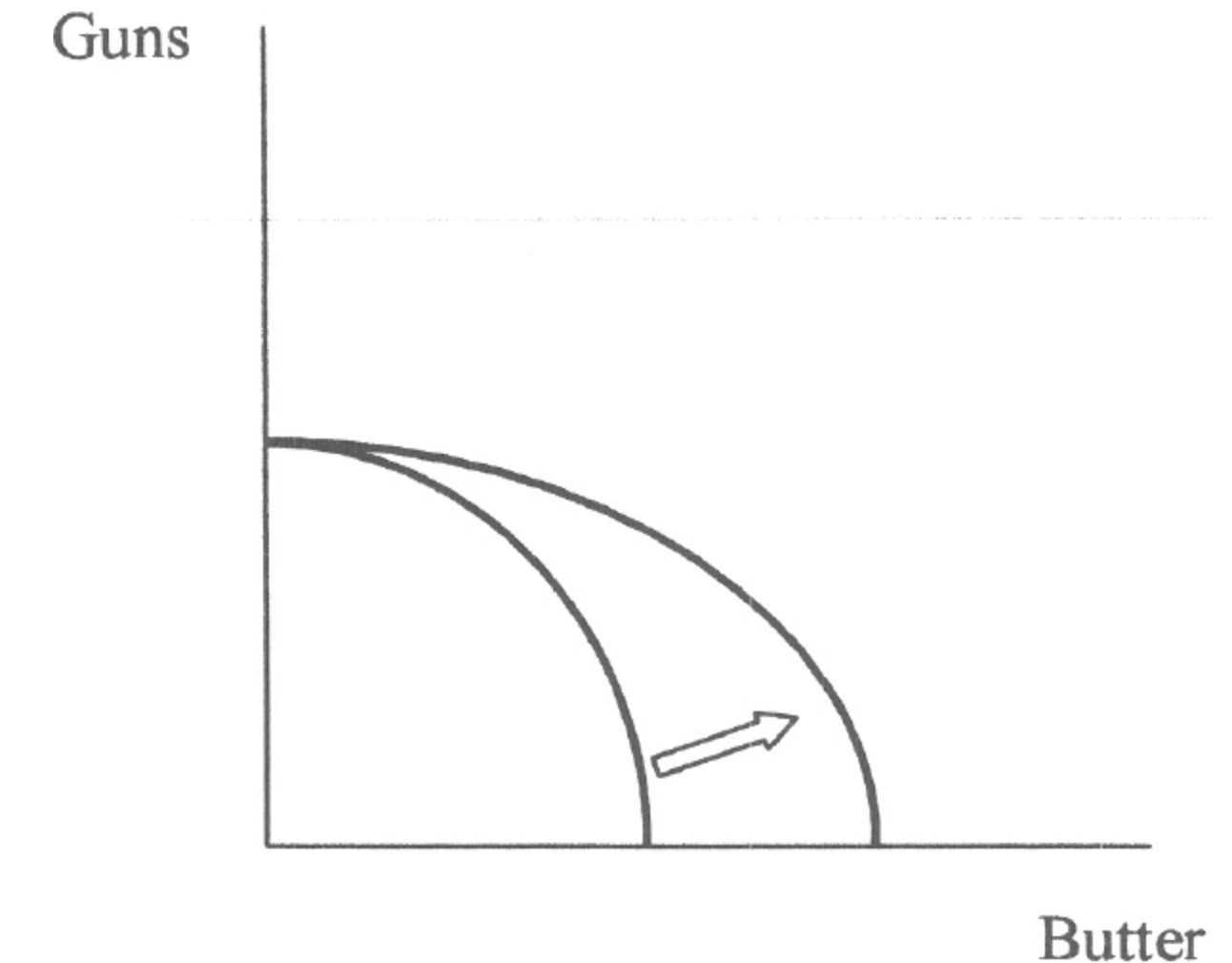
43. The shift depicted in the diagram above could have been caused by
(A) better production methods in the gun industry.
(B) an increase in the number of cows in the economy.
(C) an increase in the number of workers in the economy.
(D) a technological setback in the gun industry.
(E) a reduction in farmland available due to pollution.
44. Suppose the real interest rate in a country rises. What can be expected to happen to the demand for this nation’s currency and, therefore, the value of its currency and net exports?
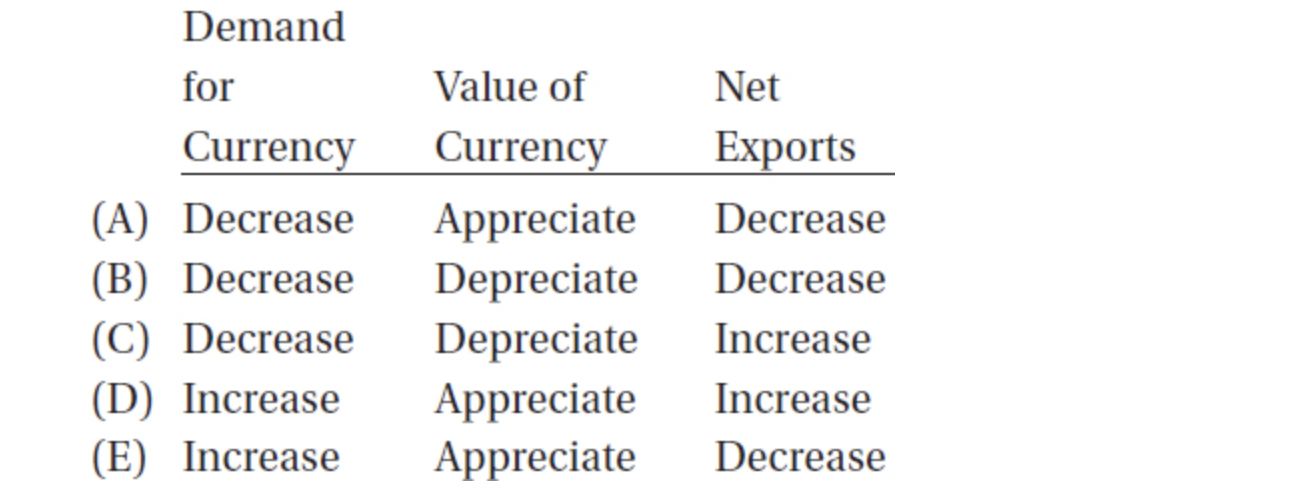
45. In the short run, a decrease in aggregate demand will cause the price level to ______ and real GDP to ______.
(A) decrease; decrease
(B) decrease; increase
(C) remain unchanged; decrease
(D) increase; decrease
(E) increase; increase
46. In the long run, an economy in recession can return to full employment once nominal wages ______ and the price level ______.
(A) decrease; decreases
(B) decrease; increases
(C) increase; remains unchanged
(D) increase; decreases
(E) increase; increases
47. If the cost of the basket of goods and services the Bureau of Labor Statistics uses to calculate the consumer price index rises from $200 in the base period to $400 in the current period, then the consumer price index
(A) equals 0.5 in the current period.
(B) has risen 5 percent from the base to the current period.
(C) equals 50 in the current period.
(D) equals 200 in the current period.
(E) has risen 200 percent.
48. Contractionary monetary policy implies which of the following about the discount rate, the nominal interest rate, and aggregate demand?
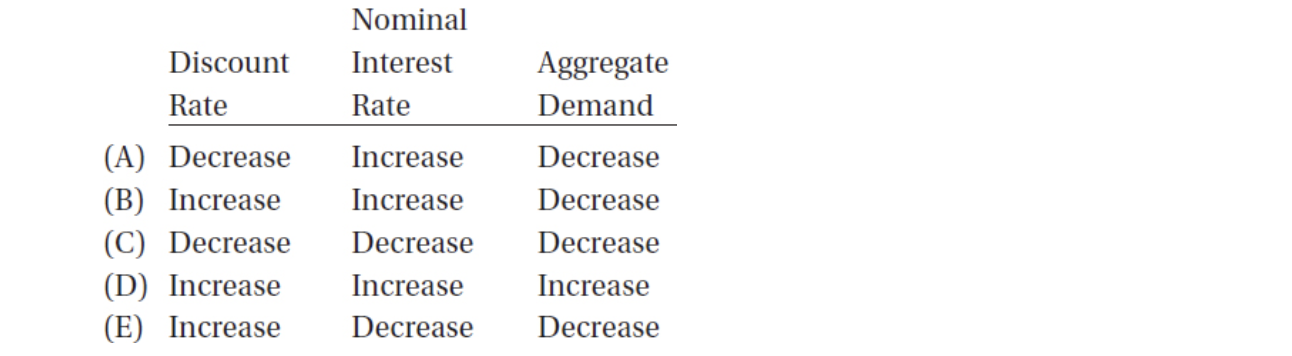
49. A decline in the demand for money could be the result of
(A) higher prices.
(B) more money placed in checking accounts.
(C) higher returns on bonds.
(D) fewer credit cards.
(E) open market purchases by the central bank.
50. An important assumption underlying the idea that an increase in the money supply causes a proportional increase in the price level is that the
(A) marginal propensity to consume is constant.
(B) money supply is continuous.
(C) exchange rate is fixed.
(D) velocity of money is stable.
(E) exchange rate is flexible.
51. Which of the following policies is most likely to bring about economic growth in the long run?
(A) Imposing tariffs to protect domestic industries from foreign competition
(B) Increasing taxes on savings
(C) Increasing government spending
(D) Increasing the money supply
(E) Promoting improvements in the education of the population
52. An increase in the price level and a decrease in real GDP in the short run could be the result of
(A) a decrease in aggregate supply.
(B) a decrease in the money supply.
(C) an increase in aggregate supply.
(D) an increase in consumer confidence.
(E) an increase in the money supply.
53. In 2021, the United States had a trade deficit. Therefore,
(A) net exports were positive.
(B) net foreign purchases of U.S. assets were positive.
(C) America’s government spent more than it took in.
(D) the U.S. balance of trade was positive.
(E) the government had to make payments to foreign countries of $600 billion.
54. GDP measures a country’s level of
I. production.
II. stability.
III. income.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and II
(E) I and III
55. Which of the following lists contains only central bank actions that will decrease interest rates in a banking system that has limited reserves?
(A) Raise the interest on bank reserves; lower the discount rate; sell bonds.
(B) Raise the interest on bank reserves; lower the discount rate; buy bonds.
(C) Raise the interest on bank reserves; raise the discount rate; sell bonds.
(D) Lower the interest on bank reserves; lower the discount rate; sell bonds.
(E) Lower the interest on bank reserves; lower the discount rate; buy bonds.
56. Which of the following lists contains only policies that will close an inflationary gap?
(A) Increase the money supply; run a federal budget deficit.
(B) Decrease the money supply; run a federal budget deficit.
(C) Decrease the money supply; increase taxes; reduce government spending.
(D) Increase the money supply; increase taxes; reduce government spending.
(E) Decrease the money supply; decrease taxes; reduce government spending.
57. Suppose the exchange rates are 0.5 British pound per dollar, 10 Mexican pesos per dollar, and 100 Chinese yuan per dollar. Further suppose that a Big Mac costs 3 dollars in America, 2 pounds in England, 50 pesos in Mexico, and 200 yuan in China. In which country is a Big Mac most expensive?
(A) America
(B) England
(C) Mexico
(D) China
(E) England and China are equally most expensive.
58. Potential GDP will fall, ceteris paribus, if
(A) the unemployment rate rises.
(B) the retirement age is lowered.
(C) tariffs protecting domestic jobs are eliminated.
(D) more immigration is allowed.
(E) the minimum wage is raised.
59. If nominal GDP = $1,500 and real GDP = $1,000, then the GDP deflator equals
(A) −$500.
(B) 66.67.
(C) 150.
(D) $500.
60. Imagine someone who is not looking for work because he is embarrassed in the interview process when his inability to read is revealed. However, this person would take just about any job that was offered. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, this person is
(E) in the labor force and unemployed.
(A) in the labor force and employed.
(B) not in the labor force.
(C) not in the labor force but counted as unemployed.
(D) not in the labor force but counted as employed.
Section II—Free-Response Questions
1. Country X is in short-run equilibrium at a level of output below full employment.
(a) Draw a correctly labeled graph of aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, and long-run aggregate supply that depicts the situation in Country X.
(b) Identify an appropriate fiscal policy to bring about full employment in Country X.
(i) Show the effects of the fiscal policy on the graph from part (a). Be clear about which curve(s) is/are shifting which way.
(ii) State how the fiscal policy affects output, the price level, and the level of employment.
(c) Draw a correctly labeled graph of the money supply and money demand showing the equilibrium nominal interest rate.
(i) Show the effects of the changes in the price level and output from (b) (ii) above on the graph of the money supply and money demand. Be clear about which curve(s) is/are shifting which way.
(ii) Explain how the change in the equilibrium nominal interest rate will impact investment expenditures.
2. (a) Draw a correctly labeled diagram of the supply and the demand for the U.S. dollar vis-à-vis the euro. Be sure to label all curves and axes.
(b) Now suppose U.S. consumers significantly increase their demand for European products.
(i) Show the effects of the change in U.S. consumer tastes on the graph from part (a). Be clear about which curve(s) is/are shifting which way.
(ii) State how the value of the dollar will be affected by the change in U.S. consumer tastes.
(c) U.S. net exports decreased when U.S. consumers demanded more European products. State how U.S. net exports will be affected once the value of the dollar has changed.
(d) Draw a correctly labeled diagram of the supply and the demand for the euro vis-à-vis the U.S. dollar. Be sure to label all curves and axes.
(e) Now suppose U.S. consumers significantly increase their demand for European products.
(i) Show the effects of the change in U.S. consumer tastes on the graph from part (d). Be clear about which curve(s) is/are shifting which way.
(ii) State how the value of the euro will be affected by the change in U.S. consumer tastes.
(f) European net exports increased when U.S. consumers demanded more European products. State how European net exports will be affected once the value of the euro has changed.
3. Describe how an open market purchase of $7 million by the Federal Reserve will affect the money supply. Assume bank reserves are limited.
(a) Assuming a required reserve ratio of 5 percent, what is the maximum amount by which the money supply can change due to the open market operation?
(b) How will your answer (a) above change if banks decide to hold reserves over and above the required amount?
(c) Suppose a large corporation makes the open market purchase of $7 million. Explain how the money supply will be affected in this case.
(d) Suppose the banking system has ample reserves. Explain how the federal funds rate will be affected by the open market purchase.




