AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024- Microeconomics Practice
1. Which of the following would NOT be considered a characteristic of a market or capitalistic economy but that of a command or communist economy?
(A) Protection of private property
(B) Negative externalities
(C) The price system to allocate resources
(D) Competition among firms
(E) Centralized decision making
Use this graph for question 2.
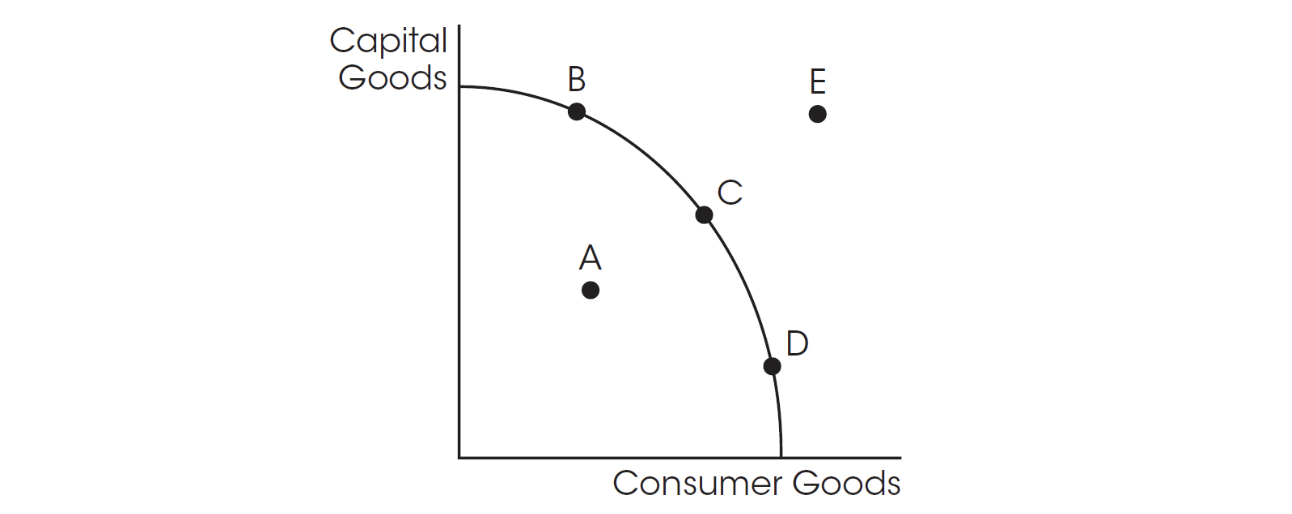
2. In the graph above, which movement would show a movement from inefficiency to efficiency?
(A) B to C
(B) C to B
(C) C to E
(D) A to C
(E) C to A
3. According to the law of comparative advantage, the U.S. should specialize production in ________ and Germany should specialize production in _________.
(A) peanuts; neither good
(B) peanuts; oranges
(C) oranges; oranges
(D) oranges; peanuts
(E) oranges; neither good

4. The table shows the quantity of chocolate candy bars consumed and the total utility. In eating which candy bar would the consumer begin to experience diminishing marginal utility?
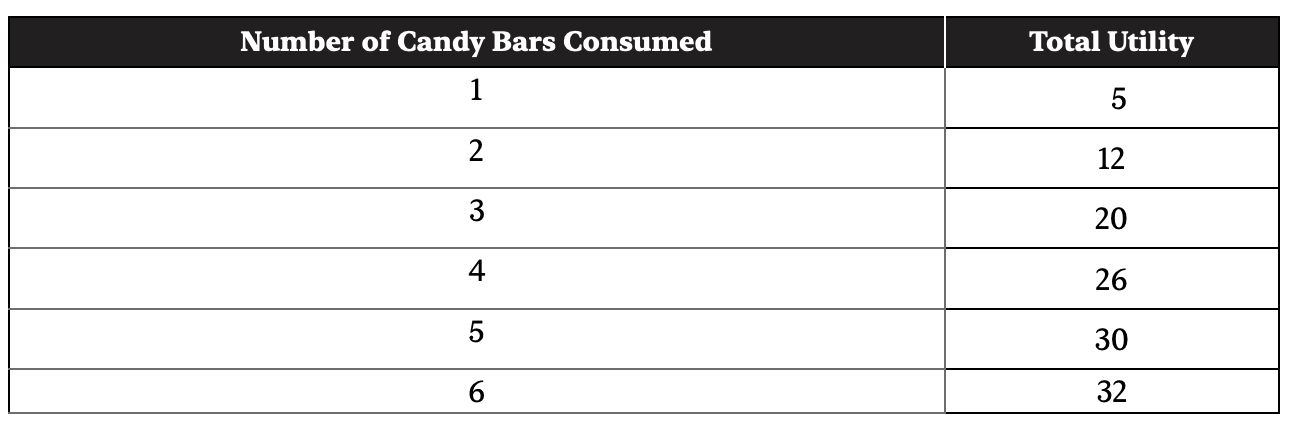
(A) 1st
(B) 2nd
(C) 3rd
(D) 4th
(E) 5th
5. Assume Ahmed spends all his income on two goods: pizza and video games. The current cost of pizza is $6 and of video games is $20, and at his consumption level the marginal utility from eating pizza is 18 and from playing video games is 40. In order to maximize his utility, Ahmed should
(A) consume more pizza and buy fewer video games.
(B) buy more video games and consume less pizza.
(C) consume more of both.
(D) consume less of both.
(E) keep consumption at his current level.
6. Assume a friend offers to give you a “free” ticket to a local professional baseball team’s game that night. You decide to attend the game. The game takes five hours and costs you $15 for transportation. If you had not attended the game, you would have worked 5 hours at your part-time job for $8 an hour. What is the opportunity cost to you of attending the game?
(A) $0
(B) $23
(C) $40
(D) $55
(E) $65
7. Which of the following would shift the demand curve for avocados to the right?
(A) A decrease in the price of a complementary good for avocados
(B) An increase in productivity of avocado farmers
(C) A decrease in the price of avocados
(D) A decrease in the price of a substitute for avocados
(E) The imposition of a price floor in the avocado market
Use the following graph for questions 8 and 9.
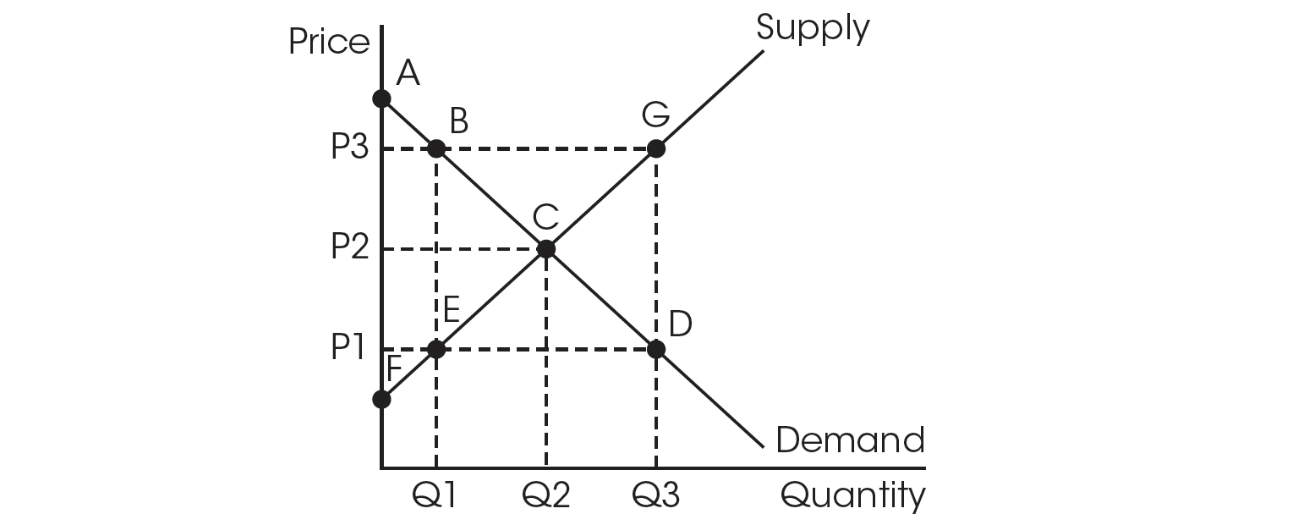
8. Assume the perfectly competitive market shown above is in equilibrium, but then the government adds a price ceiling at P1. With the price ceiling in effect, please choose the correct area of the consumer surplus and deadweight loss.

9. Assume the perfectly competitive market shown above is in equilibrium, but then the government adds a price floor at P3. With the price floor in effect, please choose the correct area of the consumer surplus and deadweight loss.

10. If the supply of good X decreases and this leads to an increase in both the price and quantity for good Y, which of the following is true?
(A) Good Y is a substitute for good X.
(B) Good Y is a complement of good X.
(C) Good Y is an inferior good.
(D) Good Y is a normal good.
(E) Good X is independent of good Y.
Please use this graph for question 11.
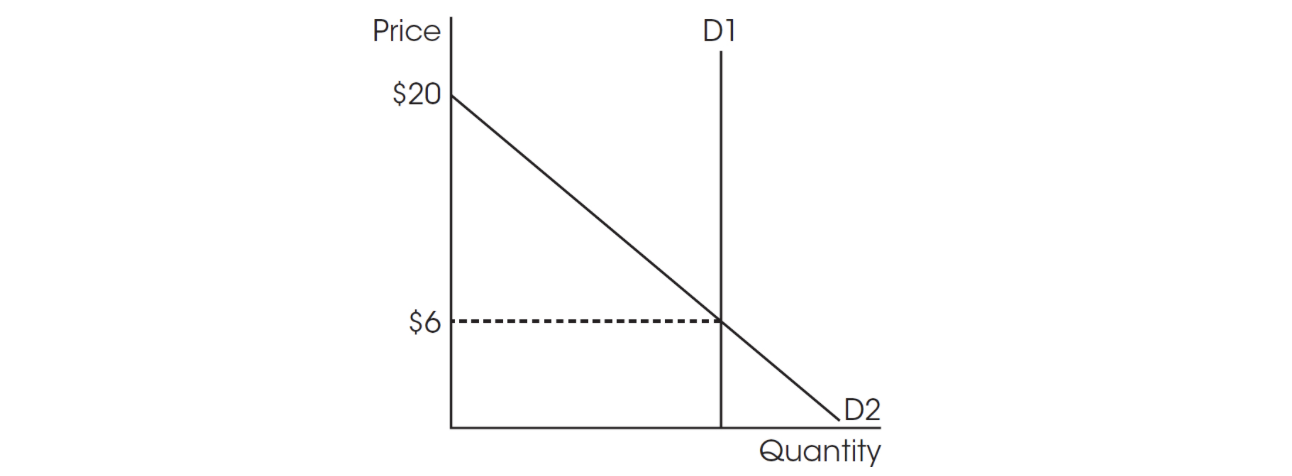
11. According to the graph, what combination below best describes the elasticity of demand curves D1 and D2 at a price of $6?

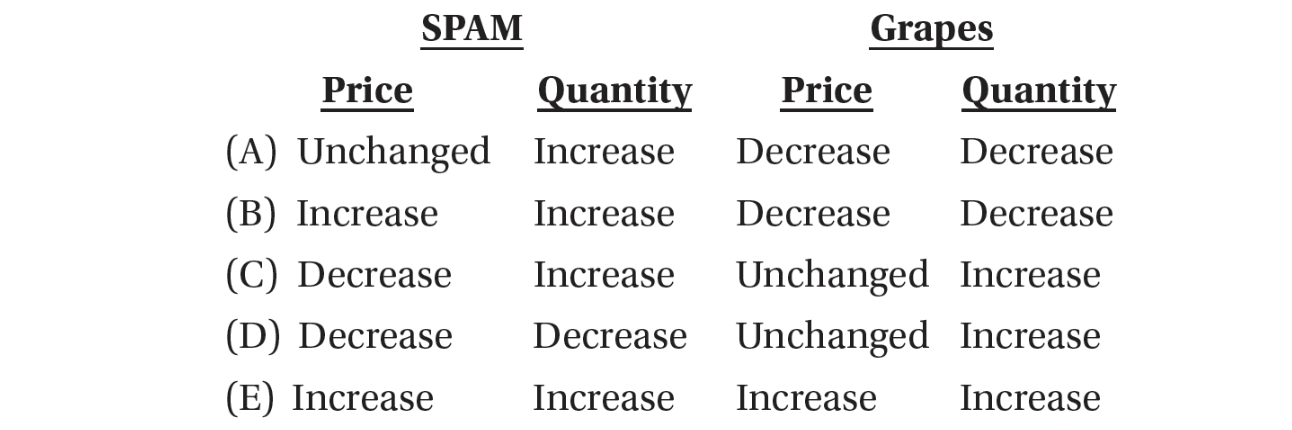
12. SPAM (meat in a can) is considered an inferior good and grapes are a normal good. If consumers’ income decreases, what would an economist predict to happen to the price and quantity of these two goods?
Use the following graph for question 13.
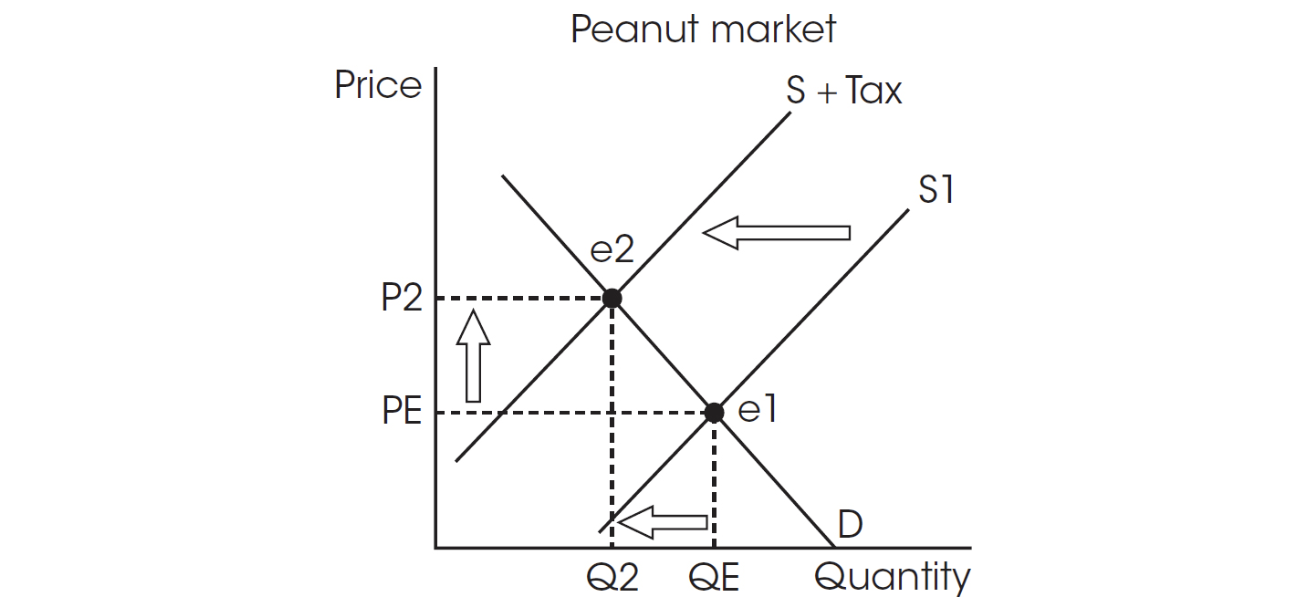
13. The graph shows a market in equilibrium at PE and QE. Then the government imposes an excise tax on peanuts, with supply shifting to the left at P2, Q2. What will happen to each of the following after the imposition of the sales tax?

14. If a 10% increase in the price of a good leads to a 5% decrease in the quantity demanded of that good, demand is
(A) perfectly elastic.
(B) relatively elastic.
(C) unit elastic.
(D) relatively inelastic.
(E) perfectly inelastic.
15. Assume the elasticity of demand for fidget spinners is 4. A 20 percent decrease in the price causes the quantity demanded for fidget spinners to increase by
(A) 5%.
(B) 20%.
(C) 40%.
(D) 80%.
(E) 160%.
16. This table shows the total production of widgets with different numbers of workers used. Which of the following is true?
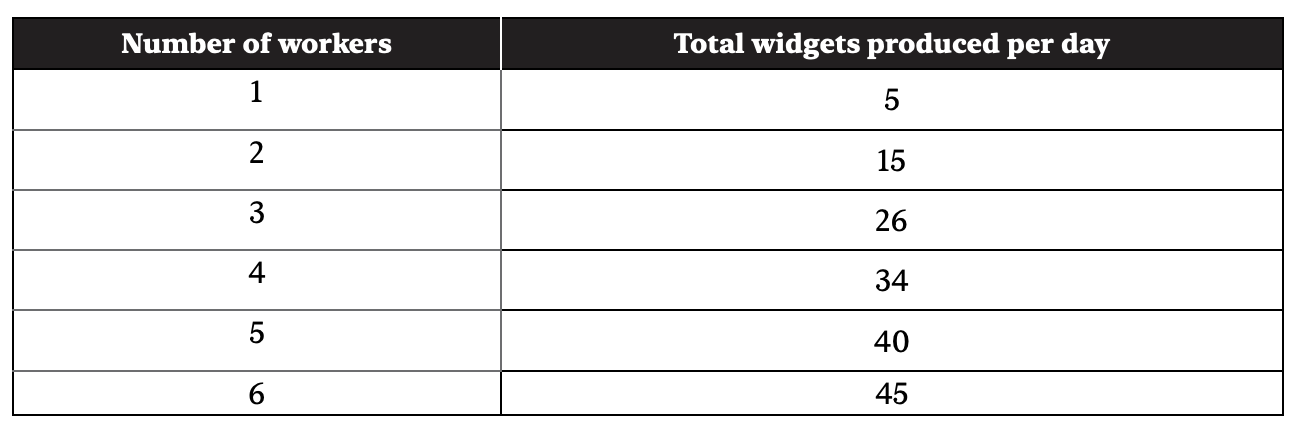
(A) Marginal product is greatest at 6 workers.
(B) Diminishing marginal returns begin with the 2nd worker.
(C) At 6 workers, both marginal and total product equal 45.
(D) The firm should hire 6 workers to maximize profit.
(E) Diminishing marginal returns begin with the 4th worker.
17. This graph best depicts which of the following concepts?
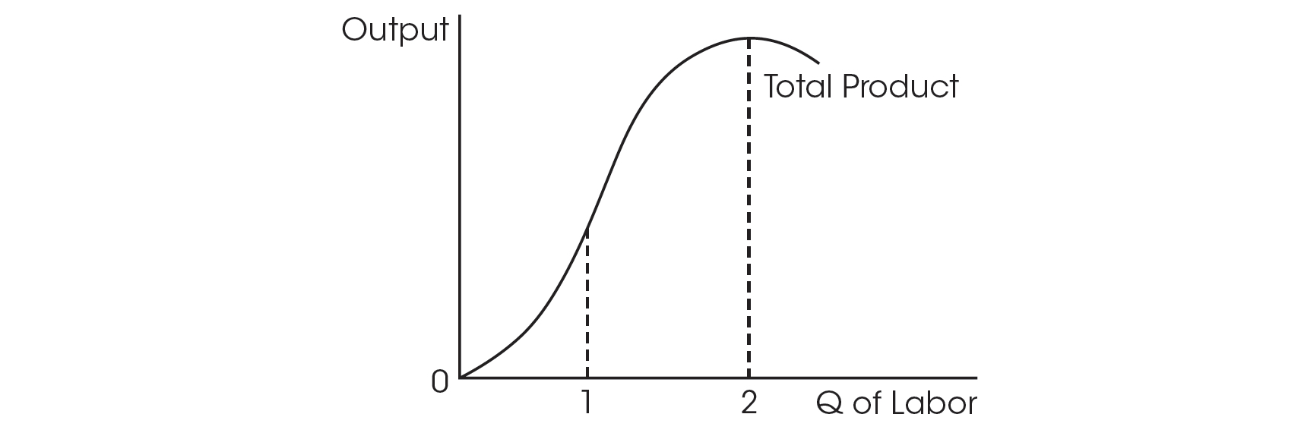
(A) The law of diminishing marginal returns in production
(B) The law of increasing opportunity cost
(C) The law of diminishing marginal utility in consumption
(D) Absolute advantage
(E) Economies of scale
Use this chart for questions 18 and 19.
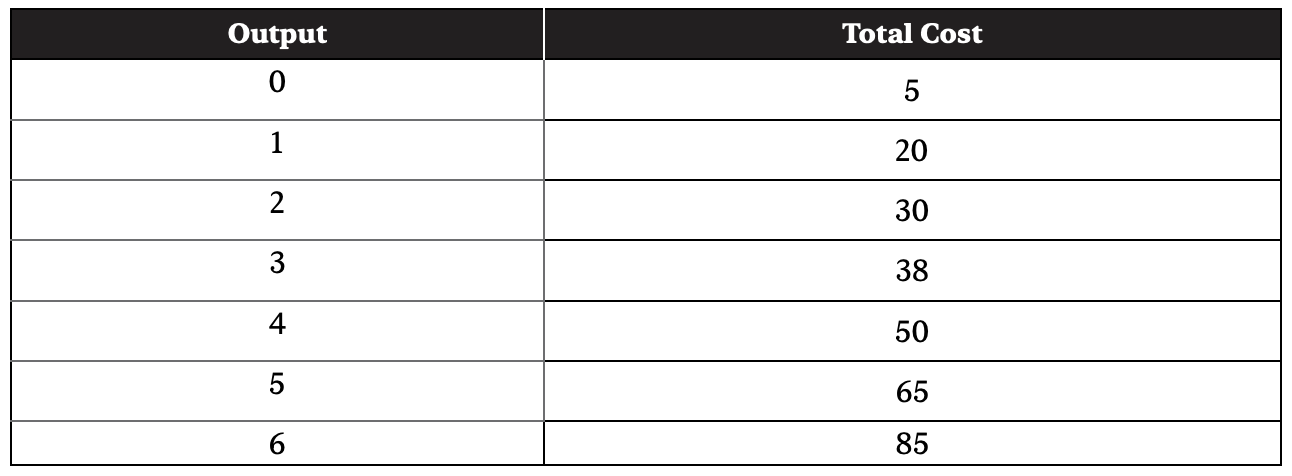
18. What is the marginal cost of producing the 5th unit of output?
(A) 5
(B) 10
(C) 13
(D) 15
(E) 20
19. What is the total variable cost of producing the 4th unit of output?
(A) 5
(B) 12
(C) 12.5
(D) 45
(E) 50
20. If a company has an average total cost of $100 and a marginal cost of $90 at the 4th unit of output, then which of the following must be true?
(A) The average total cost of producing the 3rd unit is less than $100.
(B) The average total cost of producing the 3rd unit is more than $100.
(C) The average fixed cost curve is increasing as production moves from 3 to 4 units.
(D) The average variable cost of producing the 4th unit is more than $100.
(E) The marginal cost curve has intersected the average total cost curve before the 4th unit.
21. Fields’ Flour Corporation can produce 500 units of output a day employing 40 workers and 10 robots. Which of the following combinations correctly shows constant returns to scale?
.png)
22. This graph shows a perfectly competitive market. Which of the following statements are true at the firm’s profit-maximizing level of output?
I. The firm is incurring economic losses.
II. The firm is earning economic profits.
III. The firm is earning a normal profit.
IV. Price is greater than ATC.
V. Firms will exit the industry.
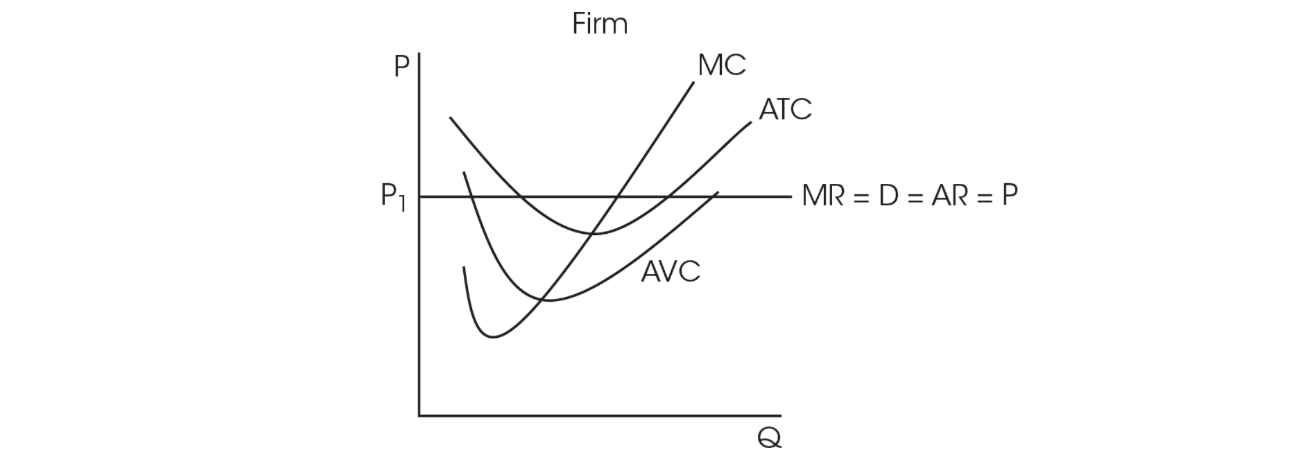
(A) I and II
(B) I, III, and V
(C) II and IV
(D) I, II, and IV
(E) I, III, and V
23. If a firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale, which of the following is correct?
(A) Long-run average total costs are increasing as output increases.
(B) Long-run average total costs are decreasing as output increases.
(C) Firms will enter the industry if firms are experiencing diseconomies of scale.
(D) The firm is incurring economic losses.
(E) Long-run average total costs remain constant as output increases.
24. Jacob was a corporate lawyer, who quit his job to open a yoga studio. His income as a lawyer was $100,000, and he earned $60,000 as a yoga studio entrepreneur. He also took $10,000 of his savings out of his bank savings account to invest in his business, where he was earning 10% interest. What is Jacob’s economic profit from his yoga studio?
(A) −$41,000
(B) −$40,000
(C) $40,000
(D) $60,000
(E) $70,000
25. Why do perfectly competitive firms earn zero economic profit in the long run?
(A) Perfectly competitive firms have lower costs than other market structures.
(B) Perfectly competitive firms have more technological innovation than other market structures.
(C) Perfectly competitive firms have higher start-up costs than other market structures.
(D) It is difficult for other firms to enter and exit a perfectly competitive industry.
(E) It is easy for other firms to enter and exit a perfectly competitive industry.
26. At a production level of zero, ABC Corporation has a total cost of $10. The marginal cost of producing the first unit is $40, and the marginal cost of producing the second unit is $20. What is the total average cost of producing two units?
(A) $15
(B) $20
(C) $35
(D) $60
(E) $70
27. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive firm?
(A) It should shut down if price is less than average variable cost where marginal revenue = marginal cost.
(B) In long-run equilibrium, it is allocatively efficient but not productively efficient.
(C) It is a price taker.
(D) Demand, marginal revenue, and average revenue are all equal.
(E) There are low barriers to entry into the market.
28. In which of the following market structures are mutual interdependence and game theory used to describe how firms relate to one another?
(A) Oligopoly
(B) Monopoly
(C) Monopolistic competition
(D) Perfect competition
(E) Both monopoly and oligopoly
29. In a monopoly that practices perfect price discrimination, which of the following is correct regarding the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and consumer surplus?
(A) Demand > marginal revenue and consumer surplus is negative.
(B) Demand > marginal revenue and consumer surplus is positive.
(C) Demand > marginal revenue and consumer surplus is zero.
(D) Demand = marginal revenue and consumer surplus is positive.
(E) Demand = marginal revenue and consumer surplus is zero.
Use this graph for questions 30, 31, and 32.
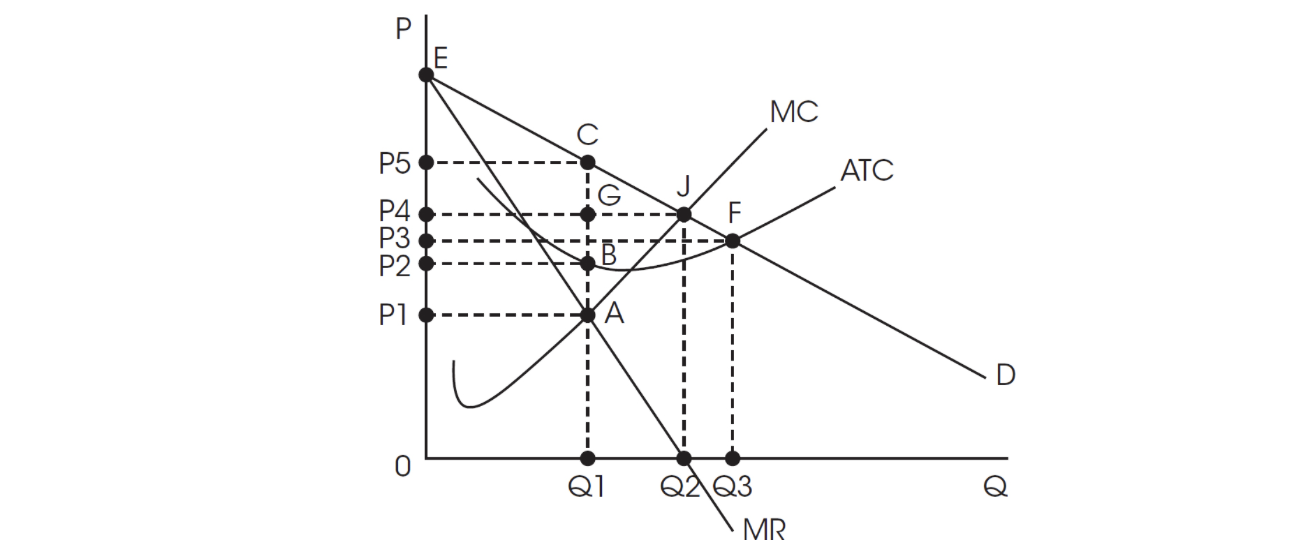
30. Assume the monopoly in the graph is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output. Choose the correct combinations of price, quantity, and deadweight loss.

31. Assume the monopoly in the graph is producing at the point where it maximizes total revenue. Choose the correct combinations of price, quantity, and deadweight loss.

32. Assume the monopoly in the graph is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output. What is the area of economic profit?
(A) P4, G, B, P2
(B) 0, P5, C, Q1
(C) P2, P5, C, B
(D) P1, P5, C, A
(E) P2, E, C, B
33. Which of the following is true for monopolistically competitive firms in long-run equilibrium?
(A) They are price takers.
(B) Their demand curves are equal to the marginal revenue curves.
(C) There are positive economic profits
(D) There are high barriers for firms to enter the market.
(E) They sell similar but differentiated products.
Use the game theory matrix here for questions 34 and 35.
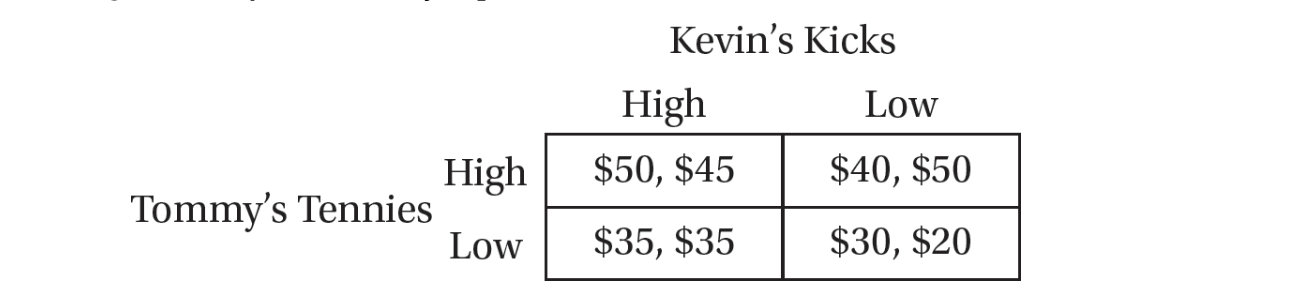
34. In a small town there are only two shoe sellers, Tommy’s Tennies and Kevin’s Kicks. They are both trying to decide whether to price high or low. The first number in each box refers to the daily profit for Tommy’s Tennies, and the second number refers to Kevin’s daily profit. Based on the numbers in the game theory matrix, which of the following is true?
(A) Pricing high is a dominant strategy for Tommy’s Tennies.
(B) Pricing high is a dominant strategy for Kevin’s Kicks.
(C) Pricing low is a dominant strategy for Tommy’s Tennies.
(D) Pricing low is a dominant strategy for Kevin’s Kicks.
(E) Neither firm has a dominant strategy.
35. In a small town there are only two shoe sellers, Tommy’s Tennies and Kevin’s Kicks. They are both trying to decide whether to price high or low and know all the information in the payoff matrix. The first number in each box refers to the daily profit for Tommy’s Tennies, and the second number refers to Kevin’s daily profit. Based on the numbers in the game theory matrix, what is the Nash equilibrium?

36. Which of the following correctly describes monopolistically competitive firms in long-run equilibrium? (D = demand, MR = marginal revenue, MC = marginal cost, ATC = average total cost.)
(A) MR = MC, P > ATC, D > MR
(B) MR > MC, P = ATC, D = MR
(C) MR = MC, P < ATC, D < MR
(D) MR < MC, P = ATC, D > MR
(E) MR = MC, P = ATC, D > MR
37. If the regulators of a natural monopoly mandate the price to be set where price = average total cost, what best describes this situation?
(A) The firm is pricing at the socially optimal price.
(B) The firm is pricing at the fair-return price.
(C) The firm is pricing at the unregulated price.
(D) The firm is producing an output level where MR = MC.
(E) The firm is realizing economic profits.
38. Why do most governments in market economies enforce antitrust laws?
(A) To ensure oligopolies don’t have monopoly power
(B) To prevent too much competition in an industry
(C) To ensure natural monopolies price at the socially optimal level of output
(D) To ensure oligopolies reach a Nash equilibrium
(E) To prevent price ceilings from being imposed on a market
39. A worker’s marginal revenue product is best described as
(A) the total revenue a firm makes when selling a product.
(B) the change to a firm’s revenue when employing an additional worker.
(C) the change to a firm’s profit when employing an additional worker.
(D) the total amount of a firm’s labor costs.
(E) the change in resource cost divided by total revenue.
40. Assume a perfectly competitive labor market is initially in equilibrium with a downsloping demand curve and an upsloping supply curve. If the government then sets a binding minimum wage, which of the following is correct?
(A) There would be a shortage in the labor market.
(B) The quantity of labor supplied would be greater than the quantity of labor demanded.
(C) The number of workers hired would remain the same.
(D) The number or workers hired would increase.
(E) The market would remain in equilibrium regardless of the wage paid.
Use this chart for question 41.
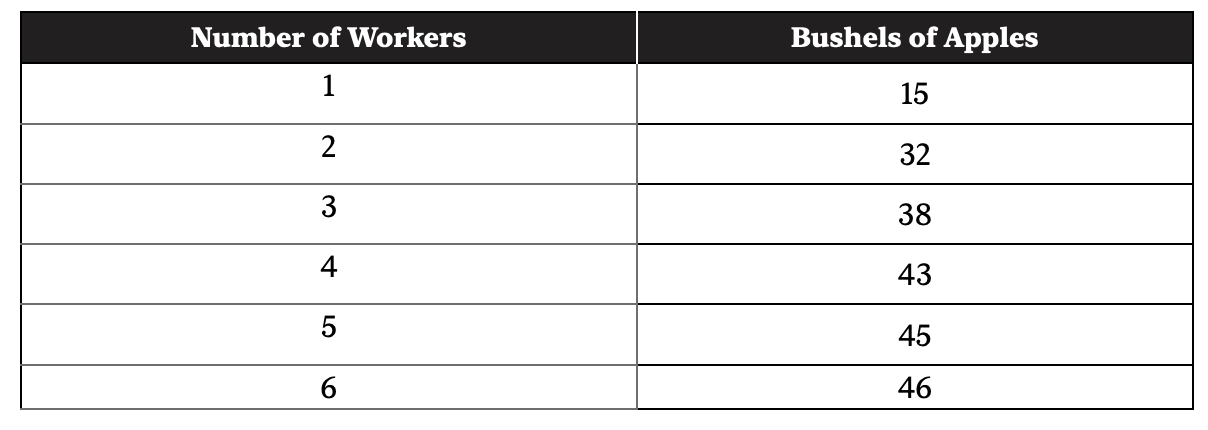
41. Assuming both perfectly competitive labor and product markets, if a bushel of apples sells for $10 and each hired worker costs $20, how many workers should be hired to maximize profits?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
(E) 6
42. Assume a firm producing computer screens uses only two inputs in the production process, labor and robots. The price of a robot is $100 per unit, and labor is $20 per unit. At current output levels, the robot’s marginal product is 1,000 and labor’s is 100. In order to lower total production costs, how should

Use this graph for question 43.
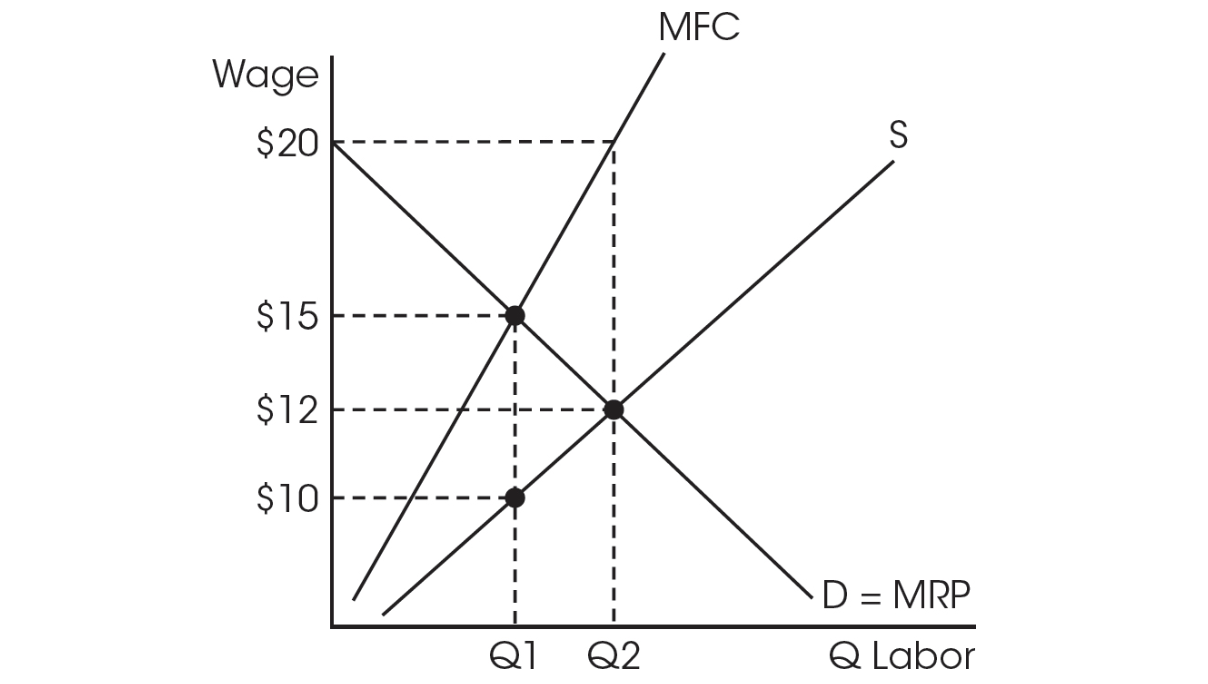
43. According to this labor market graph, what is the quantity and wage paid for both a monopsony and a perfectly competitive labor market?

44. This table shows the total product for a perfectly competitive firm. If the product sells for $10, what is the marginal revenue product for the 4th worker hired?
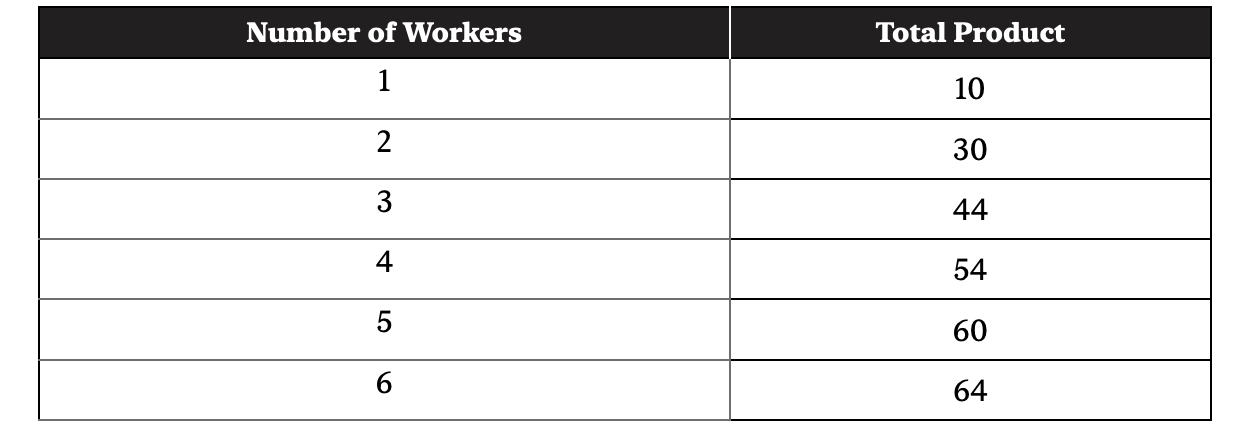
(A) $10
(B) $27
(C) $40
(D) $54
(E) $100
45. Which of the following is the best example of a pure public good?
(A) National defense
(B) Internet service
(C) Garbage pick-up services
(D) A publicly funded sports stadium
(E) The U.S. Postal Service
Use this graph for question 46.
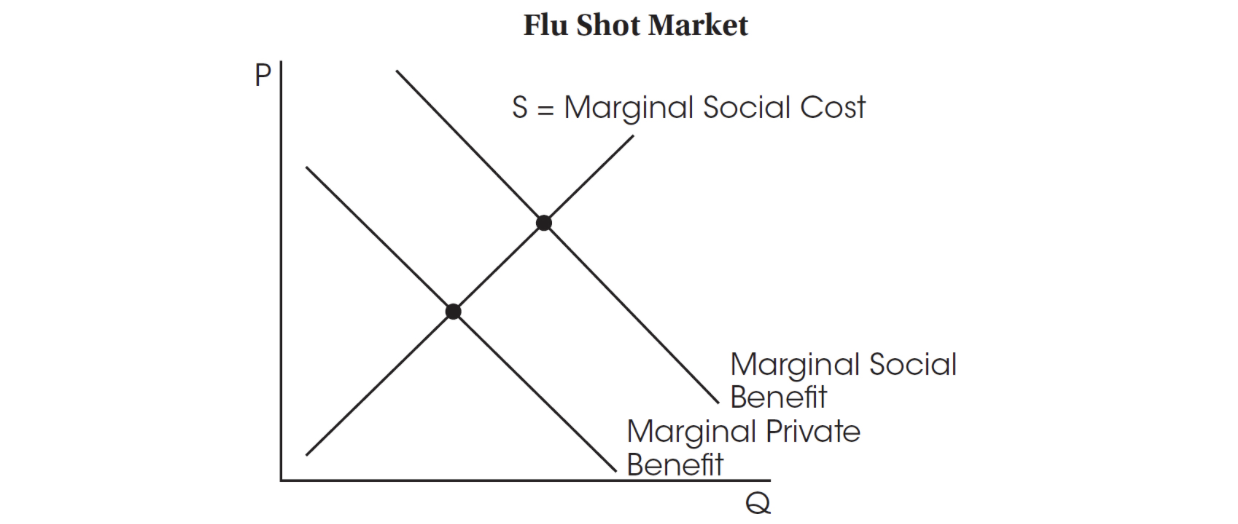
46. Which of the following is true based on the graph?
(A) Producers should have a per-unit tax imposed to allow for production at the socially optimal output level.
(B) The marginal private benefit is greater than the marginal social benefit at the free-market output level.
(C) Producers should be given a per-unit subsidy to allow for production at the socially optimal output level.
(D) There are no externalities present at the free-market quantity.
(E) At the socially optimal quantity, marginal private benefit is greater than the marginal social benefit.
Use this graph for question 47.
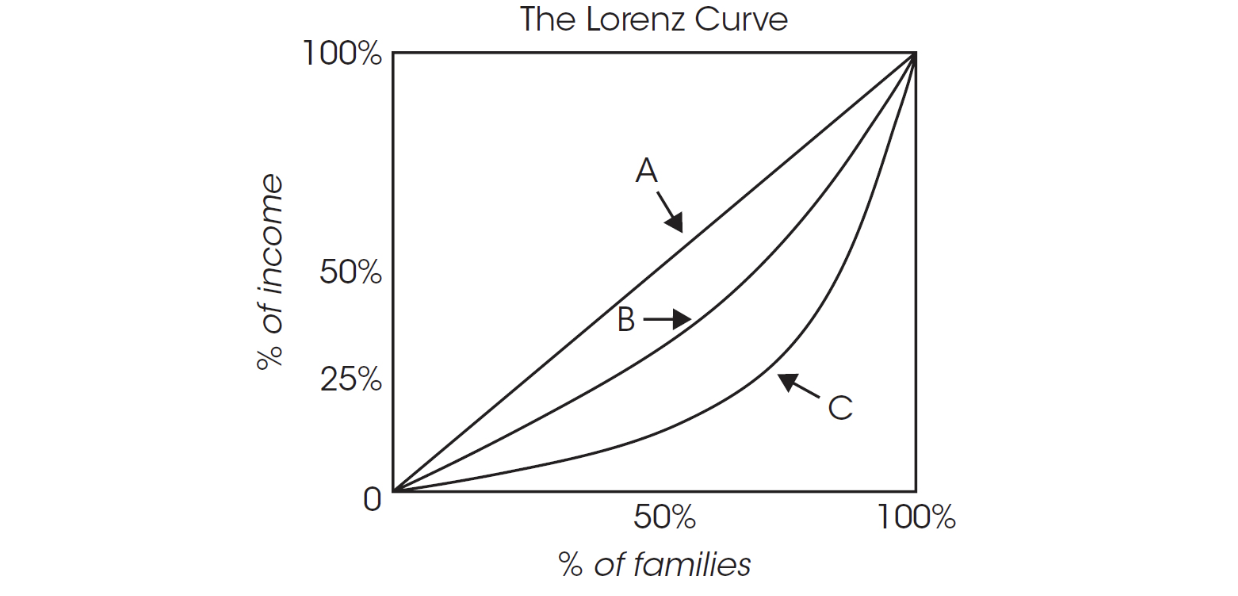
47. Which of the following is true based on this graph, where lines A, B, and C each represent a country?
(A) Country A has more income inequality than B or C.
(B) Country B has more income inequality than A or C.
(C) Country C has more income inequality than A or B.
(D) Countries A, B, and C all have an equal amount of income inequality.
(E) Country A has income inequality but less than B and C.
48. Clearing lakes and waterways of pollution will result in increased efficiency if
(A) the marginal social cost is greater than the marginal social benefit.
(B) the marginal social benefit is greater than the marginal social cost.
(C) the marginal social cost is positive.
(D) the marginal external benefit is less than the marginal social cost.
(E) companies that pollute are given a per-unit subsidy.
49. If residents of a city oppose a new highway being built through local neighborhoods, what economic concept best describes their opposition?
(A) Free-rider problem
(B) Economic rent
(C) Private goods
(D) Monopolies
(E) Externalities
50. Of the following, which is the best representation of a positive externality?
(A) Enjoying the beauty of a neighbor’s meticulously cared for flowers
(B) Using high-speed Internet access
(C) Paying for a ticket to a sporting event
(D) Being disturbed from a neighbor’s loud music
(E) Getting a car ride from a friend




